Advancements in Reasoning with OpenAI's o1 Model
Learning to Reason with LLMs
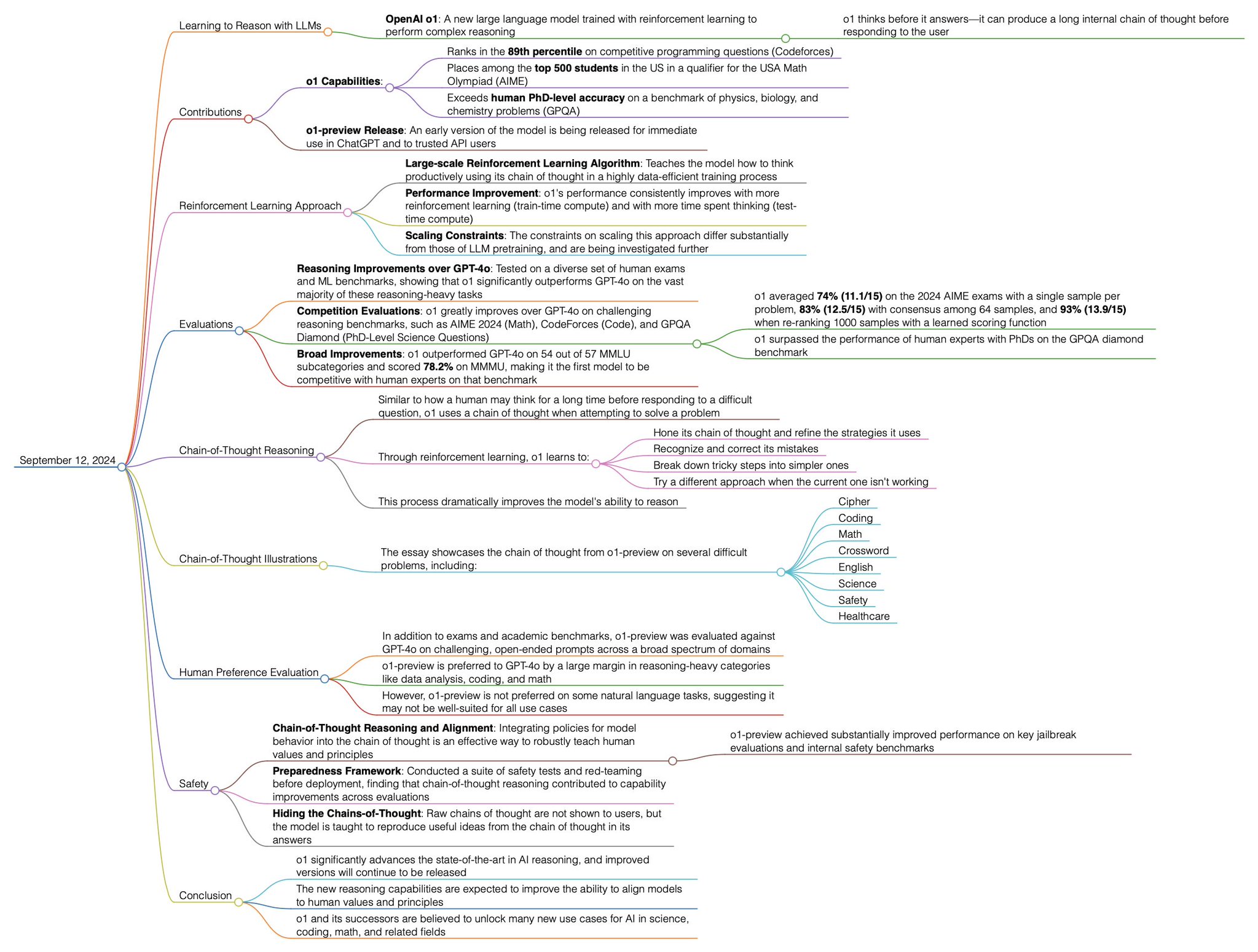
OpenAI's o1 Model
- Overview: A new large language model with reinforcement learning for complex reasoning. It improves performance by producing an internal chain of thought before responding.
- Context: The release is an early version intended for use in ChatGPT and by trusted API users.
o1 Capabilities
- Competitive Rankings:
- Scores in the 89th percentile on competitive programming questions (Codeforces).
- Among the top 500 students in the USA Math Olympiad (AIME).
- Accuracy:
- Exceeds performance of human PhD-level experts on physics, biology, and chemistry problems (GPOA).
o1-preview Release
- Access: Early version available to select users for immediate feedback and testing.
Reinforcement Learning Approach
- Large-scale Learning Algorithm:
- Optimizes chain of thought through data-efficient training methods.
- Performance Improvements:
- Consistent enhancements with increased reinforcement learning.
- Scaling Constraints:
- Strategies for scaling are in development to differ from standard LLM pretraining.
Reasoning Improvements Over GPT-4.0
- Benchmark Testing:
- Outperforms GPT-4.0 across various human exam benchmarks.
- Demonstrates significant improvement in reasoning tasks, such as the 2024 AIME exams, solving 11/15 problems correctly with a single sample per problem.
Competition Evaluations
- Performance Metrics:
- AIME 2024 (Math): 11/15 problems solved.
- CodeForces (Coding): Ranks in 89th percentile.
- GPOA Diamond (PhD-Level Science Questions): Surpasses human experts.
Broad Improvements
- MMMU Subcategories:
- Exceeds 78.2% performance on MMMU, setting a new competitive benchmark.
Chain-of-Thought Reasoning
- Learning Methods:
- Refines and aligns the model's response strategies with how humans solve problems.
- Recognizes errors and adjusts approach to improve accuracy.
Human Preference Evaluation
- Comparison to GPT-4.0:
- Preferred for data analysis, coding, and mathematics.
- Not preferred for some natural language tasks, suggesting domain-specific optimization.
Chain-of-Thought Illustrations
- Examples:
- Displayed in the essay include challenges in:
- Cipher
- Coding
- Math
- Crossword
- English
- Science
- Safety
- Healthcare
- Displayed in the essay include challenges in:
Safety
- Integration with Policies:
- Policies for behavior and principles integrated into the model for trustworthy responses.
- Preparedness Framework:
- Safety tests and red-teaming assessments ensure secure implementation.
- Hiding the Chains-of-Thought:
- The strategy to obfuscate unnecessary details from the user's perspective.
Conclusion
- State-of-the-Art Advancement:
- o1 sets new standards in AI reasoning and handling complex problems with improved safety.
- Future versions will build on and refine these advances, unlocking more scientific, coding, and mathematical capabilities.
Reference:
openai.com
Learning to Reason with LLMs | OpenAI
www.forbes.com
OpenAI Unveils O1 - 10 Key Facts About Its Advanced AI Models
www.theverge.com
OpenAI releases o1, its first model with 'reasoning' abilities