Transport of Lysosomal Hydrolases to Lysosomes Explained
The Transport of Newly Synthesized Lysosomal Hydrolases to Lysosomes
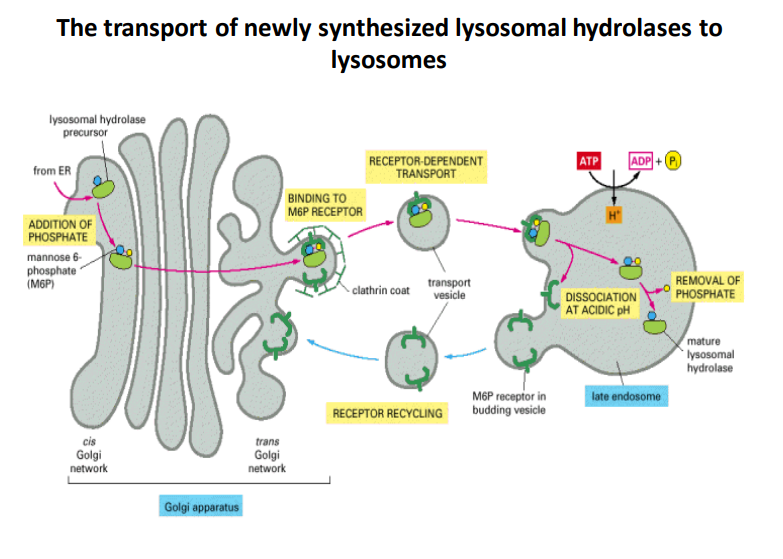
Overview
- Lysosomal hydrolases are enzymes that play a crucial role in the degradation of various biomolecules within lysosomes. This process is vital for cellular metabolism and the recycling of cellular components.
Key Processes
-
Synthesis of Lysosomal Hydrolases
- Origin: Newly synthesized lysosomal hydrolases are produced in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
- Importance: Proper synthesis is necessary for the function of lysosomes.
-
Addition of Phosphate
- Process: After synthesis, mannose-6-phosphate (M6P) is added to the hydrolases.
- Function: This phosphate addition serves as a signal for subsequent transport to lysosomes.
-
Receptor-Dependent Transport
- Binding to M6P Receptor: Hydrolases bind to M6P receptors located in the trans-Golgi network (TGN).
- Significance: This binding is crucial for targeting the hydrolases to lysosomes efficiently.
-
Formation of Transport Vesicles
- Mechanism: Once bound to the receptor, the hydrolase-receptor complex is encapsulated in a transport vesicle coated with clathrin.
- Purpose: This step ensures that the enzymes are transported safely to their destination.
-
Receptor Recycling
- Process: Following the delivery of hydrolases, the M6P receptor is recycled back to the Golgi apparatus for further use.
- Efficiency: This recycling mechanism helps maintain a stock of receptors for continuous transport.
-
Maturation in Late Endosome
- Acidic pH Activation: In the late endosome, the internal environment becomes acidic, promoting the dissociation of the hydrolase from the receptor.
- Removal of Phosphate: The M6P group is also removed under acidic conditions, preparing the hydrolase for its active role.
- Final Destination: The mature lysosomal hydrolase is then sent to the lysosome, where it can carry out its function in degradation.
Additional Notes
- Energy Requirement: The transport process involves ATP, indicating it is an energy-dependent mechanism.
- Lysosomal Function: The effectiveness of lysosomal hydrolases is crucial for cellular health and the prevention of lysosomal storage diseases.
- Pathway Importance: Understanding this transport pathway aids in insights into various diseases linked to lysosomal dysfunctions.
Extended readings:
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Transport from the Trans Golgi Network to Lysosomes - NCBI
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Lysosomal Storage Disease - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf
www.sciencedirect.com
Lysosome Enzyme - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics