Cybersecurity Domain Map: Key Areas and Insights
The Map of Cybersecurity Domains
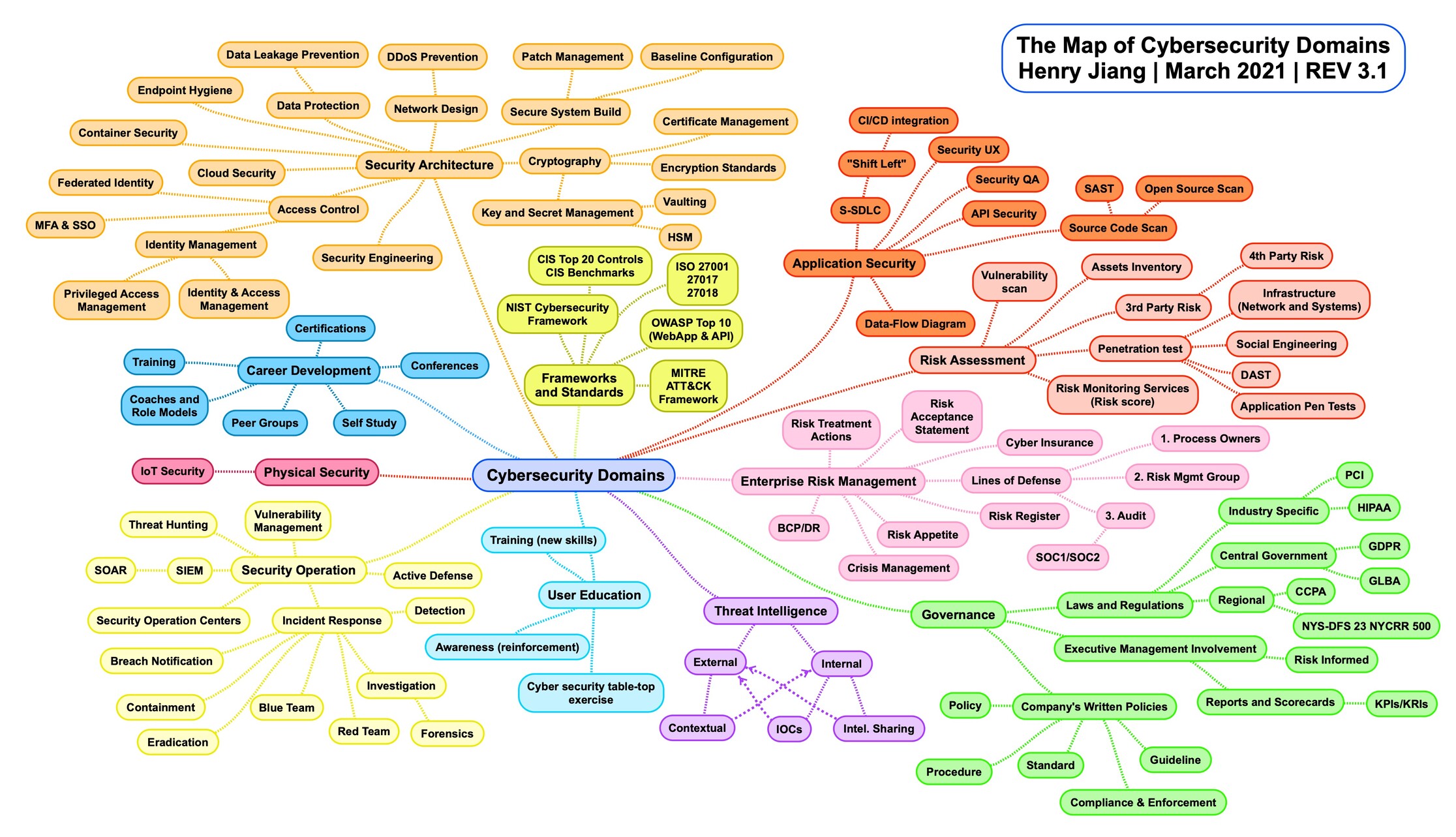
Overview
This image presents a comprehensive map of various cybersecurity domains. It emphasizes the interconnectedness of diverse areas within cybersecurity, illustrating how elements such as security architecture, risk assessment, and threat intelligence contribute to overall security strategy.
Main Categories
1. Security Architecture
- Key Components:
- Data Protection: Important for safeguarding sensitive information against breaches.
- Encryption Standards: Essential for ensuring data confidentiality and integrity during transmission.
- Thoughts: Effective security architecture is foundational for establishing a secure organization. Integration of various controls and standards, such as CIS and OWASP, enhances security posture.
2. Application Security
- Key Areas:
- Vulnerability Scan: Identifies potential weaknesses in applications before they can be exploited.
- SAST (Static Application Security Testing) : Analyzes source code for vulnerabilities, allowing for early detection in the development lifecycle.
- Thoughts: Application security is critical given the rise in web-based threats. Proactive measures, such as regular scanning and implementing secure coding practices, can significantly reduce risk.
3. Risk Assessment
- Components:
- Risk Treatment Actions: Steps taken to mitigate identified risks.
- 3rd Party Risk: Evaluates risks associated with external vendors and partners.
- Thoughts: Regular risk assessments aid in aligning security measures with the organization's threat landscape. Understanding third-party risks is vital as these can be potential attack vectors.
4. Cybersecurity Domains
- Career Development:
- Certifications: Verifying skills through recognized certifications can enhance career prospects.
- Training and Conferences: Continuous learning is essential in the ever-evolving field of cybersecurity.
- Thoughts: The cybersecurity landscape is dynamic, making ongoing education and networking vital for professionals. Staying updated with the latest threats and technologies is crucial.
5. Threat Intelligence
- Types:
- External vs. Internal: Knowing both internal vulnerabilities and external threats helps create a robust defense.
- Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) : Useful for identifying security incidents early on.
- Thoughts: Leveraging threat intelligence allows organizations to stay ahead of threats by proactively addressing vulnerabilities and understanding ongoing cyber threats.
6. Governance
- Elements:
- Policy and Procedure: Establishing clear guidelines and protocols ensures consistent security practices across the organization.
- Executive Management Involvement: Engagement from leadership emphasizes the importance of cybersecurity at all organizational levels.
- Thoughts: Good governance is crucial for regulatory compliance and establishing a security culture within the organization. A top-down approach ensures accountability and resource allocation for security initiatives.
Summary Table
| Category | Key Areas/Elements | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|
| Security Architecture | Data Protection, Encryption Standards | Protects sensitive information |
| Application Security | Vulnerability Scan, SAST | Proactive detection of application weaknesses |
| Risk Assessment | Risk Treatment Actions, 3rd Party Risk | Aligns security measures with organizational risks |
| Cybersecurity Domains | Certifications, Training, Conferences | Continuous learning and professional growth |
| Threat Intelligence | External/Internal, IOCs | Early detection and understanding of threats |
| Governance | Policy, Procedure, Executive Management Involvement | Establishes strong security practices |
Reference:
www.linkedin.com
Cybersecurity Domain Map ver 3.0 - LinkedIn
derechodelared.com
[PDF] The Map of Cybersecurity Domains Henry Jiang - Derecho de la Red
www.stationx.net
Top Cyber Security Domains to Build a Successful Career - StationX