Exocytosis: Constitutive vs. Regulated Secretory Pathways
Exocytosis: The Constitutive and Regulated Secretory Pathways
-
Exocytosis Definition
- Exocytosis is a cellular process where substances are expelled from a cell by vesicles that fuse with the plasma membrane. This mechanism is crucial for various physiological functions, including secretion of hormones, neurotransmitters, and other molecules.
-
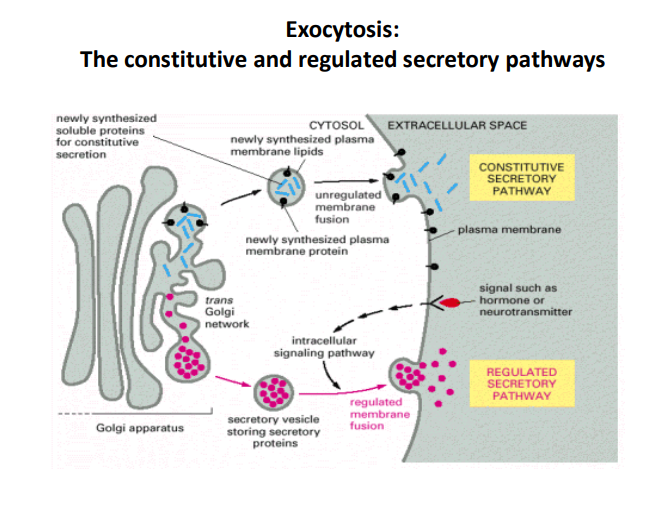
Constitutive Secretory Pathway
- This pathway is responsible for the continuous delivery of proteins and lipids to the plasma membrane and extracellular space.
- Key Characteristics:
- Unregulated membrane fusion means that vesicles continuously release substances without the need for specific signals.
- It operates in various cell types for maintaining the extracellular environment and membrane composition.
- Includes the delivery of newly synthesized plasma membrane proteins and lipids.
-
Regulated Secretory Pathway
- Unlike the constitutive pathway, this pathway is activated by specific signals (e.g., hormones or neurotransmitters).
- Key Characteristics:
- Performed by secretory vesicles that store proteins, which are only released upon receiving a signal.
- The process involves an intracellular signaling pathway that triggers the vesicles to fuse with the plasma membrane.
- Essential in processes such as the release of insulin by pancreatic cells or neurotransmitters by nerve cells.
-
Golgi Apparatus Role
- The Golgi apparatus plays a crucial role in processing and packaging proteins for both secretory pathways.
- Proteins synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum are transported to the Golgi apparatus, where they undergo modifications before being sorted for exocytosis.
-
Signaling Molecules
- The regulated pathway is often activated by signaling molecules, illustrating the importance of external cues in cellular processes.
- Understanding these signaling pathways can provide insights into various biological functions and the development of certain diseases where exocytosis is impaired.
Extended readings:
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Transport from the Trans Golgi Network to the Cell Exterior: Exocytosis
www.sciencedirect.com
Secretory Pathway - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
www.sciencedirect.com
Exocytosis - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics