**Title: Key Insights on Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems**
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
ERP Modules
-
Basic MRP
- Thoughts: Basic Material Requirements Planning (MRP) focuses on ensuring that the materials required for production are available when needed. This helps in minimizing inventory costs and preventing production delays.
-
Finance
- Thoughts: The Finance module integrates various financial processes, allowing organizations to track revenue, expenses, and investment efficiently. This is crucial for maintaining financial health and making informed strategic decisions.
-
Human Resources
- Thoughts: The Human Resources module manages employee data, recruitment, payroll, and performance evaluations. Effective management of human resources is essential for maximizing workforce productivity and ensuring a positive workplace culture.
-
Supply Chain Management (SCM)
- Thoughts: SCM integrates the flow of goods and services from suppliers to customers. It optimizes logistics, inventory management, and supplier relationships, which can lead to reduced costs and improved customer satisfaction.
-
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Thoughts: CRM focuses on managing a company’s interactions with current and potential customers. By improving customer engagement and satisfaction, businesses can enhance loyalty and increase sales.
These modules offer crucial functionalities that enhance operational efficiency, facilitate decision-making, and ultimately contribute to the strategic goals of an organization. Understanding and implementing these modules can lead to more streamlined processes and better resource management.
Reference:
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
Overview of ERP
- Definition: ERP is an extension of the Material Requirements Planning (MRP) system designed to integrate and automate various business processes involving customers and suppliers.
- Purpose: The primary goal of ERP is to streamline and optimize operations across different departments by providing a unified platform for data and processes.
Key Features of ERP
-
Automation and Integration of Business Processes
- Thoughts: Automating repetitive tasks reduces human error and increases efficiency.
- Additional Info: Integrating different business functions (like finance, sales, and inventory) allows for better coordination and fewer operational silos.
-
Shared Databases and Business Practices
- Thoughts: A common database ensures that all departments have access to the same information, enhancing collaboration.
- Additional Info: This helps in maintaining consistency in data across various functions and drives unified decision-making processes.
-
Real-Time Information Production
- Thoughts: Access to real-time data is crucial for timely decision-making and responsiveness to market changes.
- Additional Info: Real-time insights can lead to improved customer service and faster reaction to supply chain disruptions.
Coordination of Business Activities
- Description: ERP systems facilitate the coordination of activities from supplier evaluation to customer invoicing.
- Thoughts: This end-to-end visibility is essential for maintaining strong supplier and customer relationships.
- Additional Info: Effective coordination helps in identifying bottlenecks in the supply chain, leading to optimized inventories and improved cash flow management.
Reference:
ERP in the Service Sector

-
ERP systems have been developed for various sectors:
- Sectors include: Health care, government, retail stores, hotels, and financial services.
- Thoughts: This highlights the versatility of ERP systems. Their adaptability allows organizations from different industries to leverage technology for operational efficiency.
- Additional Information: Each of these sectors requires different functionalities from ERP systems, such as patient management in healthcare or inventory management in retail.
- Sectors include: Health care, government, retail stores, hotels, and financial services.
-
Also called efficient consumer response (ECR) systems:
- Thoughts: The term ECR emphasizes the systems' ability to respond effectively to consumer needs, making it crucial for businesses aiming to enhance customer satisfaction.
- Additional Information: ECR systems focus on reducing overall supply chain costs while increasing the responsiveness to customer demand.
-
Objective is to tie sales to buying, inventory, logistics, and production:
- Thoughts: This integration ensures that all parts of the business are aligned, which is vital for maintaining efficiency and meeting customer expectations.
- Additional Information: By linking these elements, businesses can better forecast demand, manage stock levels, and streamline operations, ultimately leading to improved customer service and profitability.
Reference:
SAP’s ERP Modules
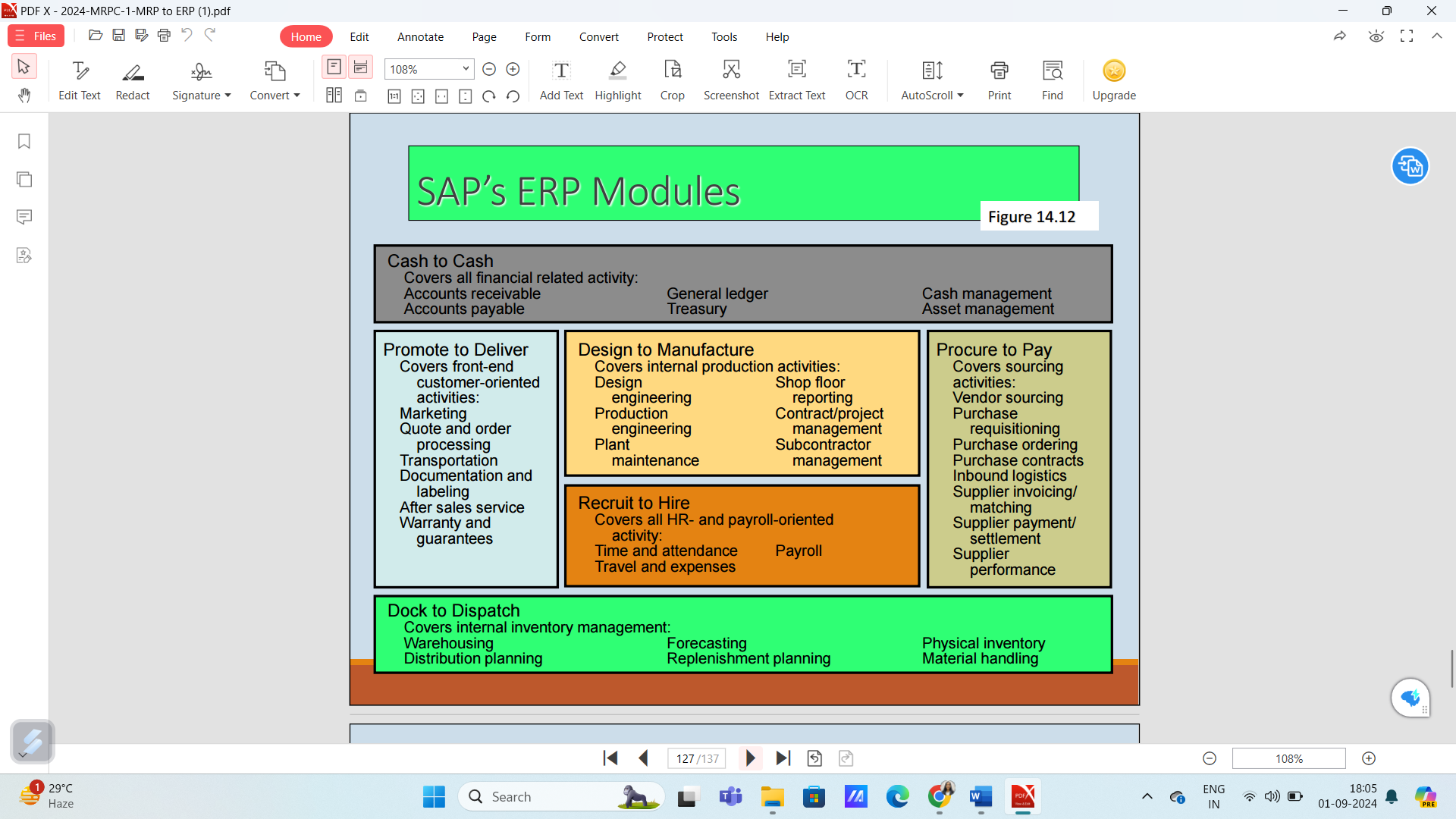
This image provides an overview of various modules within SAP's Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system. Each module addresses specific business functions, enabling organizations to streamline their processes and enhance efficiency.
Cash to Cash
- Overview: This module covers all financial-related activities.
- Components:
- Accounts receivable
- Accounts payable
- Thoughts: Managing cash flow is critical for businesses; efficient processing here can significantly impact overall financial health.
Promote to Deliver
- Overview: Focuses on front-end customer-oriented activities.
- Components:
- Marketing:
- Quote and order processing
- Transportation
- Documentation and labeling
- After sales service
- Warranty and guarantees
- Marketing:
- Thoughts: This module emphasizes customer satisfaction and efficient service delivery, crucial for maintaining competitive advantage.
Design to Manufacture
- Overview: Covers internal production activities.
- Components:
- Design engineering
- Production management
- Plant maintenance
- Subcontractor management
- Shop floor reporting
- Contract/project management
- Thoughts: Effective design and manufacturing processes enhance product quality and reduce time to market, reinforcing the importance of integration across departments.
Recruit to Hire
- Overview: Focuses on HR and payroll activities.
- Components:
- Time and attendance
- Payroll
- Travel and expenses
- Thoughts: Streamlined recruitment and payroll processes can help attract talent and maintain employee satisfaction, which is vital for organizational success.
Procure to Pay
- Overview: Covers sourcing activities.
- Components:
- Vendor sourcing
- Purchase requisitioning
- Purchase ordering
- Purchase contracts
- Inbound logistics
- Supplier invoicing/matching
- Supplier payment/settlement
- Supplier performance
- Thoughts: This module enhances supplier relationships and manages procurement costs effectively, maximizing budget efficiency.
Dock to Dispatch
- Overview: Involves internal inventory management.
- Components:
- Warehousing
- Distribution planning
- Forecasting
- Replenishment planning
- Physical inventory
- Material handling
- Thoughts: Efficient inventory management reduces waste and increases operational efficacy, ensuring products are available when needed without unnecessary overstocking.
| Module | Description | Key Components |
|---|---|---|
| Cash to Cash | Covers all financial related activity | Accounts receivable, Accounts payable |
| Promote to Deliver | Covers front-end customer-oriented activities | Marketing, Order processing, Warranty |
| Design to Manufacture | Covers internal production activities | Design, Production management, Plant maintenance |
| Recruit to Hire | Covers all HR- and payroll-oriented activity | Time and attendance, Payroll |
| Procure to Pay | Covers sourcing activities | Vendor sourcing, Purchase requisitioning, Supplier payment |
| Dock to Dispatch | Covers internal inventory management | Warehousing, Forecasting, Physical inventory |
Reference:
Advantages of ERP Systems

-
Provides integration of the supply chain, production, and administration
- ERP systems unify various business processes under a single platform, allowing for seamless data flow across departments. This integration helps in monitoring the supply chain efficiently, facilitating better decision-making and resource management.
-
Creates commonality of databases
- By utilizing a centralized database, ERP systems ensure that all departments work with the same data, reducing discrepancies and improving data accuracy. This leads to better reporting and analytics, as all users reference the same source of information.
-
Can incorporate improved best processes
- ERP systems are often built to include industry best practices, enabling organizations to adopt more efficient processes. This can lead to increased productivity and operational efficiency, as employees can leverage tried-and-true methods rather than creating their own systems.
-
Increases communication and collaboration between business units and sites
- With all information accessible in one system, employees from different departments or geographical locations can share insights and collaborate more effectively. This fosters teamwork and can accelerate project delivery and problem-solving capabilities.
-
Has an off-the-shelf software database
- Many ERP solutions come with pre-built templates and modules that organizations can utilize without heavy customization. This can speed up implementation times and ease the initial setup process, making it easier for companies to get started with using ERP.
-
May provide a strategic advantage
- Organizations that successfully implement ERP systems can gain a competitive edge in the market. The efficiencies and clearer insights enabled by ERP can lead to better customer service, quicker response times, and ultimately, higher profitability.
Reference:
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
Overview of ERP Systems
- ERP systems have the potential to:
- Reduce transaction costs:
- By streamlining operations and integrating various business processes, companies can minimize the costs associated with transactions. This includes reducing paperwork and manual errors.
- Increase the speed and accuracy of information:
- ERP systems facilitate real-time data access, allowing for quicker decision-making and ensuring that information is up to date. This is critical for timely responses to business needs.
- Reduce transaction costs:
Strategic Emphasis
- Facilitates a strategic emphasis on JIT systems and integration:
- Just-In-Time (JIT) systems aim to reduce waste and improve efficiency by receiving goods only as they are needed. ERP can enhance JIT practices by synchronizing supply chain activities, leading to lower inventory costs and increased responsiveness to customer demand.
Conclusion
Implementing an ERP system can significantly transform business operations by reducing costs, enhancing data accuracy, and promoting integrated approaches like JIT in managing resources effectively.
Reference:
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Notes
-
Customization of ERP
ERP systems can be tailored to fulfill specific business needs, allowing organizations to align the software functionalities with their operational processes. This adaptability can improve user satisfaction and operational efficiency. -
Integration with Enterprise Application Integration (EAI)
EAI tools enable ERP systems to seamlessly connect with various software applications within an organization, enhancing data flow and system communication. This integration is crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of ERP systems.
Potential Integrations of ERP Systems:
| Integration Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Warehouse Management | ERP can manage inventory control, shipping, and receiving processes, ensuring the efficiency of warehouse operations. |
| Logistics | Integration can optimize transportation, route planning, and delivery schedules, enhancing supply chain management. |
| Electronic Catalogs | ERP systems can synchronize with online catalogs, improving product visibility and streamlining order processing. |
| Quality Management | Allows tracking of quality control processes and compliance with standards, which can enhance product reliability. |
- Importance of Integrating with Quality Management
Quality management integration ensures that businesses can monitor and maintain product standards throughout the production process. This not only minimizes defects but also boosts customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Reference:
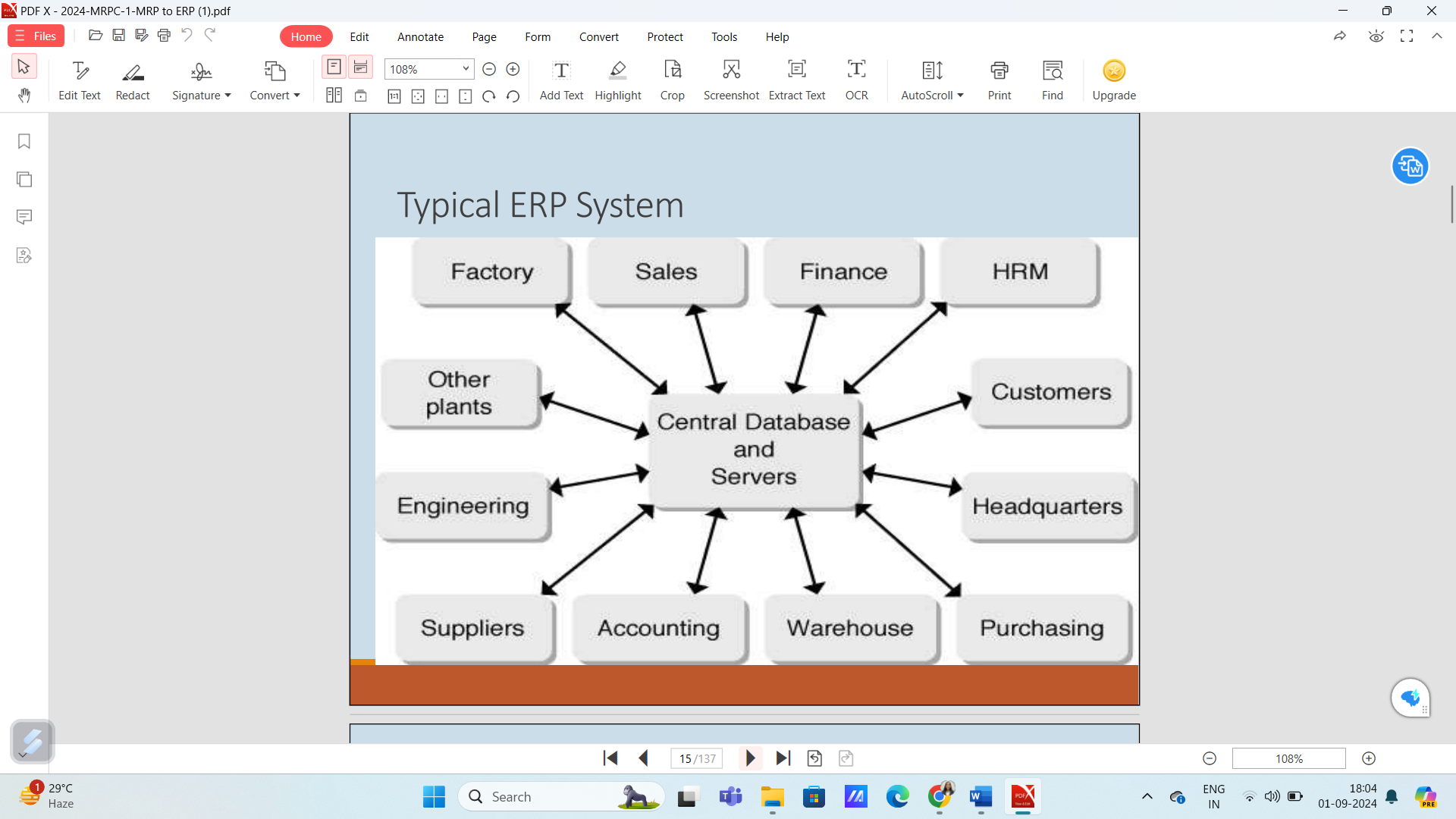
Typical ERP System
-
Central Database and Servers
- The heart of the ERP system where all data is stored and managed. A central database allows for real-time data access and helps in decision-making across various departments. It ensures consistency and accuracy of data, leading to better operational efficiency.
-
Factory
- Represents the production aspect of the business. It connects directly to the central database to track production schedules, inventory levels, and manufacturing processes, optimizing resource allocation and minimizing downtime.
-
Sales
- This department relies on data from the central database to manage customer orders, track sales performance, and forecast demand. Effective sales management can significantly impact revenue and customer satisfaction.
-
Finance
- The finance department uses the ERP system to manage budgets, financial reporting, and compliance. Integrating finance with other departments ensures that financial decisions are informed by operational realities.
-
HRM (Human Resource Management)
- HRM deals with employee data, recruitment, training, and development. The integration with the central database helps streamline payroll processing and enhances workforce management.
-
Customers
- This node signifies the importance of customer relationship management (CRM). Data from sales and finance can be utilized to enhance customer service, tailor marketing efforts, and understand customer behaviors.
-
Headquarters
- Represents the administrative core of the business that oversees operations across different departments and plants. They rely on the ERP system for strategic decision-making and performance analysis.
-
Other Plants
- Similar to the factory, this aspect addresses operations in various locations. Integration among plants ensures efficiency, consistency in quality, and coordinated logistics.
-
Engineering
- Focused on product development and design, engineering can streamline processes and innovations by accessing data from multiple departments, leading to efficient project management and product launches.
-
Suppliers
- The integration with suppliers in the ERP system facilitates effective supply chain management, enabling businesses to manage supplier relationships, track deliveries, and optimize inventory levels.
-
Accounting
- Critical for financial record-keeping and analysis. The accounting module integrates closely with finance and other departments to ensure that financial information reflects business operations accurately.
-
Warehouse
- This module helps manage inventory levels, storage space, and logistics. Real-time updating of stock levels aids in reducing excess inventory and ensuring that production runs smoothly.
-
Purchasing
- Involves sourcing and procurement of goods and services. Efficient purchasing processes supported by the ERP system can help in negotiating better terms with suppliers and ensuring timely availability of materials.
| Department | Functionality |
|---|---|
| Factory | Manages production, inventory and scheduling |
| Sales | Tracks customer orders and sales performance |
| Finance | Oversees budgets, reporting and compliance |
| HRM | Manages employee data and recruitment |
| Customers | Focuses on customer relationship management |
| Headquarters | Coordinates operations and strategic decision-making |
| Other plants | Manages operations in various locations |
| Engineering | Streamlines product development and project management |
| Suppliers | Facilitates supply chain management |
| Accounting | Handles financial record-keeping and analysis |
| Warehouse | Manages inventory and logistics |
| Purchasing | Oversees procurement processes |
Reference:
ERP Systems

-
Definition of ERP Systems:
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems are comprehensive computer systems designed to integrate various application programs across different departments within an organization.
- This integration is crucial as it helps streamline processes, improve data accuracy, and enhances overall operational efficiency.
-
Components of ERP Systems:
- ERP systems incorporate applications in key areas such as:
- Accounting: Manage financial transactions, reporting, and compliance.
- Sales: Track customer interactions, sales orders, and lead management.
- Manufacturing: Oversee production schedules, inventory management, and supply chain logistics.
- Other Functions: This may also include human resources, project management, and customer relationship management (CRM).
- ERP systems incorporate applications in key areas such as:
-
Integration Mechanism:
- The integration of different functions is achieved through a centralized database.
- A shared database allows all application programs to access and manipulate the same data, resulting in:
- Reduced data redundancy
- Increased accuracy of information
- A holistic view of organizational operations, which aids in decision-making processes.
Additional Thoughts:
- Implementing an ERP system can be resource-intensive and requires careful planning and training.
- The choice of an ERP system should align with the specific needs of the organization to ensure maximum benefit.
- Continuous updates and evaluations are essential for the ERP system to adapt to changing business environments and technological advancements.
Summary:
ERP Systems play a crucial role in unifying various business processes, facilitating better management, and driving efficiency through integrated technology and centralized data.
Reference: