DMARC - Mind Map
DMARC Mind Map Notes
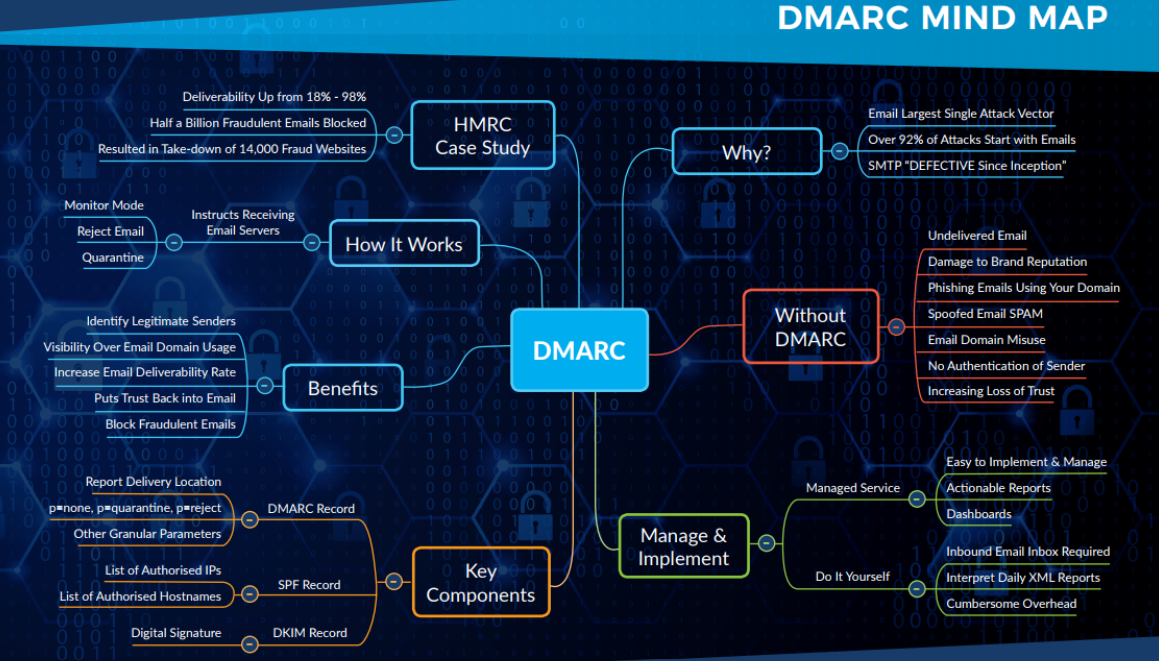
Overview of DMARC
- DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) is an email authentication protocol designed to improve email security.
- It allows domain owners to specify which mechanisms are employed to authenticate emails coming from their domain, giving them control over how their emails are handled.
Importance of DMARC
- Why DMARC?
- Email is the largest single attack vector, with over 92% of attacks beginning with an email.
- SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is criticized for being defective since its inception, leading to vulnerabilities.
Without DMARC
- Risks:
- Undelivered Email: Emails may not reach their intended recipients.
- Damage to Brand Reputation: Misuse of the domain can harm how a brand is perceived.
- Phishing Emails: Attackers can send fraudulent emails that appear to be from your domain.
- Spoofed Email SPAM: Users may receive spam that looks legitimate.
- Email Domain Misuse: Unauthorized use of a domain can lead to trust degradation.
- No Authentication of Sender: Without validation, it becomes difficult to confirm the sender’s identity.
- Increasing Loss of Trust: Continuous misuse can cause recipients to doubt the authenticity of all emails from the domain.
How DMARC Works
-
Modes:
- Monitor Mode: This mode instructs receiving email servers on how to handle emails while assessing the situation.
- Reject Email: Instructs recipients to reject authentication failures.
- Quarantine: Urges recipients to place suspicious emails in a hold state.
-
Identification:
- It helps identify legitimate senders and provides visibility over email domain usage.
Benefits of DMARC
- Email Deliverability: Significantly increases the rate at which legitimate emails are delivered, going up from 18% to as much as 98% after implementation.
- Fraud Prevention: Blocks fraudulent emails, maintaining the integrity of communications.
- Restoration of Trust: Puts trust back into email communications.
Key Components
- DMARC Record: The main record that specifies the policy for email authentication.
- SPF Record: Sender Policy Framework record that specifies which IP addresses are authorized to send emails on behalf of the domain.
- DKIM Record: DomainKeys Identified Mail that provides an added layer of email validation.
Reporting
- Report Delivery Location: Mechanisms for reporting how emails are handled (e.g., success or failures).
- Granular Parameters:
p=none: No action is taken.p=quarantine: Marked for further inspection.p=reject: Emails are rejected outright.
Implementation Strategies
-
Manage & Implement Options:
- Do It Yourself: Organizations may choose to implement DMARC manually.
- Managed Service: Hire services to manage DMARC settings and monitor integrity.
-
Actionable Reports: DMARC provides actionable insights through reports that help refine email handling.
-
Dashboard: Tools for visualizing data and tracking email authentication status.
Additional Considerations
- Inbound Email Inbox Required: There needs to be a dedicated system to handle incoming messages and reports that DMARC generates.
- Cumbersome Overhead: Some organizations may find DMARC implementation complex, requiring additional resources to manage effectively.
Reference:
www.mimecast.com
What Is DMARC? - Mimecast
www.linkedin.com
DMARC: Benefits, Challenges, and Implementation Guide - LinkedIn
www.valimail.com
8 ways DMARC improves your email deliverability - Valimail