"Overview of Software Development Life Cycle Models"
Software Development Life Cycle
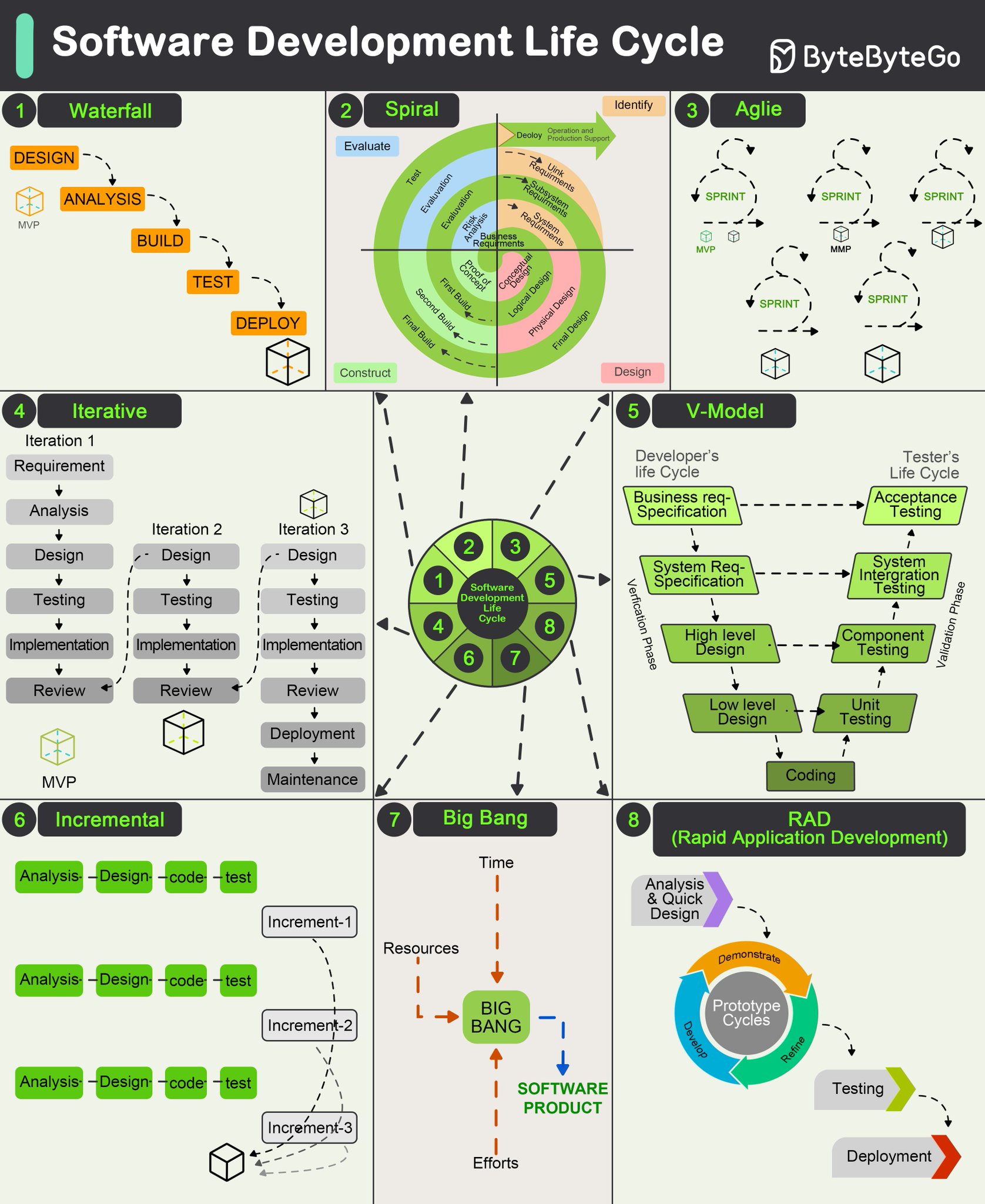
1. Waterfall
- Phases: DESIGN, ANALYSIS, BUILD, TEST, DEPLOY
- Key Points:
- Linear sequential model.
- Each phase depends on the output of the previous phase.
- Easy to manage due to its rigid structure. However, not flexible in handling changes.
2. Spiral
- Phases: Evaluate, Test, Risk Analysis, Design, Build, Verify, Plan Next Iteration, Develop, Identify Risks
- Key Points:
- Combines iterative development with systematic aspects of the waterfall model.
- Focus on risk analysis and minimization.
- Allows for incremental releases of the product, or incremental refinement through each iteration around the spiral.
3. Agile
- Phases: SPRINT 1, SPRINT 2, SPRINT 3, etc.
- Key Points:
- Promotes collaboration, customer feedback, and small, rapid releases.
- Projects are divided into small sprints, usually lasting 1-4 weeks.
- Offers flexibility and encourages continuous improvement.
4. Iterative
- Phases: Iteration 1, Requirement, Analysis, Design, Testing, Implementation, Review, Iteration 2, Iteration 3, Deployment, Maintenance
- Key Points:
- Involves developing a system in repeated cycles (iterations).
- Each iteration delivers a part of the software, which is reviewed and improved in the next iteration.
- Best for projects with unclear or dynamic requirements.
5. V-Model (Validation and Verification Model)
- Phases:
- Developer’s Life Cycle: Business Req. Specification, System Req. Specification, High Level Design, Low-Level Design, Coding
- Tester’s Life Cycle: Acceptance Testing, System Integration Testing, Component Testing, Unit Testing
- Key Points:
- Extension of the waterfall model, mapping testing phases to each development stage.
- Ensures verification and validation activities are performed simultaneously.
- Can be rigid; does not handle changes easily.
6. Incremental
- Phases: Increment-1, Increment-2, Increment-3
- Each increment follows this cycle: Analysis, Design, Code, Test
- Key Points:
- Divides the system into smaller segments (increments).
- Each segment is developed and delivered separately.
- Useful for iterative enhancements and additions.
7. Big Bang
- Phases:
- Time, Resources, Efforts -> BIG BANG -> SOFTWARE PRODUCT
- Key Points:
- Involves little to no planning.
- All resources are invested in the development, leading to a single release.
- High risk, as fundamental issues can't be identified early.
- Suitable for small projects with unknown requirements.
8. RAD (Rapid Application Development)
- Phases: Analysis & Quick Design, Prototype Cycles (Design, Refine, Demonstrate), Testing, Deployment
- Key Points:
- Focuses on rapid prototyping and quick feedback over strict planning.
- Involves stakeholder interaction and refining prototypes.
- Accelerates the development process, delivering components more quickly.
Reference:
existek.com
SDLC Models: Agile, Waterfall, V-Shaped, Iterative, Spiral - Existek
medium.com
SDLC Models Explained: Agile, Waterfall, V-Shaped, Iterative, Spiral
www.geeksforgeeks.org
Top 8 Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Models used in ...