SaaStr 2024 - Key Customer Success Topics for Investor Discussions
10 Customer Success Topics Investors Will Grill You About

Keynote Speaker
- Speaker: Nick Mehta
- Title: CEO
- Company: Gainsight
- Thoughts: As CEO of Gainsight, Nick Mehta has significant expertise in customer success, which he'll share in this talk. Gainsight is known for its customer success platform, and his insights are expected to be highly valuable.
Main Topic
- Title: 10 Customer Success Topics Investors Will Grill You About
- Thoughts: This title implies that the session will cover critical customer success areas that are of interest to investors. It suggests a focus on preparedness and key performance metrics that attract investor scrutiny.
Context and Relevance
SaaStr Annual Conference
- Conference: SaaStr Annual
- Thoughts: This is a major event in the SaaS (Software as a Service) industry, where founders, executives, and investors gather to share knowledge and network. The SaaStr Annual conference is renowned for its focus on best practices and growth strategies for SaaS companies.
Visual Elements
- Design: The visual design includes a sky with clouds and geometric shapes, creating an informal yet professional atmosphere.
- Thoughts: The use of clouds and geometric shapes indicates a theme of innovation and broad thinking, suggesting that the topics discussed will be forward-looking and strategic.
Additional Thoughts on Content
- Customer Success: This session seems particularly useful for SaaS startups and companies looking to secure funding or gain investor trust by excelling in customer success.
- Key Areas: Anticipate that the discussion might cover metrics like customer retention rates, customer lifetime value (CLV), net promoter score (NPS), and strategies for scaling customer success operations.
By providing this information, attendees can better prepare for investor meetings and align their customer success strategies with investor expectations.
Reference:
Key Insights on Company Metrics and Evaluations

Importance of Retention Metrics
- Gross and Net Retention:
- Retention metrics are vital to any company exceeding a few million in Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR).
- Both Gross and Net Retention are crucial indicators used to assess business health.
Evaluation Criteria
- Retention as North Star Metric:
- Gross and Net retention metrics are considered the "North Star" for evaluation.
- These metrics guide the assessment of:
- Strength of Product-Market Fit:
- Indicates how well the product satisfies the demand in the market.
- Quality of Execution:
- Reflects the efficiency and effectiveness in delivering the product or service.
- Customer Love for the Solution:
- Measures the satisfaction and loyalty of the customers towards the company’s offerings.
- Strength of Product-Market Fit:
Visual Elements
- Image of Ajay Agarwal:
- The quotation is attributed to Ajay Agarwal from Bain Capital Ventures.
- His visual presence reinforces the reliability and professionalism of the statement.
Related Organizations
- BCV:
- Represented in the lower left corner, indicating Bain Capital Ventures.
- BCV is likely involved in the evaluation and investment in such companies.
- SaaStr Annual:
- The logo suggests the context is part of a discussion or presentation at the SaaS annual event, a major gathering for SaaS companies and professionals.
Additional Context
- Metric Deep Dive:
- Understanding Gross Retention involves looking at the total amount retained without considering any upsells.
- Net Retention accounts for both the retained revenue and any expansion revenue, showing a fuller picture of customer growth and retention.
Summary
This image emphasizes the critical role of gross and net retention metrics in evaluating the performance and growth potential of companies with significant ARR. These metrics are essential in measuring product-market fit, execution quality, and customer satisfaction, guiding investors and stakeholders in making informed decisions.
Reference:
SaaS Investment Quote by Jeff Lieberman

Key Quote
- Quote: "If I was allowed only one metric to make a SaaS investment, it would be GRR...and by quite some margin."
- Thoughts/Ideas: The speaker emphasizes the importance of Gross Revenue Retention (GRR) as the key metric for evaluating SaaS investments. This suggests that GRR is a critical indicator of a company's ability to retain revenue from existing customers, which might be more important than other metrics like customer acquisition costs or net revenue retention.
Person Quoted
- Name: Jeff Lieberman
- Affiliation: Insight Venture Partners
- Thoughts/Ideas: Information about his affiliation with Insight Venture Partners highlights his expertise and credibility in investment, especially in the SaaS sector. It may suggest that Insight Venture Partners prioritizes GRR in their investment strategies.
Event
- Occasion: SaaStr Annual
- Thoughts/Ideas: SaaStr Annual is a major SaaS (Software as a Service) conference, which further emphasizes the significance of the viewpoints shared. This setting suggests the advice is geared towards SaaS founders and investors who attend such industry-specific events.
Visual Elements
- Design:
- Theme: Cloud-themed graphic design with elements of hexagonal shapes and cloud imagery.
- Color Scheme: Combination of blue and white, giving a professional and modern look.
- Logo: SaaStr Annual logo and Insight Venture Partners logo are present.
- Thoughts/Ideas: The imagery and logos reinforce the brand identity and the context of the conference, adding visual appeal and contextual relevance.
Additional Notes
- GRR (Gross Revenue Retention) : This metric measures the percentage of revenue retained from existing customers over a specific period, excluding any additional sales or expansion revenue.
- Importance: High GRR indicates low churn rates and stable revenue from the core customer base, which is a positive sign for investors.
Reference:
Gainsight 2024 CS Benchmark Report
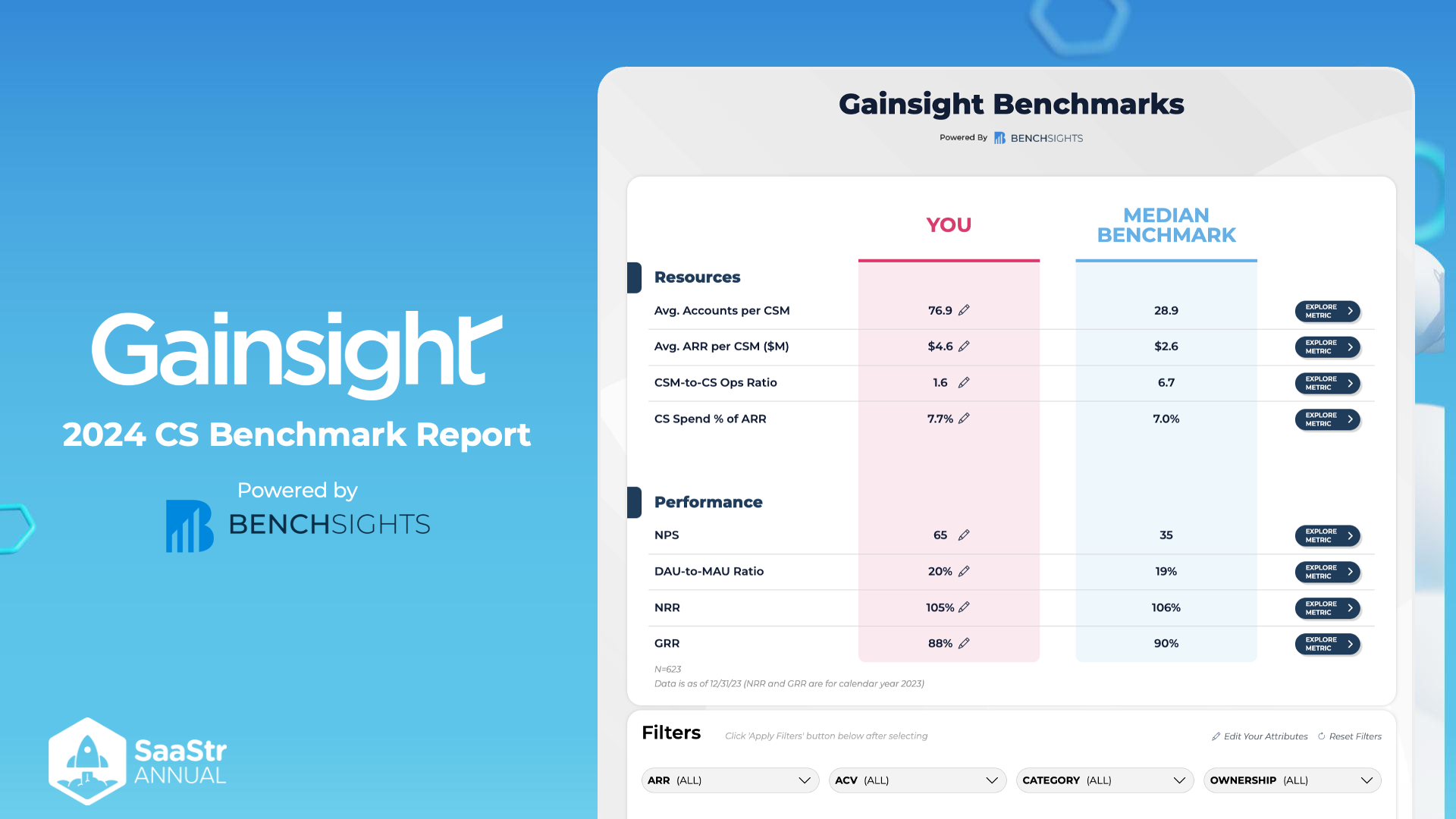
Overview
The image presents a summary of the Gainsight 2024 Customer Success (CS) Benchmark Report. The report is powered by BenchSights and provides key metrics comparing the user's data against the median benchmark.
Key Metrics
Resources
| Metric | You | Median Benchmark |
|---|---|---|
| Avg. Accounts per CSM | 76.9 | 28.9 |
| Avg. ARR per CSM (4.6 | $2.6 | |
| CSM-to-CS Ops Ratio | 1.6 | 6.7 |
| CS Spend % of ARR | 7.7% | 7.0% |
Thoughts/Ideas:
- Avg. Accounts per CSM: Your account managers handle significantly more accounts (76.9) compared to the median (28.9). This might indicate higher efficiency or a need for more resources depending on performance and client satisfaction.
- Avg. ARR per CSM ($M): The Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) per Customer Success Manager (CSM) is considerably higher than the median benchmark.
- CSM-to-CS Ops Ratio: The ratio is much lower than the median, suggesting that there might be an imbalance in support or operational leverage.
- CS Spend % of ARR: Slightly above the median, indicating slightly higher investments in customer success compared to peers.
Performance
| Metric | You | Median Benchmark |
|---|---|---|
| NPS | 65 | 35 |
| DAU-to-MAU Ratio | 20% | 19% |
| NRR | 105% | 106% |
| GRR | 88% | 90% |
Thoughts/Ideas:
- NPS (Net Promoter Score): Your NPS is significantly higher than the median, reflecting better customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- DAU-to-MAU Ratio: Daily Active Users to Monthly Active Users ratio is slightly higher than the median, showing consistent user engagement.
- NRR (Net Revenue Retention): Just below the median, indicating good retention but with slight opportunity for improvement.
- GRR (Gross Revenue Retention): Slightly lower than the median, suggesting potential challenges in retaining revenue without upsells.
Additional Information
- Filters Section: Allows for customization and filtering by ARR, ACV, Category, and Ownership.
- Data Validity: The data is derived from a sample size (N) of 623, with a cutoff date mentioned as 12/31/23. NRR and GRR metrics are for the calendar year 2023.
Thoughts/Ideas:
- Filters: Using the filters effectively can help in tailoring the benchmark comparisons to more relevant peer sets or market segments.
- Data Validity: Ensure ongoing updates to keep comparisons relevant as market conditions and company performance evolve.
Reference:
Top 10 CS Questions Investors WILL Grill You About

-
Title Area: "Top 10"
- Thoughts: The title area uses a vibrant, eye-catching design with the number "10" prominently featured in a red banner, indicating a top ten list.
- Additional Information: This type of design is often used to quickly grab attention. It's likely the topic is very relevant or frequently asked about in the related field.
-
Focus Topic: "CS Questions Investors WILL Grill You About”
- Thoughts: The main topic is centered around questions that customer success (CS) teams might face from investors.
- Additional Information: It implies that these are critical or challenging questions that investors consider important in decision-making processes.
-
Background Design
- Thoughts: The use of clouds, geometric shapes, and stars creates a playful and engaging atmosphere.
- Additional Information: Such designs are often used in presentations and infographics to keep the viewer engaged and interested.
-
SaaStr Annual Logo
- Thoughts: The logo in the bottom left suggests that this content is related to SaaStr Annual, a well-known event or brand in the SaaS (Software as a Service) industry.
- Additional Information: SaaStr Annual is a large event bringing together SaaS founders, VCs, and executives. The logo adds credibility and context to the image.
-
Contrast and Emphasis
- Thoughts: The use of bright colors with a blue sky background makes the text stand out clearly.
- Additional Information: Effective use of color contrast ensures that key messages are easily readable and memorable.
Implications for Customer Success Teams:
- Preparation for Investor Meetings: CS teams should be well-prepared to answer tough questions about customer success.
- Thoughts: Practice and know your key metrics and customer data.
- Critical Information: Focus on crucial customer success metrics.
- Thoughts: Investors might ask about customer acquisition cost (CAC), customer lifetime value (CLV), churn rate, and net promoter score (NPS).
- Metrics and Performance: Have clear, data-supported answers.
- Thoughts: Demonstrating strong customer success metrics can instill confidence in investors regarding the scalability and sustainability of the business.
Visual Aesthetics for Presentations:
- Engaging Design: Use playful and engaging graphics.
- Thoughts: Keeps the audience interested and helps in better retention of information.
- Professional Branding: Include relevant logos and branding elements.
- Thoughts: Adds credibility and context to your presentation.
By interpreting these elements, it's clear this image is designed to inform SaaS-based customer success teams about the kind of investor scrutiny they might face and how to be prepared for it using data and strong performance metrics.
Reference:
Top 10 Questions for Customer Success and Retention

-
How does your NRR break out into various components?
- Explanation: This question seeks to understand the breakdown of Net Revenue Retention (NRR), which includes expansion, contraction, and churn within customer segments.
- Additional Information: Net Revenue Retention is a crucial metric as it reflects the company's ability to retain and grow revenue from existing customers.
-
What is your cohort-level GRR?
- Explanation: Gross Revenue Retention measures the revenue retained from a cohort of customers over a period without considering upsells or expansion revenue.
- Additional Information: GRR is a vital metric for understanding the base retention rate, providing insights into customer satisfaction and product value.
-
What are your early warning indicators in your business?
- Explanation: Identifying early warning indicators can help predict potential churn or issues within segments of your customer base.
- Additional Information: Tracking these indicators allows businesses to proactively address issues before they result in lost customers.
-
What makes your customers sticky?
- Explanation: This question explores the factors and features that contribute to customer loyalty and repeat use of products or services.
- Additional Information: Understanding 'stickiness' helps businesses to enhance customer engagement and retention strategies.
-
What do you do operationally to improve retention?
- Explanation: Discusses operational strategies and processes implemented to increase customer retention rates.
- Additional Information: Examples include personalized customer support, proactive communication, and loyalty programs.
-
What do you do to show the value your clients are receiving?
- Explanation: Highlights the methods used to demonstrate to customers the value they gain from your products or services.
- Additional Information: This could involve regular reporting, case studies, ROI calculators, and customer testimonials.
-
Who are your biggest advocates?
- Explanation: Identifying your most enthusiastic and loyal customers who promote your brand and products.
- Additional Information: Leveraging customer advocates can help in building trust and attracting new customers.
-
What is your cost structure for CS?
- Explanation: Understanding the costs involved in Customer Success (CS) operations including tools, staff, and customer engagement activities.
- Additional Information: Effective CS cost management can enhance profitability and customer satisfaction.
-
What are you doing to scale efficiently?
- Explanation: Discusses strategies and practices implemented to scale Customer Success operations sustainably and efficiently.
- Additional Information: Scaling efficiently might involve automation, advanced analytics, and streamlined processes.
-
How are you using AI in CS?
- Explanation: Explores the implementation of artificial intelligence in Customer Success operations for improving efficiency and effectiveness.
- Additional Information: AI applications can include chatbots for customer service, predictive analytics for churn prediction, and personalized customer communication.
Net Revenue Retention vs. ARR
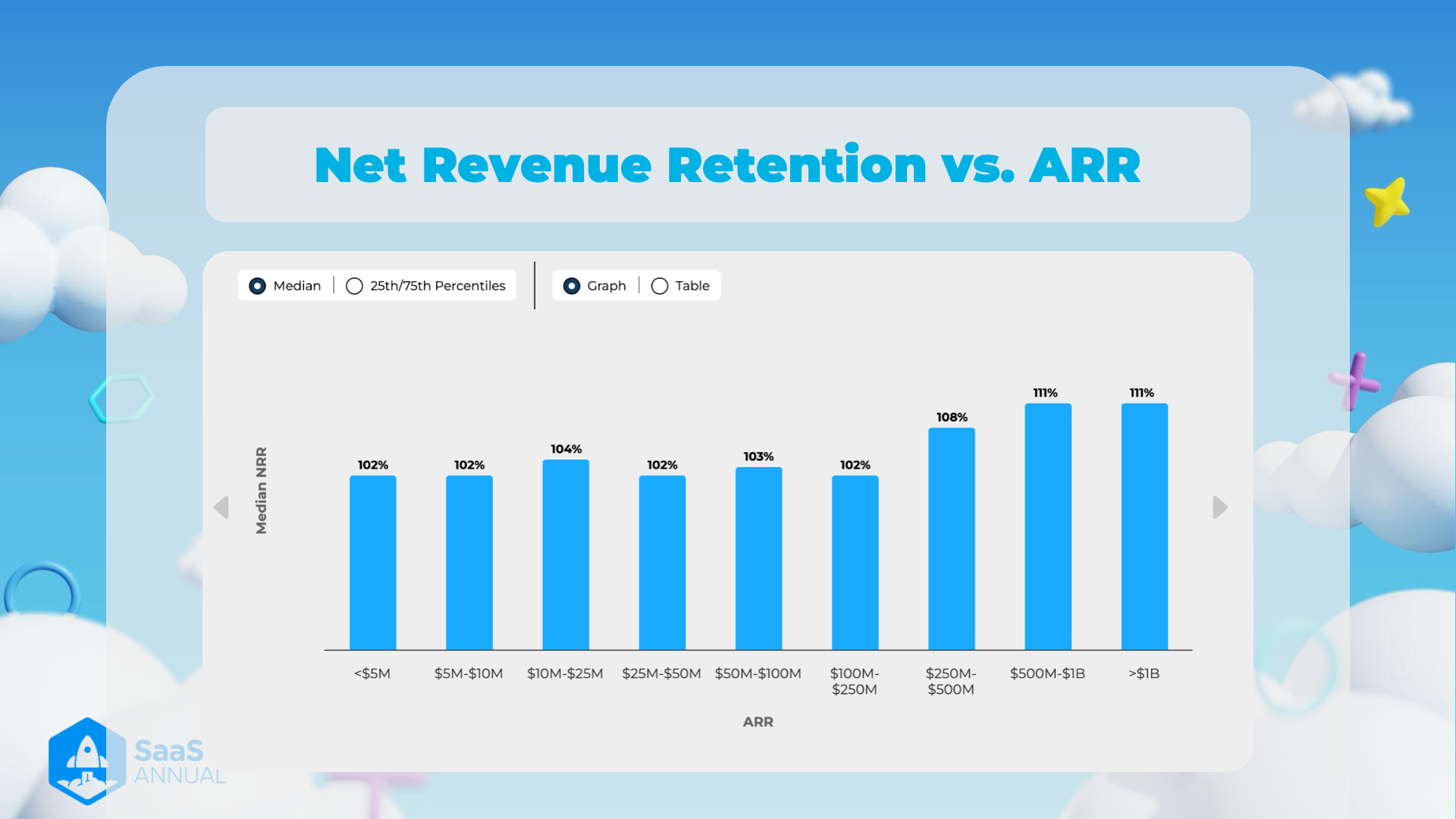
Overview:
The image presents a bar chart visualizing the relationship between Net Revenue Retention (NRR) and Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR). Key details are as follows:
- Metric focus: Median NRR
- ARR Categories: Ranges from less than 1 billion
- Presentation: Graph format with the ability to switch to table format
Notes with Explanations:
ARR Categories and Corresponding Median NRR:
- <$5M: 102%
- Companies with less than $5 million ARR have a median NRR of 102%, indicating that they are slightly growing their revenue from existing customers over time.
- 10M: 102%
- Similar to the <5M and $10M also experience a 102% median NRR.
- 25M: 104%
- As companies scale to an ARR between 25M, their median NRR improves to 104%, demonstrating a better retention and upsell rate compared to smaller companies.
- 50M: 102%
- The median NRR drops back to 102% for companies in the 50M ARR range.
- 100M: 103%
- Companies with ARR between 100M experience a slight improvement, with a median NRR of 103%.
- 250M: 102%
- For the 250M ARR category, the median NRR returns to 102%.
- 500M: 108%
- There is a significant increase in NRR for companies with ARR between 500M, with a median NRR of 108%.
- 1B: 111%
- Companies within the 1B ARR range enjoy a healthy median NRR of 111%.
- >$1B: 111%
- Similar to the previous category, companies with ARR greater than $1 billion also have a median NRR of 111%, suggesting robust retention and upsell performance at the highest revenue scales.
Analysis of Trends:
- Growth Consistency: The median NRR remains relatively consistent across different ARR categories, showing slight fluctuations.
- Significant Increases: Notable increases in NRR are observed in the 500M and 1B categories.
- High Performance for Large Firms: Companies with ARR over $250M generally show better retention and upsell rates, indicating that scale may help improve these metrics.
Additional Observations:
- Possible Factors for Higher NRR: Larger companies might have more resources for customer success initiatives, resulting in higher NRR. They may also benefit from brand loyalty and stronger market positions.
- Implications for Smaller Firms: The relatively lower NRR for smaller companies suggests they might need to focus more on retention strategies and upselling existing customers to match the performance of larger peers.
Table Format (Extracted Data):
| ARR Category | Median NRR |
|---|---|
| <$5M | 102% |
| 10M | 102% |
| 25M | 104% |
| 50M | 102% |
| 100M | 103% |
| 250M | 102% |
| 500M | 108% |
| 1B | 111% |
| >$1B | 111% |
102% Average Net Retention (Compared to 105% Last Year)
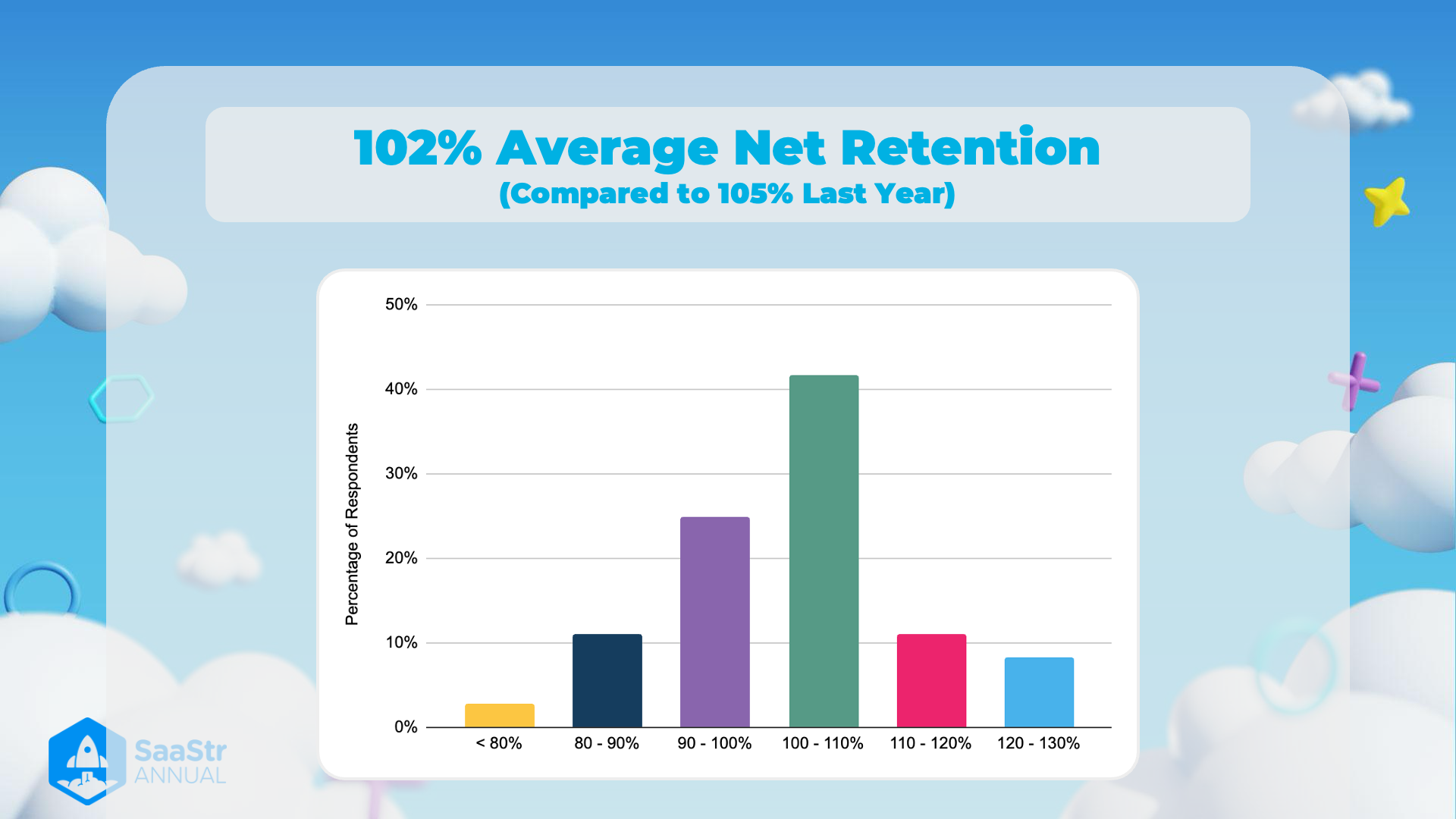
The image illustrates data regarding the average net retention for a certain year, highlighting a decline compared to the previous year.
Key Insights
1. Average Net Retention Rate:
- The average net retention rate for the current year is 102%.
- Last year's average was slightly higher at 105%.
- Thought: While a retention rate above 100% is generally positive, a decreasing trend could indicate emerging challenges in customer retention.
2. Distribution of Respondents:
- < 80%:
- Percentage of Respondents: ~2%
- Idea: Companies in this category likely face significant issues with customer churn.
- 80 - 90%:
- Percentage of Respondents: ~7%
- Idea: Slightly better retention but still a notable concern.
- 90 - 100%:
- Percentage of Respondents: ~18%
- Idea: These companies are able to retain most of their customers, with room for improvement.
- 100 - 110%:
- Percentage of Respondents: ~47%
- Idea: The largest group of respondents, indicating strong performance in retaining and expanding customer accounts.
- 110 - 120%:
- Percentage of Respondents: ~14%
- Idea: Excellent retention and expansion capabilities.
- 120 - 130%:
- Percentage of Respondents: ~12%
- Idea: Outstanding performance, indicating customers are not just staying but are purchasing more or upgrading services.
3. Visual Representation:
- The graph uses a bar chart to depict the percentage distribution of respondents across different net retention rate ranges.
- Thought: Visual aids like this can help quickly identify trends and areas of success or concern.
4. Branding:
- The bottom-left corner of the image contains the "SaaStr Annual" logo, indicating the source or context of the data.
- Idea: This suggests the image was produced in the context of an annual report or conference for SaaS (Software as a Service) businesses.
Table Format Data:
| Retention Rate Range | Percentage of Respondents |
|---|---|
| < 80% | ~2% |
| 80 - 90% | ~7% |
| 90 - 100% | ~18% |
| 100 - 110% | ~47% |
| 110 - 120% | ~14% |
| 120 - 130% | ~12% |
Understanding these data points can provide insights into how SaaS companies are performing in terms of retaining their customer base year over year.
Reference:
SaaStr Annual - Net Revenue Retention (NRR) Breakdown
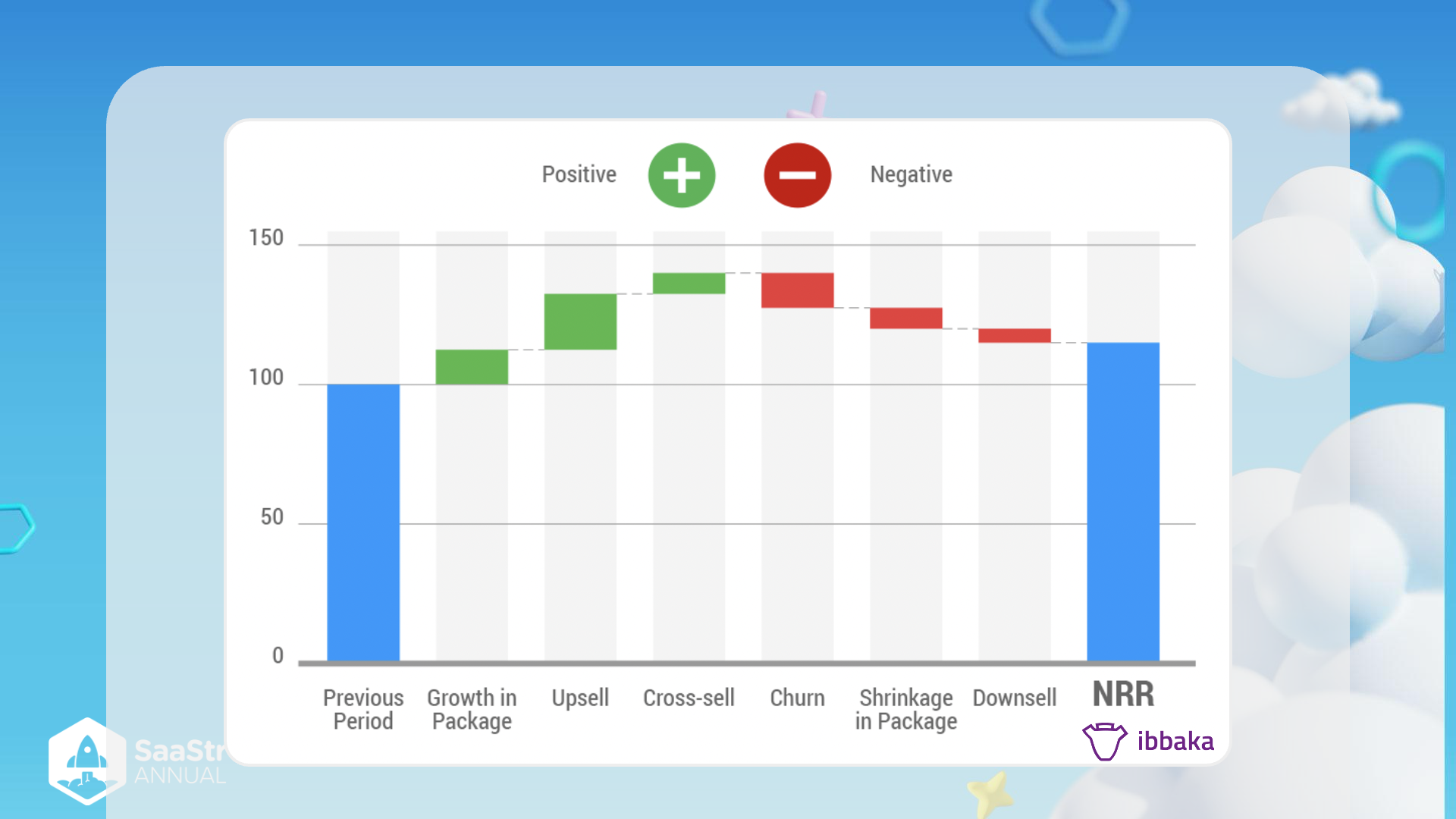
Overview
The image depicts a visual representation of different elements impacting Net Revenue Retention (NRR) for a SaaS product or service. NRR is a key metric that indicates the percentage of recurring revenue retained from existing customers.
Key Sections
1. Previous Period
- Color: Blue
- Detail: Represents the starting point at 100, which indicates the revenue from the previous period before any changes like upgrades, downgrades, or churn.
- Note: This period serves as the base for calculating growth or decline in revenue.
2. Growth in Package
- Color: Green
- Detail: Represents additional revenue generated from existing customers who increase their usage or move to a more expensive package.
- Note: Growth in package is a positive indicator, contributing to higher NRR.
3. Upsell
- Color: Green
- Detail: Additional revenue from selling higher-value features or advanced versions of the product to existing customers.
- Note: Similar to growth in package, upselling contributes positively to NRR by increasing the revenue from current customers.
4. Cross-sell
- Color: Green
- Detail: Revenue from selling complementary or additional products to existing customers.
- Note: Cross-selling helps in diversifying product usage, leading to an overall positive impact on NRR.
5. Churn
- Color: Red
- Detail: Represents revenue lost due to customers leaving or cancelling their subscription.
- Note: Churn is a negative component, reducing the overall NRR. It highlights the importance of customer retention strategies.
6. Shrinkage in Package
- Color: Red
- Detail: Revenue lost due to customers downgrading to a less expensive package or reducing their usage.
- Note: Shrinkage indicates a negative trend but often provides insight into customer satisfaction and value perception.
7. Downsell
- Color: Red
- Detail: Loss in revenue when customers switch to cheaper subscription plans.
- Note: Indicates negative customer sentiment or budget cuts, affecting NRR adversely.
Net Revenue Retention (NRR)
- Color: Blue
- Detail: The final metric, showing the overall percentage of retained revenue after considering all positive and negative changes.
- Note: A critical measure of business health, indicating the effectiveness of growth strategies and customer satisfaction levels.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the factors influencing NRR is essential for SaaS businesses to strategize customer retention and revenue growth effectively. Monitoring these segments helps in pinpointing areas for improvement and opportunities for upsell and cross-sell initiatives.
Table of Elements:
| Segment | Type | Color | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Previous Period | Baseline | Blue | Neutral |
| Growth in Package | Positive | Green | Increases |
| Upsell | Positive | Green | Increases |
| Cross-sell | Positive | Green | Increases |
| Churn | Negative | Red | Decreases |
| Shrinkage in Package | Negative | Red | Decreases |
| Downsell | Negative | Red | Decreases |
| NRR | Net Total | Blue | Varies |
By focusing on these key components, businesses can develop targeted strategies to enhance their Net Revenue Retention and achieve sustainable growth.
Gross Revenue Retention vs. ARR
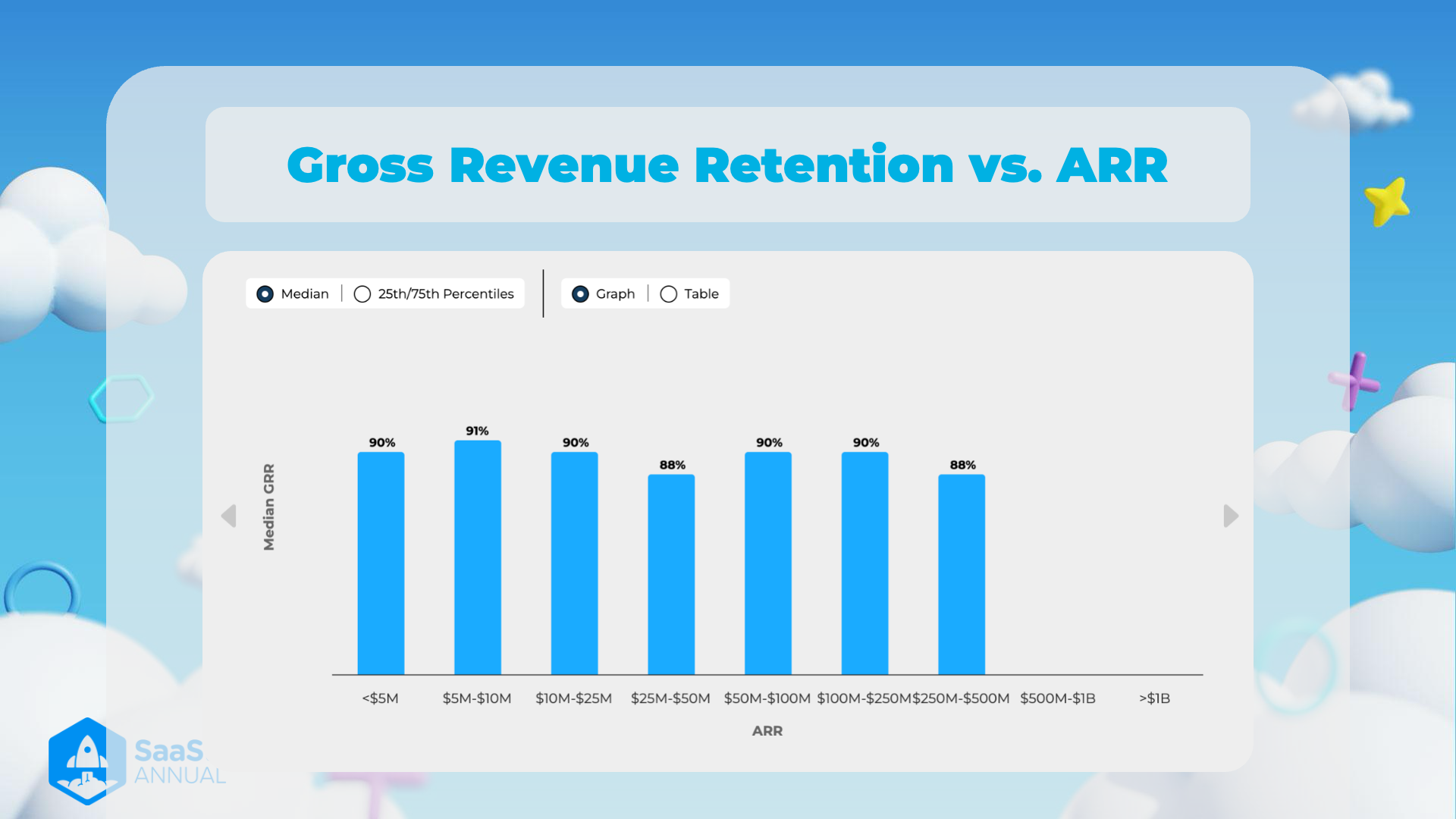
Overview
- This image presents a bar graph showcasing the relationship between Gross Revenue Retention (GRR) and Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR).
- The graph aims to provide insight into the median retention metrics across different ARR brackets.
Key Components
Labels
- Title: "Gross Revenue Retention vs. ARR"
- Clarifies the comparison metric being analyzed.
- Y-axis: "Median GRR"
- Represents the Median Gross Revenue Retention in percentage terms.
- X-axis: "ARR"
- Categories are divided into revenue brackets ranging from "<1B".
Data Points
- Median GRR by ARR Bracket
ARR Category Median GRR <$5M 90% 10M 91% 25M 90% 50M 88% 100M 90% 250M 90% 500M 88% 1B 90% >$1B 88% - The bars' heights indicate the different median GRR percentages for varying ARR brackets.
Additional Notes
- Legend:
- Median: The graph represents the median values for each ARR bracket.
- Graph/Table Toggle: Provides an option to switch between graphical and tabular representations for clarity.
- Options: Lightly highlighted options, such as viewing 25th/75th percentiles, suggest deeper data insight variables not currently showcased in the selected view.
Graph Patterns
- Most ARR brackets have a stable GRR percentage around 90%.
- This could indicate consistent revenue retention strategies across these segments.
- There's a slight dip to 88% GRR in the 50M and >$250M ARR segments.
- Companies in these ARR brackets might face unique challenges impacting revenue retention slightly more than others.
Visual Design
- The background with clouds adds a whimsical, light-hearted visual to the data presentation, likely intending to make the information more engaging.
- Visual elements, such as hexagons and stars, contribute to a tech-themed, innovative aesthetic.
- The "SaaS Annual" logo suggests that the data is related to a specific annual review or event focusing on the Software as a Service industry.
By understanding these key components and patterns, we can better understand the implications on SaaS businesses regarding revenue retention strategies at different revenue scales.
Reference:
85% Average Gross Retention
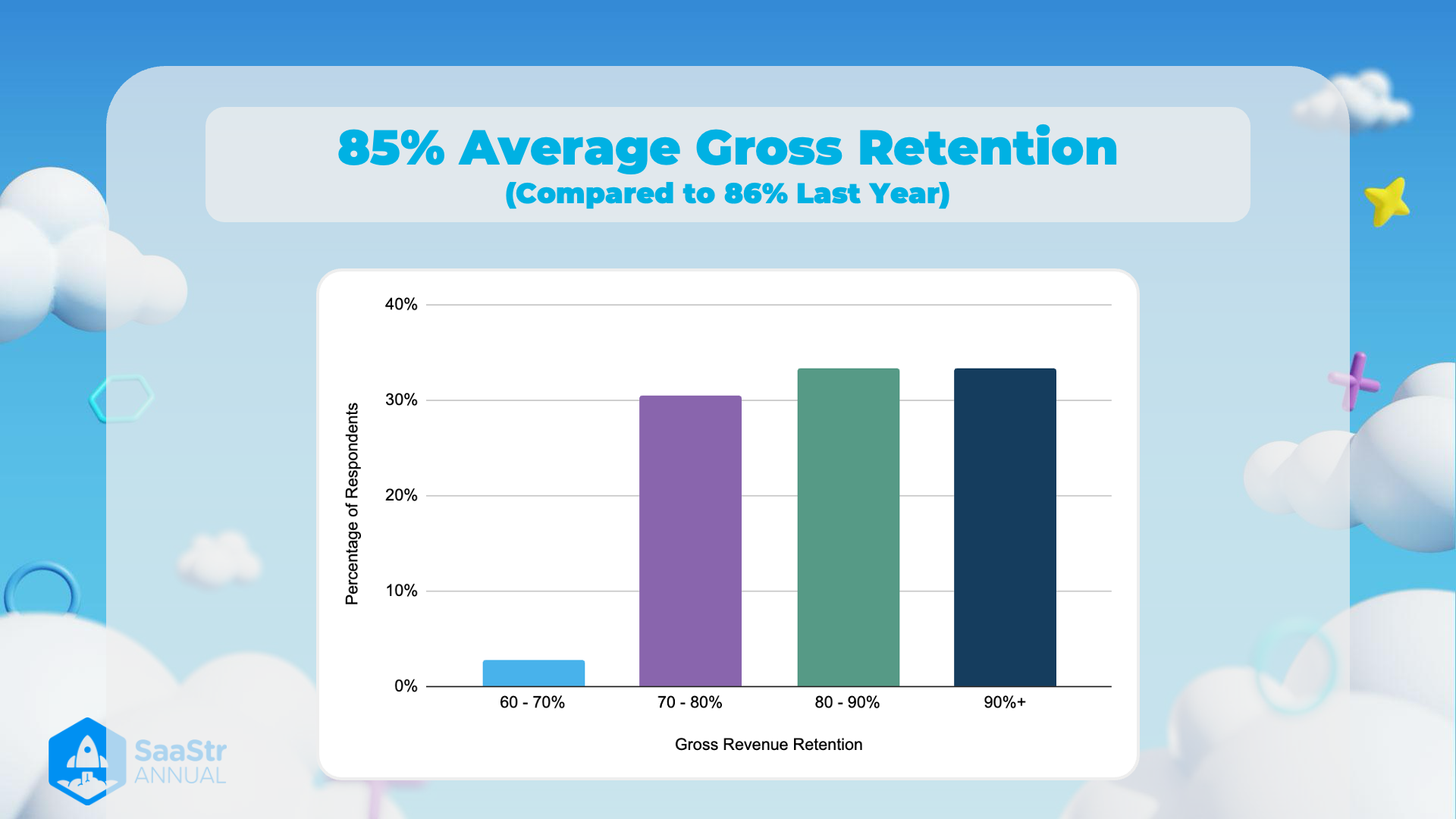
Key Points
Average Gross Retention
- Data Presented: The image showcases that the average gross retention rate is 85%.
- Comparison to Last Year: This rate is compared to last year's gross retention rate of 86%, indicating a slight decrease.
- Importance of Retention: Gross retention rate is crucial for SaaS (Software as a Service) companies as it reflects customer loyalty and potential for long-term revenue.
Distribution of Gross Revenue Retention Rates
- Categories: The chart breaks down the gross revenue retention rates into four categories:
- 60-70% : Smallest percentage of respondents.
- 70-80% : Second smallest percentage of respondents.
- 80-90% : Second highest percentage of respondents.
- 90%+ : Highest percentage of respondents.
- Explanation: This shows that most SaaS companies maintain a gross revenue retention rate above 70%, which indicates relatively high customer satisfaction and retention.
Visual Elements
- Graph Type: Bar graph representing different gross revenue retention rates.
- Color Coding: Each retention rate category is represented by a different color for easy distinction.
- Layout and Design: Graph is simple and clear with a blue-themed background indicative of the SaaS sector.
Source
- Brand Mention: The bottom left corner of the image credits "SaaStr Annual" as the source.
- Event Context: SaaStr Annual is a major event for SaaS companies, often sharing vital industry benchmarks and data.
Data Table
| Gross Revenue Retention | Percentage of Respondents |
|---|---|
| 60-70% | ~1% |
| 70-80% | ~23% |
| 80-90% | ~34% |
| 90%+ | ~36% |
Additional Thoughts
- Implication of High Retention Rates: Companies with retention rates above 90% might be leveraging excellent customer service, continuous product improvement, and effective customer success strategies.
- Strategic Focus: SaaS companies often focus on improving their gross retention rates through various customer engagement and retention strategies, such as upselling, cross-selling, and effective onboarding processes.
Conclusion
- Trend Analysis: Despite a slight drop from last year, the overall gross retention rate is still high, which is favorable for the SaaS industry.
- Strategic Importance: Retention rates can serve as a critical KPI (Key Performance Indicator) for assessing the health and long-term viability of SaaS businesses.
Reference:
SaaS Retention Analysis
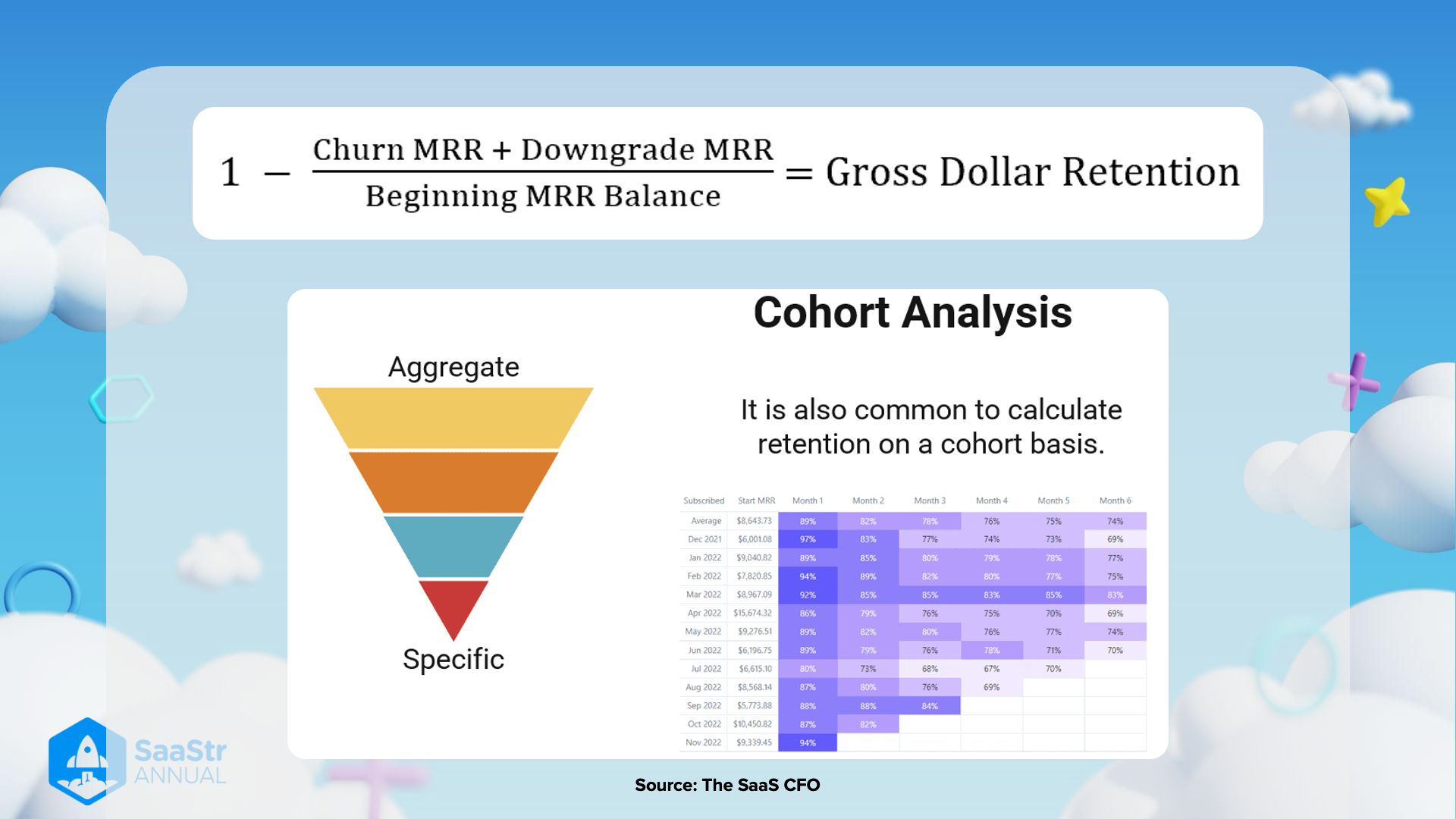
Gross Dollar Retention Calculation
Formula:
Thoughts:
- Gross Dollar Retention (GDR) measures how much of the recurring revenue is retained over a period without considering upgrades or expansions.
- High GDR indicates strong customer satisfaction and reduced churn rates, which are critical for the financial health of a SaaS company.
Funnel Analysis
Description:
- The funnel diagram demonstrates the transition from an aggregate view to a specific view.
- The purpose is to narrow down data to specifics for detailed analysis.
Thoughts:
- Aggregate Level: Provides an overall view of metrics, useful for high-level management and stakeholders.
- Specific Level: Offers detailed insights into specific segments, helping identify precise areas of improvement.
Cohort Analysis
Description:
- Caption: It is also common to calculate retention on a cohort basis.
Cohort Retention Data:
| Month | Average | Dec 2021 | Jan 2022 | Feb 2022 | Mar 2022 | Apr 2022 | May 2022 | Jun 2022 | Jul 2022 | Aug 2022 | Sep 2022 | Oct 2022 | Nov 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subscribed | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Start MRR | 6,010.08 | 7,785.49 | 9,276.51 | 8,165.75 | 8,168.34 | 9,393.45 | |||||||
| Month 1 | 89% | 97% | 93% | 82% | 92% | 81% | 80% | 83% | 81% | 87% | 92% | 86% | |
| Month 2 | 82% | 83% | 88% | 80% | 85% | 78% | 76% | 73% | 68% | 78% | 76% | 84% | |
| Month 3 | 78% | 77% | 83% | 77% | 85% | 75% | 74% | 67% | 67% | 69% | 70% | - | |
| Month 4 | 76% | 74% | 79% | 75% | 83% | 77% | 73% | 70% | 67% | 70% | - | - | |
| Month 5 | 75% | 73% | 78% | 75% | 77% | 75% | 71% | 71% | 70% | - | - | - | |
| Month 6 | 74% | 69% | 75% | 75% | 69% | 74% | 74% | 70% | - | - | - | - |
Thoughts:
- Cohort Analysis: This approach groups customers by a shared characteristic (e.g., the month they subscribed) and tracks their behavior over time.
- Application in Retention: Helps identify trends and patterns in customer retention, which can inform targeted strategies for improving customer satisfaction and reducing churn.
Additional Information:
- This analysis can reveal critical insights into how different customer segments retain over time and the effectiveness of retention strategies.
- The color shading in the table likely indicates the retention percentage more visually distinct, with darker shades showing higher retention rates.
Reference:
Net Promoter Score Explanation
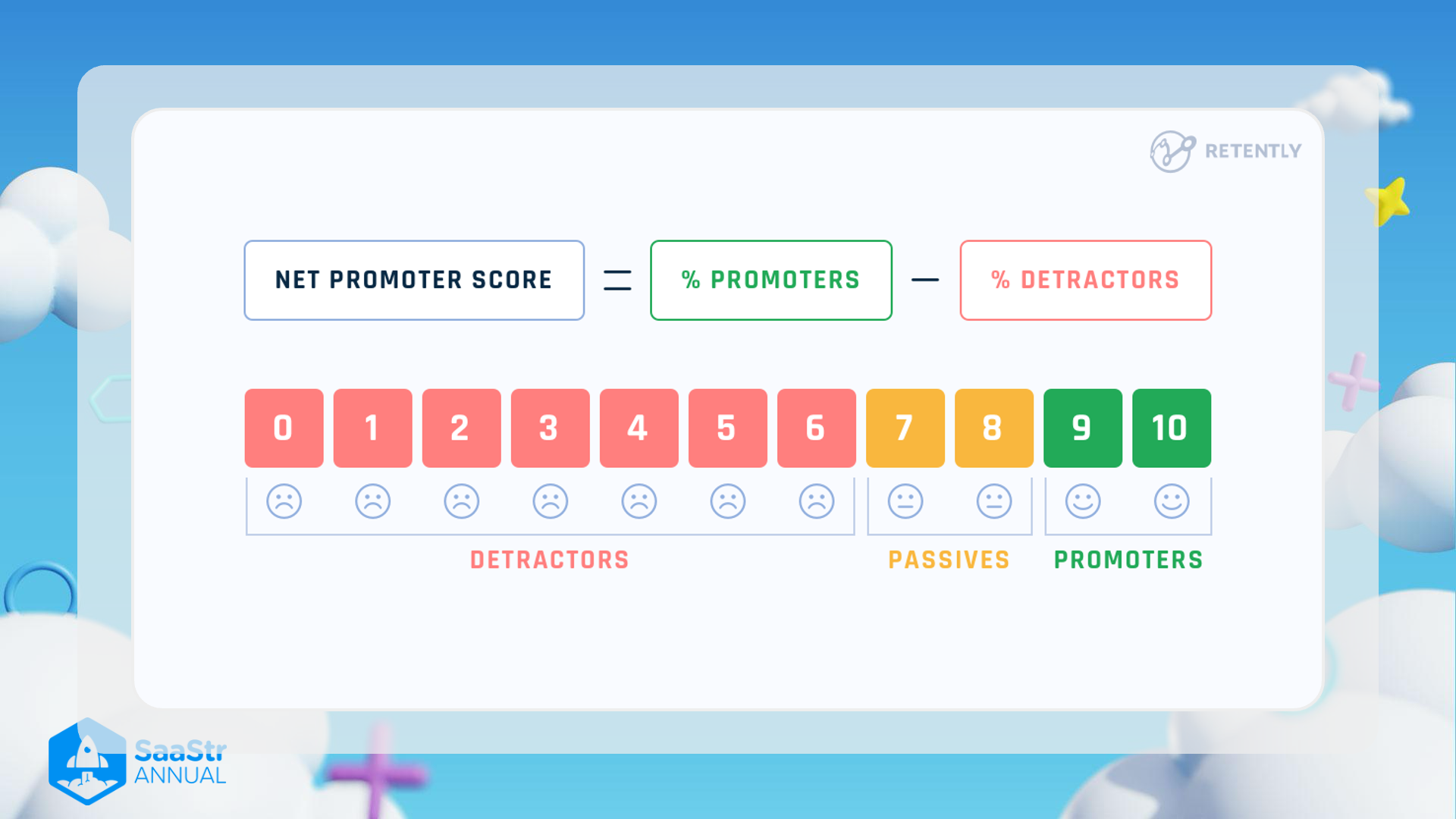
Overview
The image provides a visual explanation of the Net Promoter Score (NPS) framework, a widely used metric to gauge customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Components of the NPS Formula
NPS = % Promoters – % Detractors
- % Promoters: The percentage of respondents who rate the product or service a 9 or 10. These are highly satisfied customers likely to recommend the company.
- % Detractors: The percentage of respondents who rate the product or service between 0 and 6. These customers are dissatisfied and unlikely to recommend the company.
Rating Scale
- Detractors (0-6) :
- 0: Very Dissatisfied
- 1: Very Dissatisfied
- 2: Dissatisfied
- 3: Dissatisfied
- 4: Neutral
- 5: Neutral
- 6: Neutral
- These ratings are negatively viewed and indicate that the customer is unhappy with the product or service.
- Passives (7-8) :
- 7: Neutral
- 8: Satisfied but not enthusiastic
- These ratings are not included in the NPS calculation but can indicate areas for improvement.
- Promoters (9-10) :
- 9: Very Satisfied
- 10: Extremely Satisfied
- These ratings indicate that the customer is very happy with the product or service and is likely to recommend it.
Interpretation and Use
- NPS is a critical indicator of customer loyalty and future growth potential.
- High scores mean more Promoters than Detractors, signaling strong customer satisfaction.
- Low scores, with more Detractors, indicate widespread dissatisfaction.
Additional Points
- Application: Commonly used in surveys, the NPS question is typically: "On a scale of 0 to 10, how likely are you to recommend our product/service to a friend or colleague?"
- Insights: Regular tracking of NPS helps businesses understand customer perceptions and make improvements. Trends can reflect changes in customer satisfaction over time.
Summary Table
| Rating Range | Category | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0-6 | Detractors | Dissatisfied customers, likely to provide negative feedback |
| 7-8 | Passives | Neutral customers, satisfied but not enthusiastic |
| 9-10 | Promoters | Highly satisfied customers, likely to recommend |
By using this framework, businesses can effectively measure and enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Reference:
Early Warning Scores
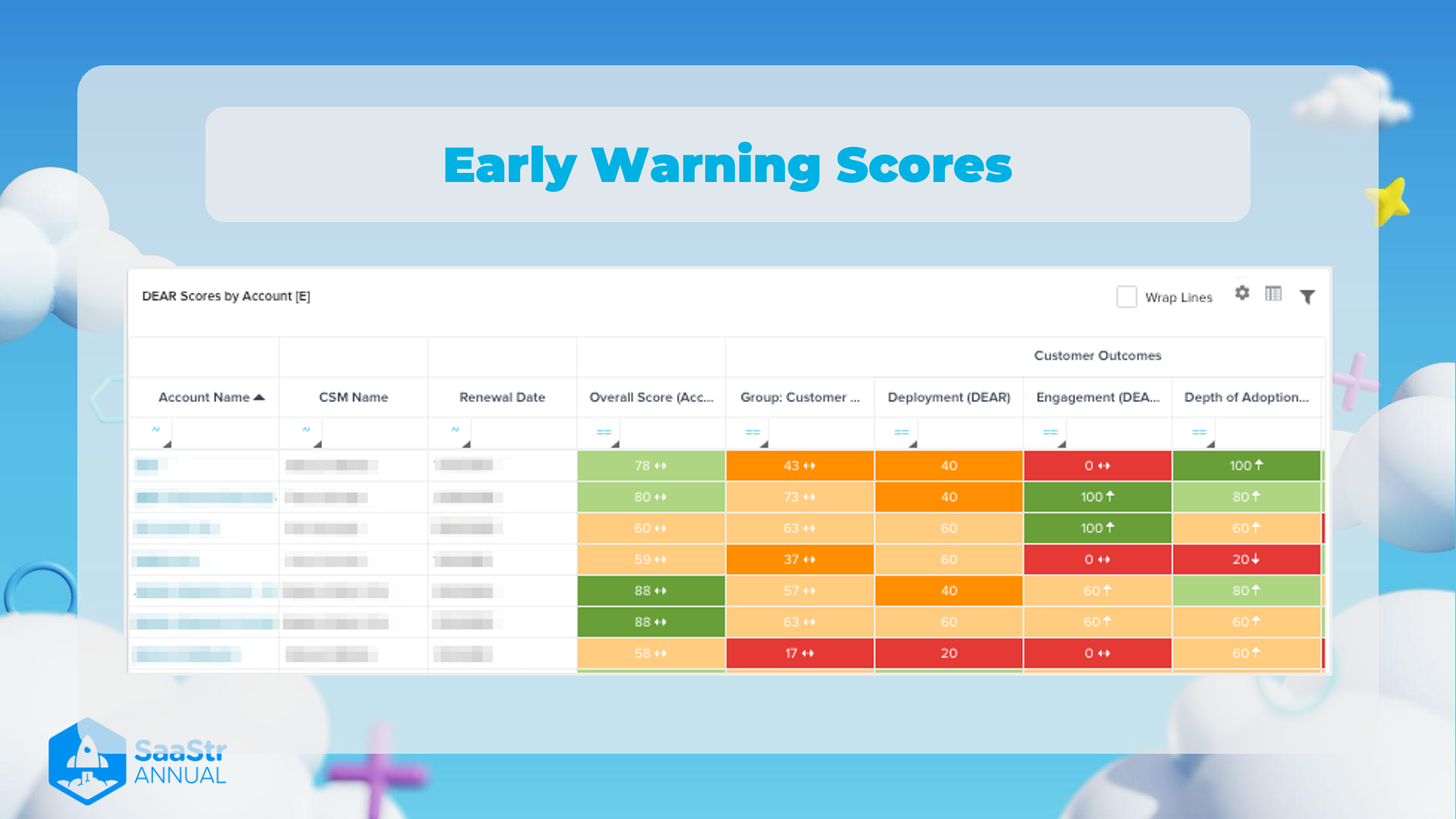
The image showcases a dashboard intended to monitor and score customer health through various metrics, known as DEAR Scores. The table helps identify potential risks in customer relationships by providing early warning scores. Here's a detailed breakdown:
General Information
- Title: Early Warning Scores
- Purpose: To monitor customer health and identify at-risk accounts by assessing different performance metrics.
- Platform: SaaStr Annual
Table Breakdown
The table titled "DEAR Scores by Account" incorporates various columns that assess and score customer health on different parameters. The table includes the following information:
Column Headers
-
Account Name
- Identifies the customer or client account.
-
CSM Name
- Customer Success Manager associated with the account.
-
Renewal Date
- Date when the client's contract is due for renewal.
-
Overall Score (Account Health)
- A composite score representing the overall health and satisfaction level of the account. Color-coded for quick visualization:
- Green indicates higher scores and healthier accounts.
- Yellow and red suggest lower scores and potential issues.
- A composite score representing the overall health and satisfaction level of the account. Color-coded for quick visualization:
-
Group: Customer Sentiment
- Customers' general perception and sentiment towards the service or product.
-
Deployment (DEAR)
- Indicates the extent to which the product/service has been deployed across the customer’s intended use-cases or departments.
-
Engagement (DEAR)
- Measures how actively the customer is interacting with the product/service.
- Higher scores reflect more active engagement.
-
Depth of Adoption (DEAR)
- Represents how deeply the customer has integrated the product/service into their workflows.
- Higher scores signify broader and deeper usage.
Sample Data
| Account Name | CSM Name | Renewal Date | Overall Score (Account Health) | Group: Customer Sentiment | Deployment (DEAR) | Engagement (DEAR) | Depth of Adoption (DEAR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ------------- | -- | ------------- | ------------------------------ | ------------------------- | ------------------- | ------------------- | ------------------------- |
| 1st Row Name | Name1 | Date1 | Green 78 ↑ | Orange 43 ↑ | Orange 40 | Red 0 ↓ | Green 100 ↑ |
| 2nd Row Name | Name2 | Date2 | Green 80 ↑ | Green 73 ↑ | Orange 40 | Green 100 ↑ | Green 80 ↑ |
| 3rd Row Name | Name3 | Date3 | Yellow 60 ↑ | Orange 63 ↑ | Orange 60 | Green 100 ↑ | Yellow 60 ↑ |
| 4th Row Name | Name4 | Date4 | Yellow 59 ↑ | Orange 37 ↑ | Orange 60 | Red 0 ↓ | Red 20 ↓ |
| 5th Row Name | Name5 | Date5 | Green 88 ↑ | Orange 57 ↑ | Orange 40 | Yellow 60 ↑ | Green 80 ↑ |
| 6th Row Name | Name6 | Date6 | Green 88 ↑ | Orange 63 ↑ | Orange 60 | Yellow 60 ↑ | Yellow 60 ↑ |
| 7th Row Name | Name7 | Date7 | Yellow 58 ↑ | Red 17 ↑ | Red 20 | Red 0 ↓ | Yellow 60 ↑ |
Thoughts and Additional Information
-
Health Tracking: This type of scoring system is crucial for customer retention strategies. By identifying potential risks early, proactive measures can be taken.
-
Visualization: The use of color-coding enhances the readability of the data, making it easy to identify high-risk accounts at a glance.
-
Customer Outcomes: Each metric contributes to the overall assessment of customer health and helps in understanding different aspects of customer interaction and satisfaction.
-
Improvement Areas: Accounts with lower scores in categories such as Engagement and Depth of Adoption might require more focused customer success initiatives to improve their health scores.
-
Proactive Interventions: Identifying low scores in sentiment and engagement early can allow for timely interventions and personalized engagement strategies, enhancing customer relationships and reducing churn.
By closely monitoring these metrics, a company can significantly improve customer satisfaction and retention rates, ultimately driving better business outcomes.
Reference:
Early Warning Sentiment
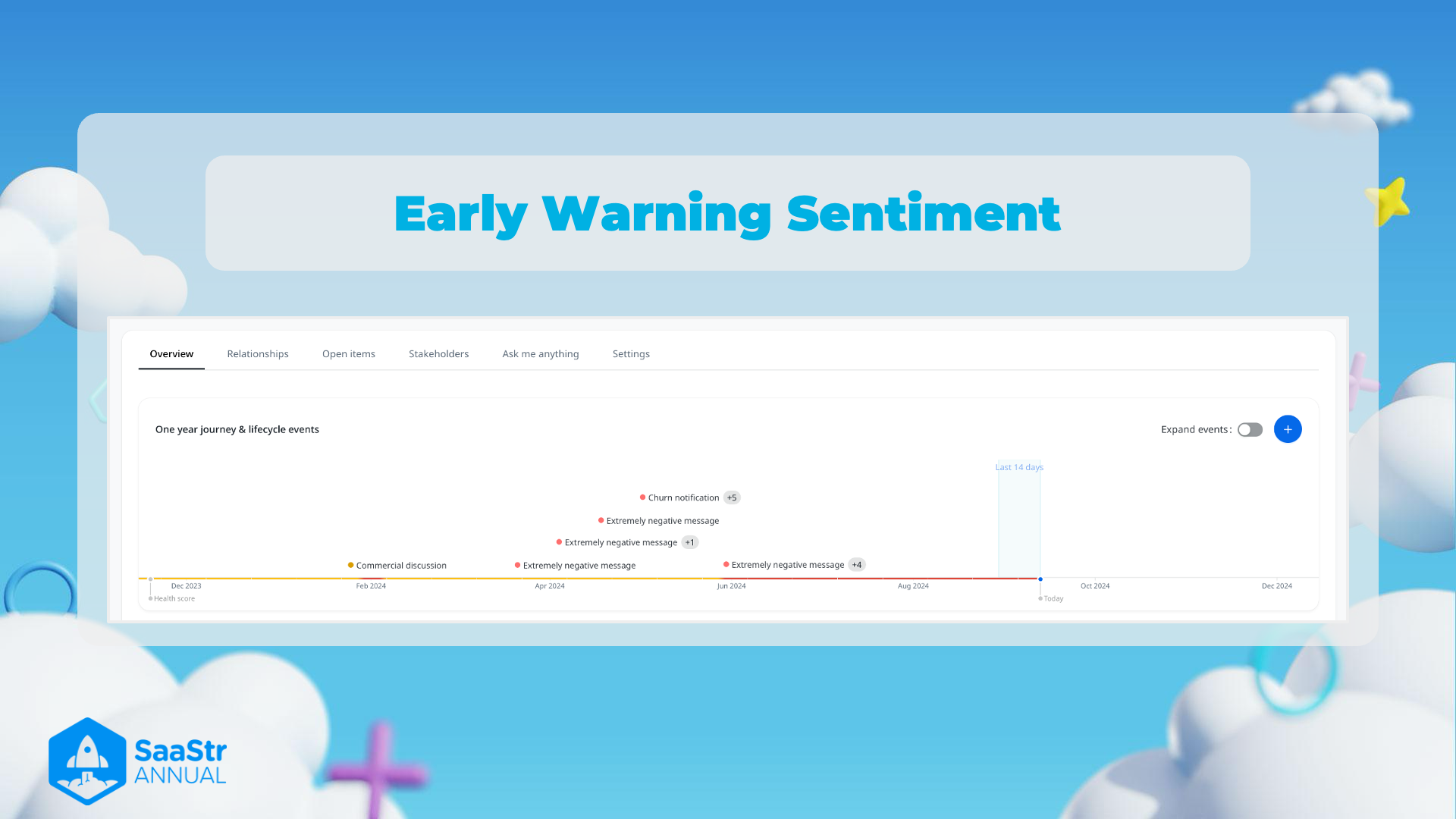
Overview of Image
The image shows a feature called "Early Warning Sentiment" designed to track events and sentiments over a one-year period. The layout indicates various sections and tabs, suggesting a dashboard interface.
Key Sections and Tabs
- Tabs:
- Overview: Default tab that provides a summary of key events and lifecycle.
- Relationships: Possibly tracks relationships related to the user or customer.
- Open items: Lists outstanding tasks or issues.
- Stakeholders: Keeps track of individuals or entities involved.
- Ask me anything: A general Q&A or help section.
- Settings: Configuration options and preferences.
Timeline Details
- Key Events:
- December 2023:
- Commercial discussion - Indicating a positive or neutral business interaction.
- February to August 2024:
- Series of extremely negative messages and a churn notification, with the latter having a count of
5.
- Series of extremely negative messages and a churn notification, with the latter having a count of
- December 2023:
Sentiment Indicators
- Extremely Negative Messages:
- Several points on the timeline (April, June, and August 2024) indicating dissatisfaction or issues.
- Specific messages have counts next to them, highlighting their significance (e.g.,
+1,+4).
- Churn Notification:
- Indicates customer churn (loss of customer) happening around June 2024, with a noted impact (
+5).
- Indicates customer churn (loss of customer) happening around June 2024, with a noted impact (
Additional Features
- Expand Events Toggle:
- Option to expand and view more events, potentially for a detailed view.
- Health Score:
- Likely a metric to track the overall status or health of the customer relationship, though specifics are not visible in the current view.
Context and Importance
- Purpose:
- The dashboard is designed to offer early warnings and track sentiment over time to prevent escalations and churn.
- Allows businesses to proactively address issues based on sentiment analysis.
- User Base:
- Useful for Customer Success Managers, Account Managers, and anyone involved in retaining customer relationships.
- Visual Design:
- Simplistic and clear, with key information easily accessible and highlighted for immediate attention.
Suggestions and Ideas
-
Proactive Measures:
- Based on negative messages, businesses can intervene early and deploy solutions, mitigating dissatisfaction.
-
Trend Analysis:
- Patterns in customer sentiment can be analyzed to improve product and service offerings.
-
Integration:
- Integration with CRM tools could automate data tracking and provide richer insights.
Conclusion
The Early Warning Sentiment dashboard is a powerful tool for tracking and responding to customer sentiment, providing actionable insights to maintain and improve customer relationships over time. It facilitates early identification of issues and ensures that corrective actions can be taken promptly.
Reference:
DAU-to-MAU Ratio vs. ACV
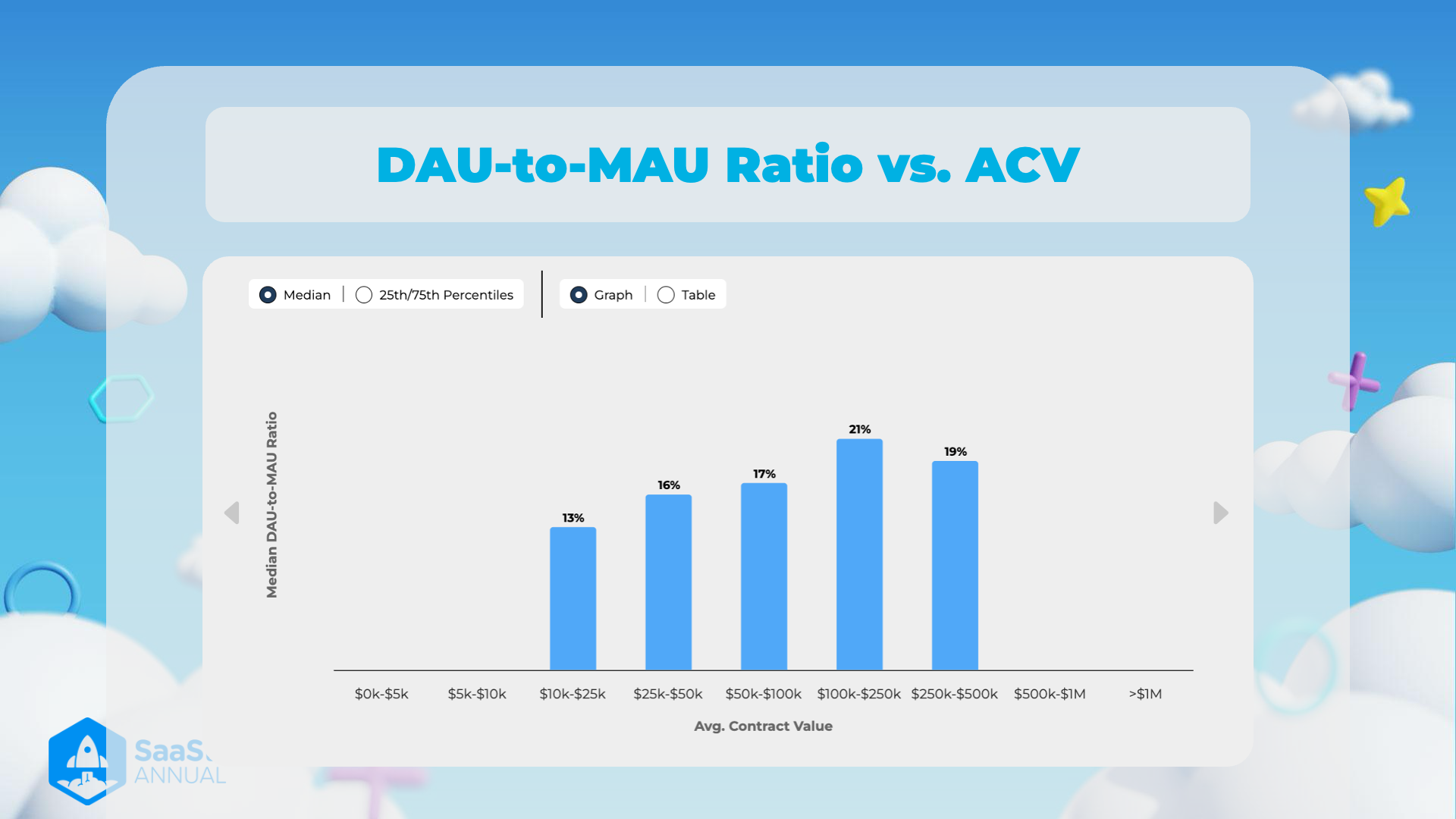
Overview
This graph displays the relationship between the Daily Active Users (DAU) to Monthly Active Users (MAU) ratio and the Average Contract Value (ACV) for various contract ranges in the SaaS (Software as a Service) industry. Key observations from this visual data can provide insights into user engagement relative to contract value.
Data Presentation
- Median DAU-to-MAU Ratio: The y-axis represents the median DAU-to-MAU ratio, indicating the percentage of users active daily compared to monthly active users.
- Average Contract Value: The x-axis categorizes different ranges of contract values, from "5k" to over "$1M".
Key Insights
- 5k: The median DAU-to-MAU ratio for this range is not explicitly displayed.
- 10k: Like the previous range, this specific data point is not provided.
- 25k: The ratio at this value is 13%.
- Insight: Lower contract values may correspond to lower daily engagement.
- 50k: The ratio increases to 16%.
- Insight: As contract value rises, the daily user engagement shows a slight increase.
- 100k: Further increase to 17%.
- Insight: A progressively increasing trend in engagement is visible.
- 250k: The peak ratio found here is 21%.
- Insight: Higher contract value tends to drive higher daily engagement.
- 500k: Slightly lower than the peak, with a ratio of 19%.
- Insight: Shows that very high value contracts still maintain high engagement.
- 1M and >$1M: Not explicitly displayed in this graph.
- Inference: Data might be available in an extended version or detailed table.
Observations and Thoughts
-
Trend Analysis:
- The data suggest a positive correlation between higher contract values and increased daily user engagement.
- There is a noticeable peak in user engagement around the 250k contract range.
-
Business Implications:
- SaaS providers might consider strategies to enhance user engagement by analyzing factors contributing to higher ratios in specific contract ranges.
- Understanding this correlation can aid in pricing strategies and customer relationship management.
-
Further Research:
- Additional detailed data, particularly for the omitted ranges, could provide a more comprehensive understanding.
- Comparative studies with additional variables, such as user satisfaction and feature usage, could enrich insights.
Graph Settings:
- Display Mode: Median values are shown.
- Data Presentation: The data is presented in graph format, with an option to view tables, likely for more detailed numerical comparison.
Conclusion
The graph effectively illustrates the relationship between DAU-to-MAU ratios and contract values, highlighting key patterns and offering strategic insights for SaaS businesses aiming to optimize user engagement relative to contract sizes.
Reference:
User Retention
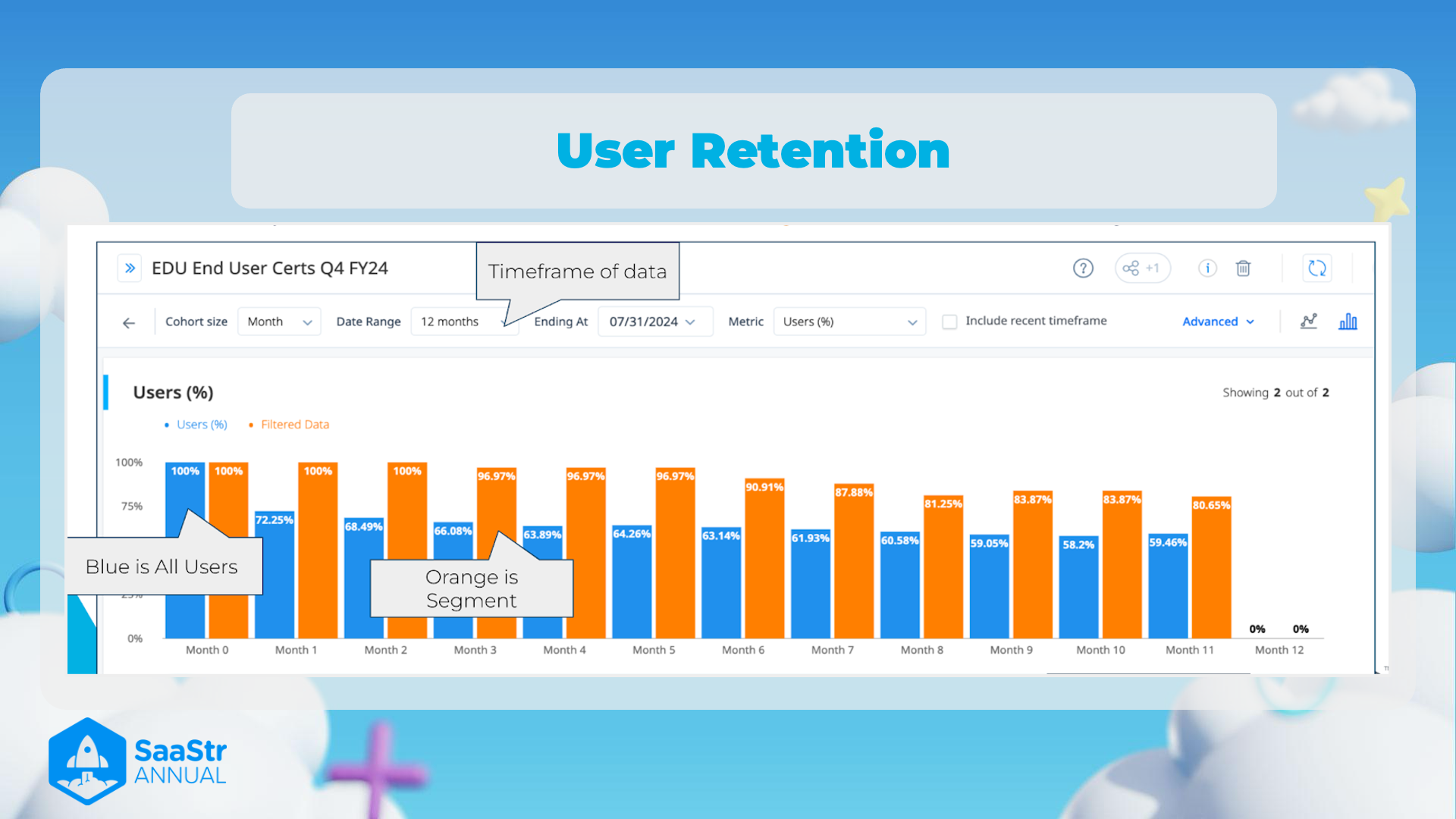
Notes and Thoughts
Title and General Context
- Title: User Retention
- This image focuses on user retention metrics specifically for EDU End User Certs in Q4 FY24.
- Retention metrics are vital for understanding user loyalty and product stickiness.
Timeframe of Data
- Date Range: 12 months, Ending at 07/31/2024
- The data covers a full year, ending mid-2024, which provides a comprehensive view of user retention over time.
- Monthly measurements are useful for observing trends and seasonal variations.
Segmentation
- Blue is All Users, Orange is Segment
- Two groups are being compared: a general user group (blue) and a specific segment (orange).
- It's essential to analyze different segments to tailor strategies for various user groups.
User Retention Trends
- Month-by-Month Analysis:
- Month 0: 100% retention for both groups.
- Month 1: Sharp drop to 72.25% (Segment) and 68.49% (All Users).
- Month 2: Decline continues, with rates at 68.49% (Segment) and 66.08% (All Users).
- Month 3: Slight increase to 96.97% (Segment), while All Users drops to 63.89%.
- Month 4: 96.97% (Segment) and decrease to 64.26% (All Users).
- Month 5: Plateau for Segment at 96.97%, but All Users drop to 63.14%.
- Month 6: Notable drop to 90.91% (Segment) and 61.93% (All Users).
- Month 7-8: Continued decline for both groups, touching 80.87% (Segment) and 60.58% (All Users) by Month 8.
- Month 9-12: Significant drop for All Users, ending at 58.2%, whereas the Segment consistently shows about 83.87% till Month 11, drops to 59.46% by Month 12.
Additional Information
- User retention is crucial for SaaS companies to measure as it affects long-term revenue and customer lifetime value.
- Understanding where the steepest drop-offs occur can help in creating targeted user engagement and retention strategies.
- Tracking segmented groups helps in recognizing which user profiles remain loyal and adjusting services or products to retain others.
Table of User Retention (%):
| Month | All Users (%) | Segment (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Month 0 | 100% | 100% |
| Month 1 | 68.49% | 72.25% |
| Month 2 | 66.08% | 68.49% |
| Month 3 | 63.89% | 96.97% |
| Month 4 | 64.26% | 96.97% |
| Month 5 | 63.14% | 96.97% |
| Month 6 | 61.93% | 90.91% |
| Month 7 | 60.58% | 87.88% |
| Month 8 | 59.05% | 81.25% |
| Month 9 | 58.2% | 83.87% |
| Month 10 | 59.46% | 83.87% |
| Month 11 | 0% | 80.65% |
| Month 12 | 0% | 0% |
Key Notes for Future Actions:
- Investigate the cause of significant drop-offs, especially noticeable between Months 1 and 2.
- Evaluate the driving factors behind high retention rates in the Segment from Months 0 to 6.
- Consider developing targeted re-engagement campaigns for user groups showing lower retention rates.
Reference:
JO Adoption Dashboard Overview
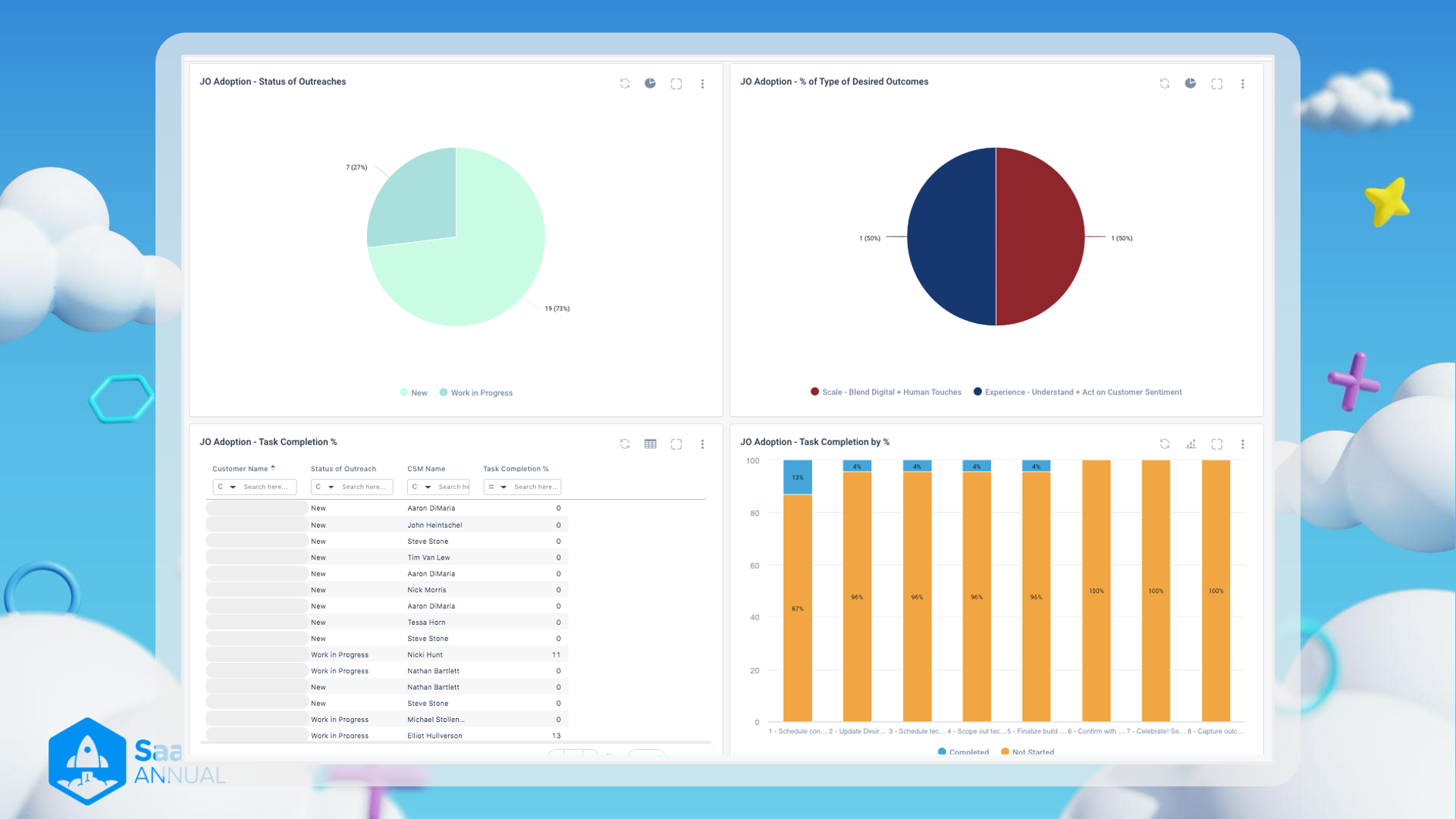
1. JO Adoption - Status of Outreaches
- Visualization: Pie Chart
- Data:
- New: 19 (73%)
- Work in Progress: 7 (27%)
- Insight: The majority of outreach statuses are new, with only a small percentage being classified as "Work in Progress". This indicates that most tasks are at the initial stage.
2. JO Adoption - % of Type of Desired Outcomes
- Visualization: Pie Chart
- Data:
- Scale - Blend Digital + Human Touches: 50% (1)
- Experience - Understand + Act on Customer Sentiment: 50% (1)
- Insight: The desired outcomes are evenly split between scaling through a blend of digital and human touches and focusing on customer sentiment and response. This suggests a balanced approach towards automation and personalized interaction.
3. JO Adoption - Task Completion %
-
Visualization: Table
-
Data:
Customer Name Status of Outreach CSM Name Task Completion % New New Aaron DiMaria 0 New New John Heintshel 0 New New Steve Stone 0 New New Tim Van Lew 0 New New Aaron DiMaria 0 New New Nick Morris 0 New New Aaron DiMaria 0 New New Tessa Horn 0 New New Steve Stone 0 Work in Progress Work in Progress Nick Hunt 11 Work in Progress Work in Progress Nathan Bartlett 0 Work in Progress Work in Progress Steve Stone 11 New New Nathan Bartlett 0 New New Michael Stolten 0 Work in Progress Work in Progress Elliot Hullerson 13 -
Insight: Most customers are marked as 'New' with 0% task completion, indicating early stages of adoption. Few 'Work in Progress' customers show some completion percentages, indicating ongoing work on tasks.
4. JO Adoption - Task Completion by %
- Visualization: Bar Chart
- Data:
- Bar Segments: 8 steps with respective completion levels
- Overall Completion: High percentage of tasks are completed (87% - 100%) with only small segments not started (4% to 13%)
- Insight: The tasks show a high completion rate overall, with a minimum of 87% tasks completed for any given step. There are few tasks that have not started, indicating efficient task management and execution.
Notes on Progress:
- The analysis shows promising engagement levels with the majority of the tasks either underway or in the early stages.
- The dual focus on automated scaling and personal customer sentiment responses could suggest a strategy to balance efficiency with customer satisfaction.
- Those involved in outreach and task management can use this data to prioritize starting new tasks and bringing 'Work in Progress' tasks to completion.
Reference:
SaaStr Annual CS Team Lifecycle Process
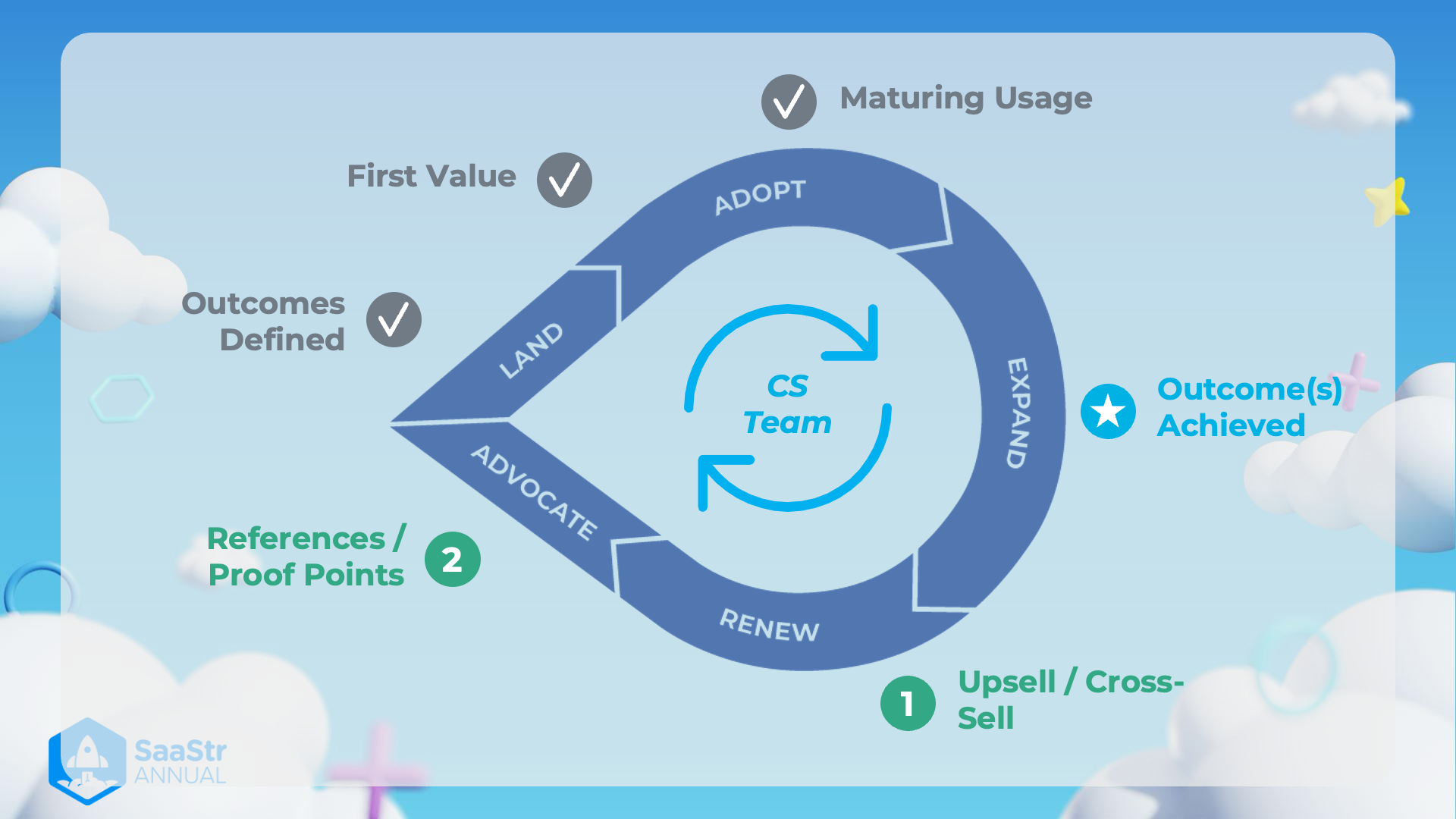
Overall Process
The image illustrates a cyclical process managed by the Customer Success (CS) team to achieve and sustain business outcomes. Each stage in this process is essential for fostering customer growth and retention.
Stages of the Process
-
Land
- Explanation: The initial phase where new customers are acquired.
- Additional Information: This involves onboarding, setting up the product/service, and ensuring the customer can start using it.
-
Adopt
-
Explanation: Customers begin to use the product and integrate it into their processes.
-
Additional Information: The focus is on ensuring customers derive initial value and see benefits early on.
-
Key Milestone:
- First Value Achieved: At this point, customers start experiencing the core benefits of the product.
-
-
Expand
-
Explanation: Customers leverage more features, increase usage, and potentially purchase additional products/services.
-
Additional Information: The aim is to grow the account by demonstrating value that leads to upselling or cross-selling.
-
Key Milestone:
- Maturing Usage: Indicates increasing customer engagement and deeper product utilization.
-
-
Renew
-
Explanation: The phase where the CS team ensures that customers are likely to renew their subscriptions/contracts.
-
Additional Information: This involves regular check-ins, performance reviews, and addressing any issues that might hinder renewal.
-
Key Milestone:
- Outcome(s) Achieved: Success metrics are met, leading customers to see the promised value.
-
-
Advocate
-
Explanation: Satisfied customers become advocates for the product/service.
-
Additional Information: Advocacy can lead to referrals, testimonials, and case studies that support sales and marketing efforts.
-
Key Milestone:
- References/Proof Points: Collection of customer success stories and references that can be used to attract new business.
-
Important Focus Points for the CS Team
-
Outcomes Defined
- Explanation: Outcomes for success are defined early in the process.
- Additional Information: Clarifying expected results ensures both the CS team and customers have aligned goals.
-
Ongoing Monitoring
- Explanation: Continuous engagement with the customer to monitor usage and satisfaction.
- Additional Information: Regular feedback loops help to adapt and improve the customer success strategy.
General Notes
- Upsell/Cross-Sell Opportunities: Identified in the Expand phase to grow account value.
- CS Team Role: They play a pivotal role throughout this lifecycle, focusing on customer satisfaction and continuous engagement.
The image effectively simplifies the complex process of customer management into a clear, visualized cycle, emphasizing the importance of each phase for achieving long-term success.
Reference:
Pre-Defined Metrics Aligned to Outcomes
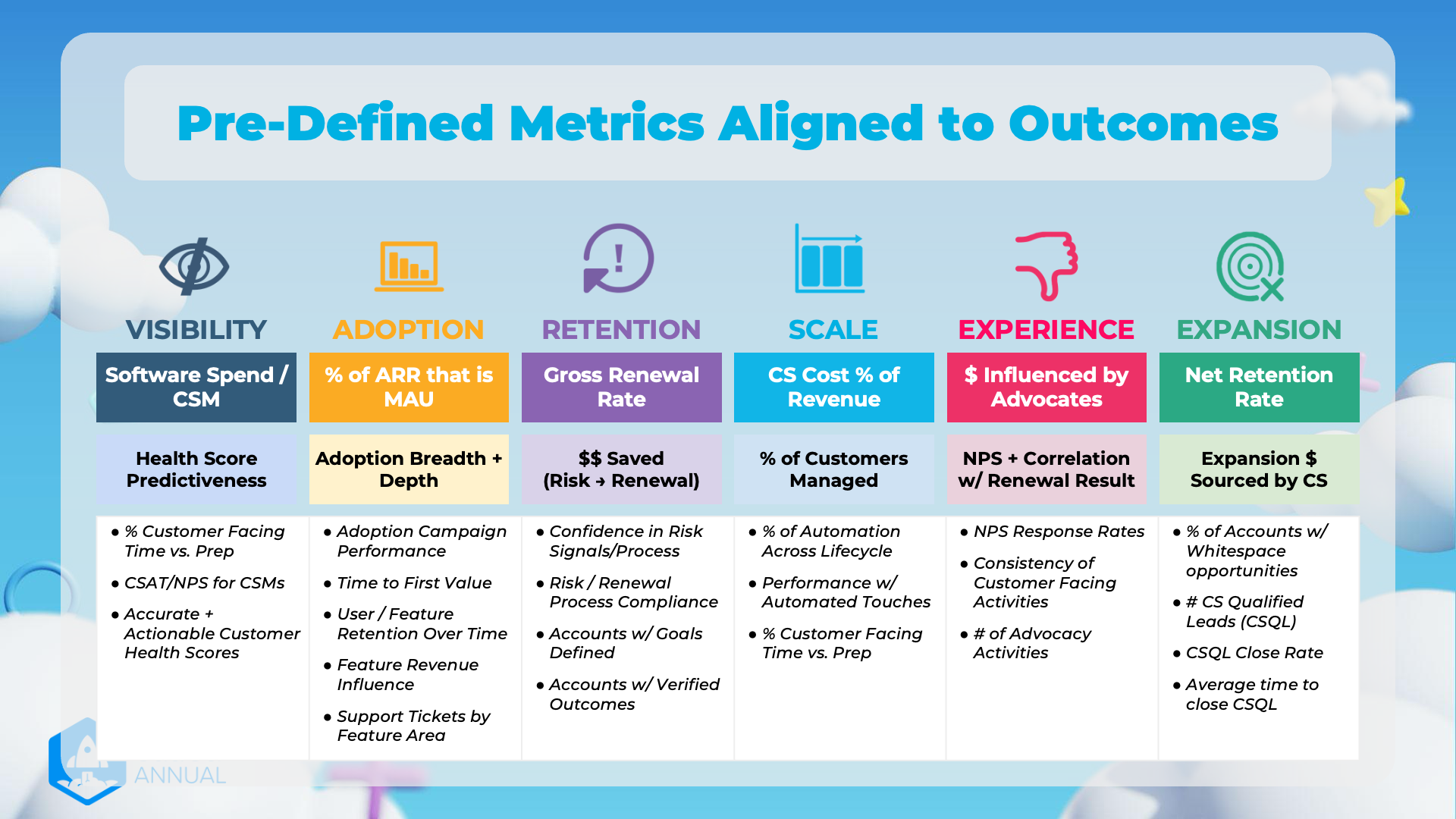
Categories and Metrics
VISIBILITY
Metrics:
- Software Spend / CSM
- Health Score Predictiveness
- % Customer Facing Time vs. Prep
- CSAT/NPS for CSMs
- Accurate + Actionable Customer Health Scores
Thoughts:
- Understanding software spend helps budget efficiently.
- Predictive health scores can proactively identify at-risk customers.
ADOPTION
Metrics:
- % of ARR that is MAU
- Adoption Breadth + Depth
- Adoption Campaign Performance
- Time to First Value
- User / Feature Retention Over Time
- Feature Revenue Influence
- Support Tickets by Feature Area
Thoughts:
- Tracking annual recurring revenue (ARR) as a monthly active user (MAU) ensures customer engagement.
- Adoption campaigns must be measurable to assess their effectiveness.
RETENTION
Metrics:
- Gross Renewal Rate
- $$ Saved (Risk → Renewal)
- Confidence in Risk Signals/Process
- Risk / Renewal Process Compliance
- Accounts w/ Goals Defined
- Accounts w/ Verified Outcomes
Thoughts:
- Renewal rates directly impact revenue sustainability.
- Saving at-risk accounts converts potential losses into gains.
SCALE
Metrics:
- CS Cost % of Revenue
- % of Customers Managed
- % of Automation Across Lifecycle
- Performance w/ Automated Touches
- % Customer Facing Time vs. Prep
Thoughts:
- Scaling customer service efficiently balances costs.
- Automation reduces manual workload, allowing for focus on strategic activities.
EXPERIENCE
Metrics:
- $ Influenced by Advocates
- NPS + Correlation w/ Renewal Result
- NPS Response Rates
- Consistency of Customer Facing Activities
-
of Advocacy Activities
Thoughts:
- Net Promoter Score (NPS) indicates customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Advocacy efforts can have a monetary impact, influencing renewals and upsells.
EXPANSION
Metrics:
- Net Retention Rate
- Expansion $ Sourced by CS
- % of Accounts w/ Whitespace opportunities
-
CS Qualified Leads (CSQL)
- CSQL Close Rate
- Average time to close CSQL
Thoughts:
- Retention coupled with expansion indicates overall growth.
- Identifying and closing new opportunities enhances revenue streams.
Summary Table
| Category | Key Metric | Supporting Metrics / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| VISIBILITY | Software Spend / CSM | - % Customer Facing Time vs. Prep - CSAT/NPS for CSMs - Accurate + Actionable Customer Health Scores |
| ADOPTION | % of ARR that is MAU | - Adoption Campaign Performance - Time to First Value - User / Feature Retention Over Time - Feature Revenue Influence - Support Tickets by Feature Area |
| RETENTION | Gross Renewal Rate | - Confidence in Risk Signals/Process - Risk / Renewal Process Compliance - Accounts w/ Goals Defined - Accounts w/ Verified Outcomes |
| SCALE | CS Cost % of Revenue | - % of Automation Across Lifecycle - Performance w/ Automated Touches - % Customer Facing Time vs. Prep |
| EXPERIENCE | $ Influenced by Advocates | - NPS Response Rates - Consistency of Customer Facing Activities - # of Advocacy Activities |
| EXPANSION | Net Retention Rate | - % of Accounts w/ Whitespace opportunities - # CS Qualified Leads (CSQL) - CSQL Close Rate - Average time to close CSQL |
These metrics are aligned to specific outcomes helping businesses measure and improve upon various parameters. They contribute to the bigger picture by offering insights and actionable data points crucial for achieving key business goals.
Reference:
Success Plan Process
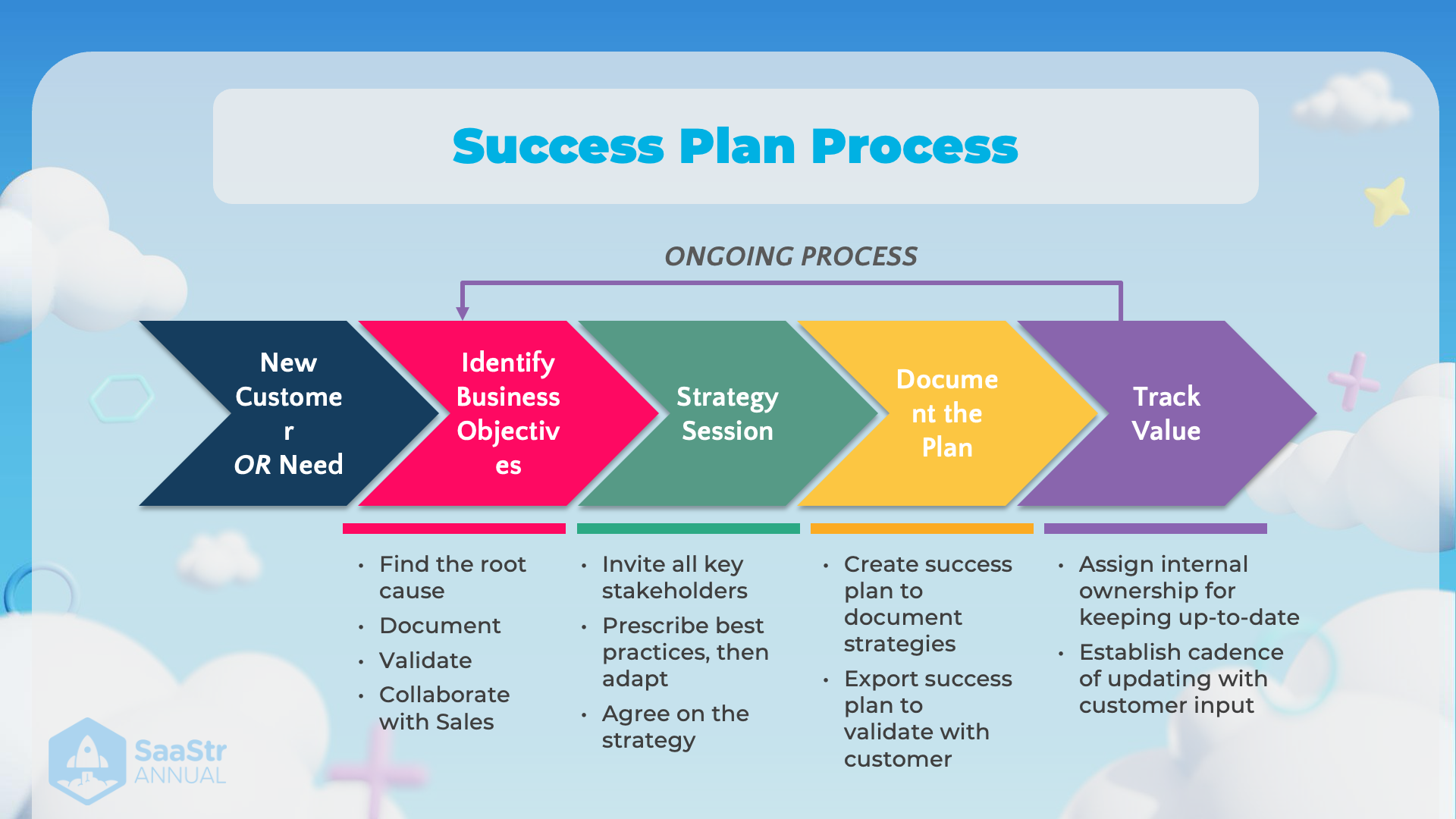
Overview
The image details a structured process for planning and ensuring the success of business initiatives and customer needs within an ongoing process. This is essential for sustained growth and alignment of business objectives with customer satisfaction.
New Customer or Need
- Find the root cause:
- Understand the underlying issues or needs of a new customer or existing need.
- Identifying the root cause helps in framing the correct business questions and directing efforts appropriately.
- Document:
- Keep a record of findings and observations to refer back to and track progress.
- Documentation is critical for maintaining a clear viewpoint and developing accurate solutions.
- Validate:
- Confirm that the identified needs or issues are accurate and relevant.
- This ensures that time and resources are being directed towards solving the right problem.
- Collaborate with Sales:
- Engage with the sales team to verify alignment on identified needs.
- Sales insights often provide valuable context and additional customer perspectives.
Identify Business Objectives
- Invite all key stakeholders:
- Bring together everyone involved in or impacted by the business strategy.
- Encourages buy-in and ensures diverse perspectives are considered.
- Prescribe best practices, then adapt:
- Recommend standard procedures and proven strategies first.
- Be flexible to adapt these practices to the specific context and needs of the business.
- Agree on the strategy:
- Ensure that all stakeholders are on the same page with the chosen strategy.
- This alignment prevents misunderstandings and sets clear expectations.
Strategy Session
- This phase involves collaborative meetings to plan and refine the strategy with stakeholders. It ensures everyone understands the objectives and their roles.
Document the Plan
- Create success plan to document strategies:
- Develop a comprehensive plan detailing the strategies and approaches to meet business objectives.
- A well-documented plan provides direction and a reference point for all involved.
- Export success plan to validate with customer:
- Share the documented plan with the customer for their input and validation.
- This step ensures that the customer’s perspective is accounted for and helps achieve customer satisfaction.
Track Value
- Assign internal ownership for keeping up-to-date:
- Designate specific individuals responsible for maintaining the plan's relevancy.
- Ownership ensures accountability and continuous oversight.
- Establish cadence of updating with customer input:
- Regularly review and update the plan based on feedback and changing circumstances.
- Frequent updates and customer input ensure the plan remains aligned with evolving needs and objectives.
Ongoing Process
- The cycle from identifying needs to tracking the value is continuous. Regular evaluations and iterations are necessary to stay responsive and relevant.
This structured approach provides a clear and systematic framework ensuring that business strategies align with customer needs, which is crucial for sustained success and growth.
Copilot: Gainsight Advocacy Information
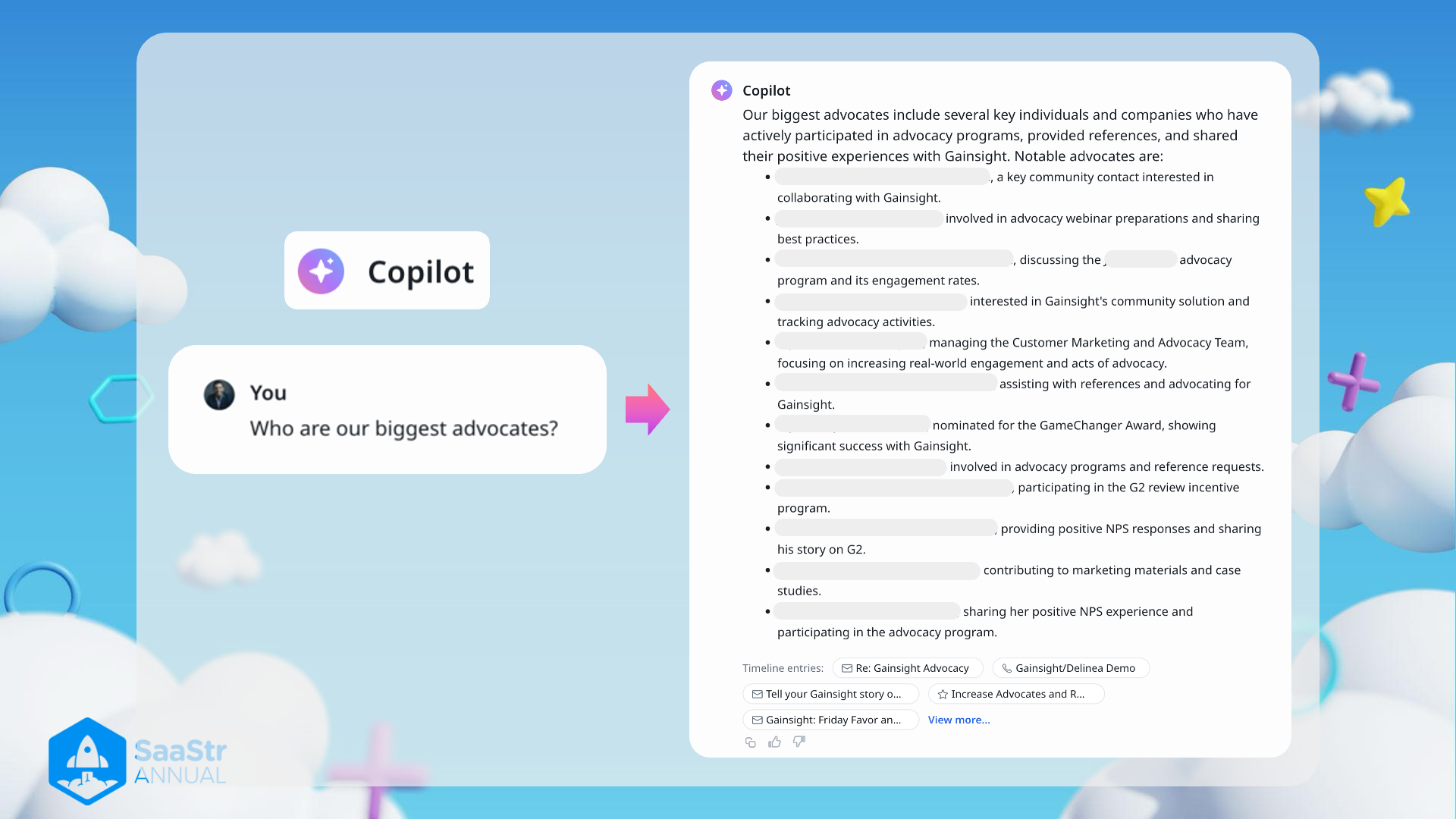
Key Points and Context
Identification of Advocates
- Collaboration Focus: Key community contacts are interested in collaborating with Gainsight.
- It might be helpful to create specific collaboration platforms or channels for these individuals to enhance their engagement.
Advocacy Involvements
- Advocacy Webinar Preparations: Individuals involved in preparing for advocacy webinars and sharing best practices.
- This indicates a high level of engagement and willingness to teach others, which can be leveraged to create more educational content.
Program Engagement
- Advocacy Program and Engagement Rates: Discussions on advocacy program engagement rates.
- Gathering this information can be useful for analyzing the effectiveness of advocacy programs and making data-driven improvements.
Community Solutions
- Interest in Gainsight's Community Solution: Tracking advocacy activities.
- Utilizing community solutions to organize and monitor advocacy activities can streamline efforts and improve efficiency.
Customer Marketing and Advocacy Team Management
- Focusing on Real-world Engagement: Managing teams to increase engagement and acts of advocacy.
- Effective team management is crucial for maintaining a high level of advocacy and ensuring that efforts translate into real-world results.
Providing References and Advocating
- Assisting with References: Advocates helping with providing references for Gainsight.
- This can be highly valuable for potential new customers looking for testimonials and success stories.
Awards and Recognition
- GameChanger Award Nominee: Significant success with Gainsight recognized by nominations for awards.
- Recognizing advocates through awards can motivate others and highlight the successes of using Gainsight.
Participation in Programs
- Advocacy Programs and Incentive Programs: Individuals involved in reference requests and G2 review incentive programs.
- These programs can encourage more active participation and contribution from advocates.
Positive Feedback and Case Studies
- Providing NPS Responses: Contributors sharing their positive experiences and success stories.
- Net Promoter Scores (NPS) can provide valuable feedback on user satisfaction and areas of improvement.
- Marketing Material Contribution: Inclusion in marketing materials and case studies.
- Having advocates contribute to marketing materials can add authenticity and credibility to the content.
Enhanced Contribution Channels
- Sharing Experiences and Advocacy Participation: Advocates sharing their experiences and actively participating in advocacy programs.
- Continuous sharing and involvement can keep the advocacy community vibrant and engaged.
Additional Notes
- Timeline Entries: Lists of specific entries related to advocacy activities such as "Re: Gainsight Advocacy," "Tell your Gainsight story," and "Increase Advocates." This could indicate a structured timeline of advocacy activities being tracked.
- These entries might represent ongoing initiatives or communication threads that can be referenced for past advocacy efforts and planning future endeavors.
Reference:
"REAL" ADVOCATES

- ACTUALLY use the product!
- Real advocates are active users of the product, ensuring authentic feedback and reliable testimonials.
- Not a friend or fellow portco
- Genuine advocates are independent users with no personal or professional affiliation, ensuring unbiased opinions.
- Full adoption
- Full integration and consistent use of the product demonstrate deep trust and dependency, providing stronger case studies.
- Strong ROI or value
- Seeing a significant return on investment or value solidifies the advocate’s support, making their endorsement more impactful.
- Massive fan
- Passionate users who actively promote the product out of sheer enthusiasm can drive organic growth through word-of-mouth.
- Texting relationship
- Close relationships between product providers and users allow for real-time feedback and a strong, personal connection, enhancing credibility.
Reference:
CS Spend % of ARR vs ARR
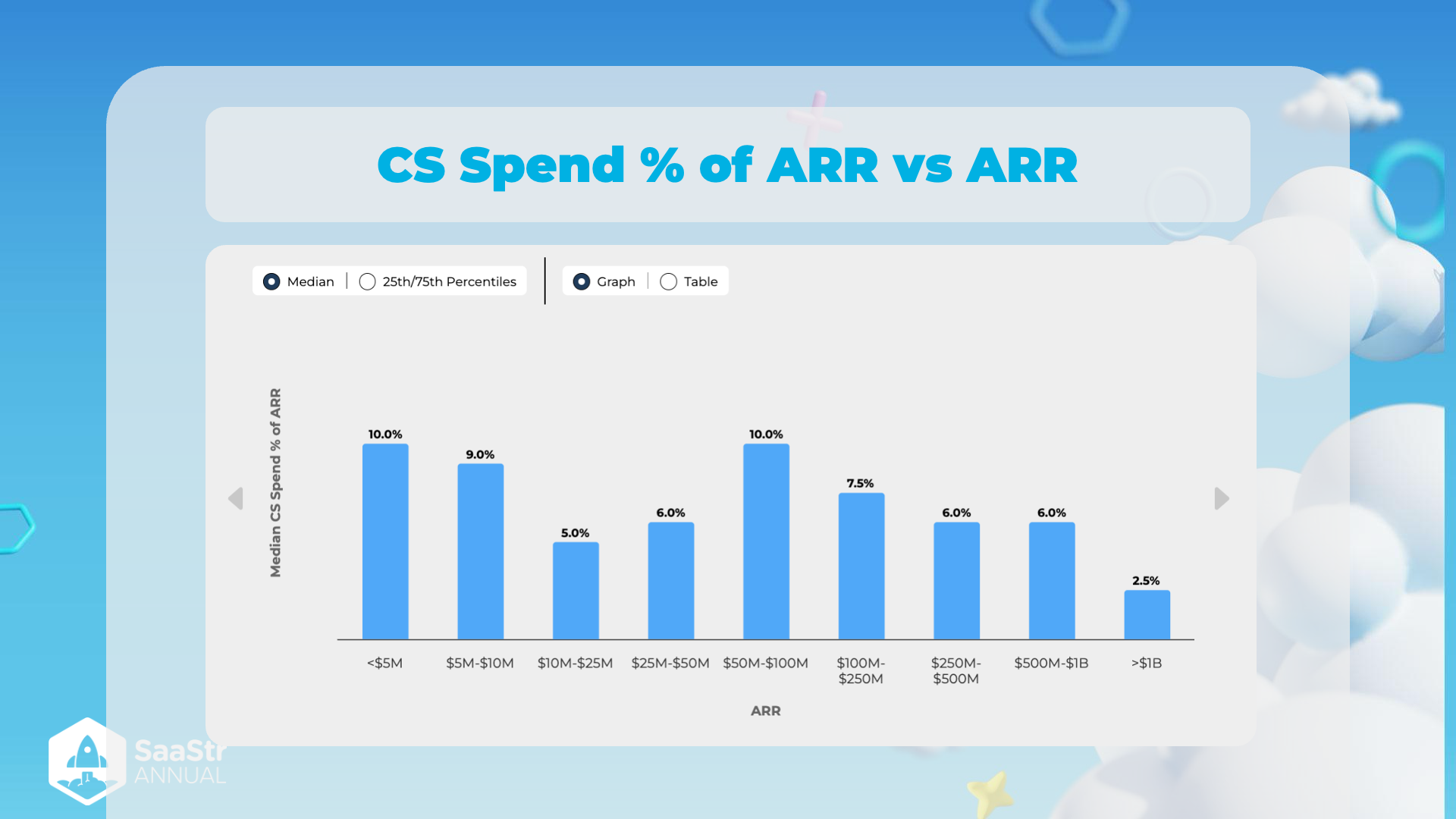
Notes
-
Title and Context
- The title of the image is: CS Spend % of ARR vs ARR
- Context: The image shows a bar graph comparing Customer Success (CS) spending as a percentage of Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) across different ARR ranges. This is useful for understanding how companies of various sizes allocate their resources towards customer success.
-
Graph Overview
- The graph is categorized by Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) ranges on the x-axis.
- The y-axis represents the Median CS Spend % of ARR.
- The blue bars indicate these percentages for different ARR ranges, indicating how much of the ARR is designated for Customer Success.
-
Median CS Spend % Analysis
- <$5M ARR: 10.0%
- CS Spend is highest among smaller companies. This might be because smaller companies need to invest more in retaining and supporting customers for growth.
- 10M ARR: 9.0%
- A slight decrease but still a high percentage of the budget is spent on CS, underscoring its importance in this growth phase.
- 25M ARR: 5.0%
- Significant drop, possibly because companies in this range have more optimized processes or are beginning to achieve economies of scale.
- 50M ARR: 6.0%
- Stabilizes slightly, potentially indicating an effort to maintain a balance between scaling and customer success investments.
- 100M ARR: 10.0%
- Another peak. Companies in this range might increase spending on CS to ensure robust customer support and retention as they reach higher revenues.
- 250M ARR: 7.5%
- Slight reduction, possibly due to improved efficiency or a shift in resource allocation.
- 500M ARR: 6.0%
- Consistent with previous patterns, suggesting a balanced approach to CS spend.
- 1B ARR: 6.0%
- No significant change, possibly indicating established processes and stabilized investment in CS.
- >1B ARR: 2.5%
- Marked reduction in CS spend percentage. Larger companies may benefit from significant economies of scale and more efficient customer success operations.
- <$5M ARR: 10.0%
-
Visual Presentation
- The image simplifies complex data into an easy-to-understand bar graph.
- Visually separates different ARR ranges, making it easy to compare data points.
- The use of consistent blue coloring keeps the focus on the data without distraction.
Table Extract
| ARR Range | Median CS Spend % of ARR |
|---|---|
| <$5M | 10.0% |
| 10M | 9.0% |
| 25M | 5.0% |
| 50M | 6.0% |
| 100M | 10.0% |
| 250M | 7.5% |
| 500M | 6.0% |
| 1B | 6.0% |
| >$1B | 2.5% |
Reference:
CS Spend % of ARR vs NRR
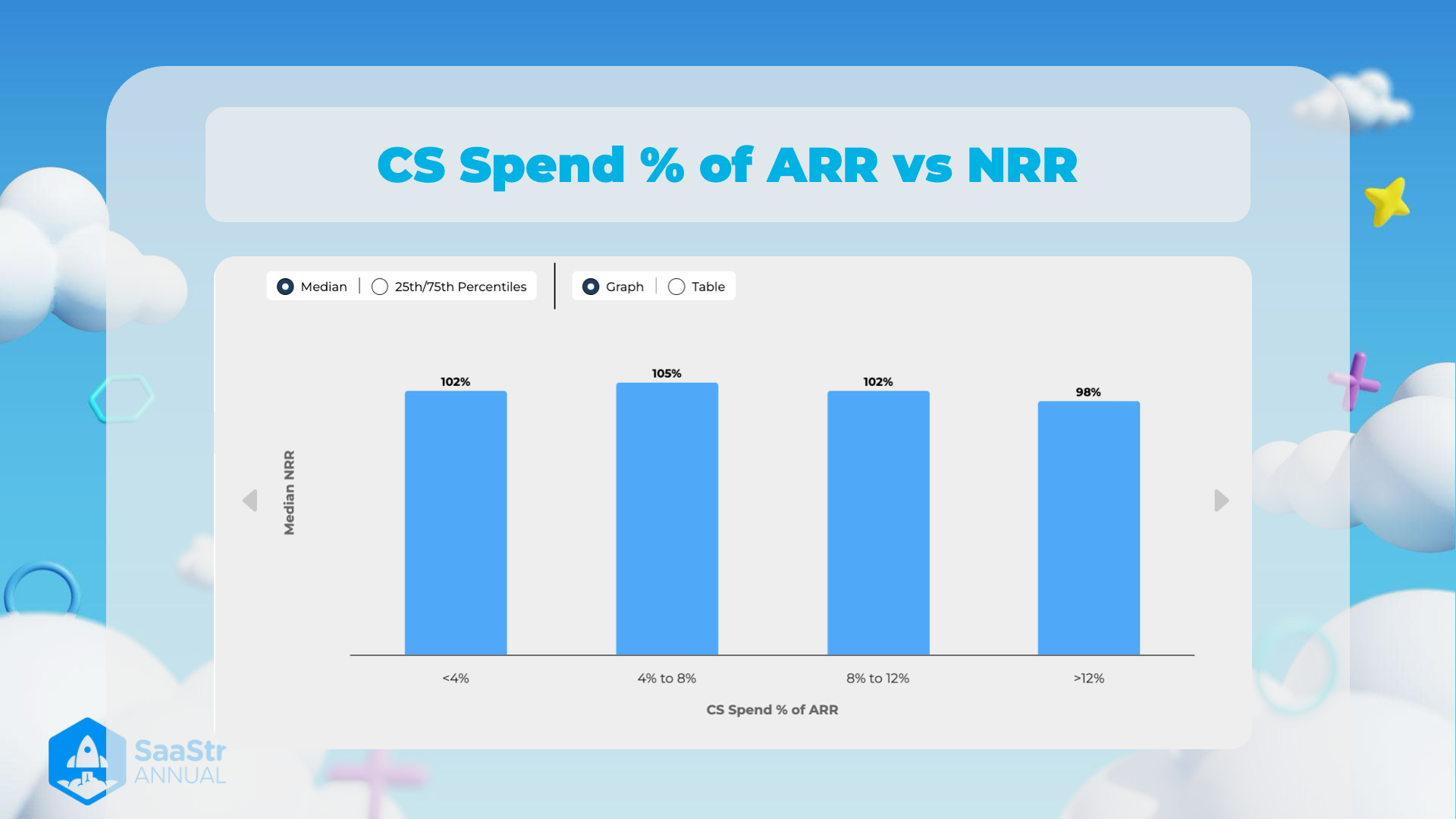
Overview
The image illustrates the relationship between Customer Success (CS) spend as a percentage of Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) and Net Revenue Retention (NRR).
Key Points
- Median NRR Values:
- <4% CS Spend: 102%
- Indicates that with a CS spend of less than 4% of ARR, the median NRR is 102%. This suggests that even with minimal CS investment, companies are able to retain and slightly grow their revenue from existing customers.
- 4% to 8% CS Spend: 105%
- With a CS spend between 4% to 8% of ARR, the median NRR is 105%. This is the highest value among all categories, implying that this level of CS investment yields the best retention and revenue growth results.
- 8% to 12% CS Spend: 102%
- For CS spend ranging from 8% to 12% of ARR, the median NRR is again 102%. This indicates a similar outcome to spending less than 4%, and it suggests diminishing returns when increasing CS spend in this range.
- >12% CS Spend: 98%
- When CS spend exceeds 12% of ARR, the median NRR drops to 98%. This shows that a very high investment in CS does not necessarily equate to higher NRR, and may even have a negative impact.
- <4% CS Spend: 102%
Additional Observations
- Optimal CS Spend:
- The data suggests that a CS spend between 4% and 8% of ARR optimally balances investment and returns, achieving the highest median NRR of 105%.
- Diminishing Returns Beyond 8%:
- Increasing CS spend beyond 8% of ARR does not provide additional NRR benefits and may lead to lower efficiency in terms of revenue retention and growth.
Structure
Considering the image structure:
- The data is presented in column chart format, allowing a visual comparison of the median NRR across different levels of CS spend percentages.
- Graph/Table Toggle: Offers flexibility to view the data in either graphical or tabular form, though the image currently displays the graph.
Source
- Event: SaaStr Annual
- Context: This analysis is likely derived from session insights, studies, or discussions on effective CS strategies in SaaS businesses.
Reference:
Average ARR / CSM $2.76M

-
Headline Information
- The image highlights the average Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) per Customer Success Manager (CSM) as $2.76M.
- This metric is crucial for understanding the revenue-generating capacity and efficiency of CSMs in SaaS (Software as a Service) businesses.
-
Aesthetic
- The background features a blue sky with white clouds and colorful shapes, indicating an uplifting and positive theme.
- The design choice can imply growth, scalability, and optimism in the SaaS industry.
-
Placement & Emphasis
- The dollar value is prominently placed in the center within a pink rectangle, drawing immediate attention to the key financial metric.
- This design reflects the importance of financial metrics in assessing business performance.
-
SaaStr Annual Logo
- Situated on the bottom left, the SaaStr Annual logo signifies the source or the event associated with this data point.
- SaaStr Annual is known for its focus on the needs and metrics relevant to the SaaS community.
-
Relevance & Utility
- Companies can use this benchmark to assess if their CSM teams are performing optimally.
- An ARR/CSM value of $2.76M might serve as a goal or KPI for CSM teams aiming for industry-standard efficiency.
-
Strategic Implications
- SaaS companies might consider adjusting their CSM deployment strategies based on this metric to either increase ARR or reduce costs.
- This data point can also be used in investor presentations to showcase the effectiveness of the company's customer success strategies.
-
Additional Context
- In a SaaS business model, ARR is a critical metric because it represents a predictable and recurring revenue stream.
- Ensuring that CSMs manage adequate ARR can lead to improved customer retention and satisfaction, fueling further growth.
Average Accounts per CSM vs ACV
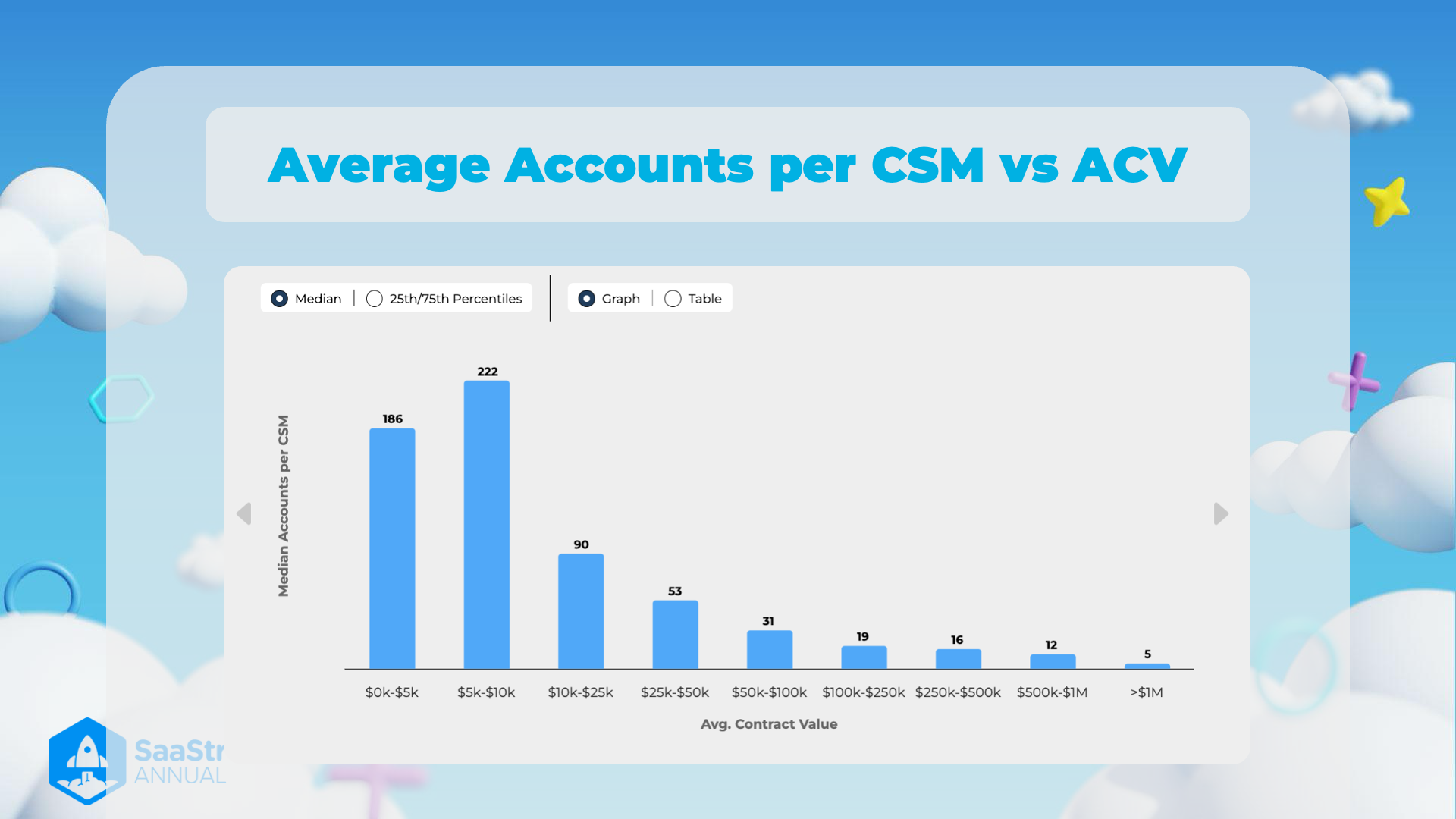
Overview
The image presents a bar graph displaying the median number of accounts managed by Customer Success Managers (CSMs) based on Average Contract Value (ACV). It showcases data segregated into different ACV ranges.
Data Presentation
The graph is organized into eight distinct ACV ranges, with the corresponding median number of accounts per CSM. An important visual aspect is the declining trend in median accounts per CSM as the ACV increases.
Table Format of the Data:
| Avg. Contract Value | Median Accounts per CSM |
|---|---|
| 5k | 186 |
| 10k | 222 |
| 25k | 90 |
| 50k | 53 |
| 100k | 31 |
| 250k | 19 |
| 500k | 16 |
| 1M | 12 |
| >$1M | 5 |
Observations and Thoughts
- High Volume, Low Value Accounts: CSMs handle a larger number of accounts in the lower ACV ranges (5k and 10k), indicating that these accounts might require less intensive management or have standardized processes that allow higher efficiency.
- Decreasing Trend: As the ACV increases, the number of accounts per CSM decreases significantly. This suggests that higher value accounts likely require more personalized and dedicated attention to ensure success, leading to fewer accounts managed by each CSM.
- Resource Allocation: These insights can be crucial for resource planning within an organization. By understanding these trends, companies can allocate CSMs based on expected workloads and ensure high-value accounts receive adequate attention.
- Potential for Automation: For lower ACV accounts, there might be an opportunity to implement automation or self-service options to manage the high volume without overburdening CSMs.
Additional Context
- Median Data Representation: The graph focuses on the median number of accounts, providing a central tendency of the data and potentially mitigating the impact of outliers.
- Visualization Choices: The choice of a bar graph effectively communicates the steep decline in accounts per CSM as the contract value increases, making it clear and easy to understand at a glance.
Reference:
CS > CSM

SaaStr Annual Logo
- Placement: Bottom-left corner of the image.
- Significance: Indicates that the event or content is related to the SaaStr Annual conference, a well-known event in the SaaS (Software as a Service) industry.
- Visual: The logo incorporates space and SaaS-related elements, such as a rocket, to emphasize growth and innovation in the SaaS field.
Cloud and Sky Theme
- Design Elements: The image features a sky-blue background with clouds, stars, and 3D geometric shapes.
- Purpose: These elements likely aim to convey an uplifting, bright, and dynamic atmosphere, aligning with themes of innovation, cloud technology, and upward growth.
Main Text: CS > CSM
- Breakdown of Acronyms:
- CS: Often stands for Customer Success.
- CSM: Typically represents Customer Success Manager or Customer Success Management.
- Interpretation: The equation "CS > CSM" suggests that Customer Success as a whole is considered more significant or valuable than the role of Customer Success Managers alone. This could imply a focus on the overall strategy and impact of customer success as a broader concept rather than just on the individuals who manage it.
- Design: The text features bold white letters with a pink shadow, making it pop against the blue background. This highlights its importance as the central message.
Additional Context
- SaaStr Annual: This is an event dedicated to bringing together SaaS entrepreneurs, executives, and investors to discuss growth strategies, best practices, and to network.
- Relevance: Customer Success (CS) is a crucial aspect of SaaS businesses, ensuring that customers achieve their desired outcomes while using the product or service. The message emphasizes a strategic approach to customer success beyond just having managers in this role.
Reference:
SaaS Customer Journey and Experience
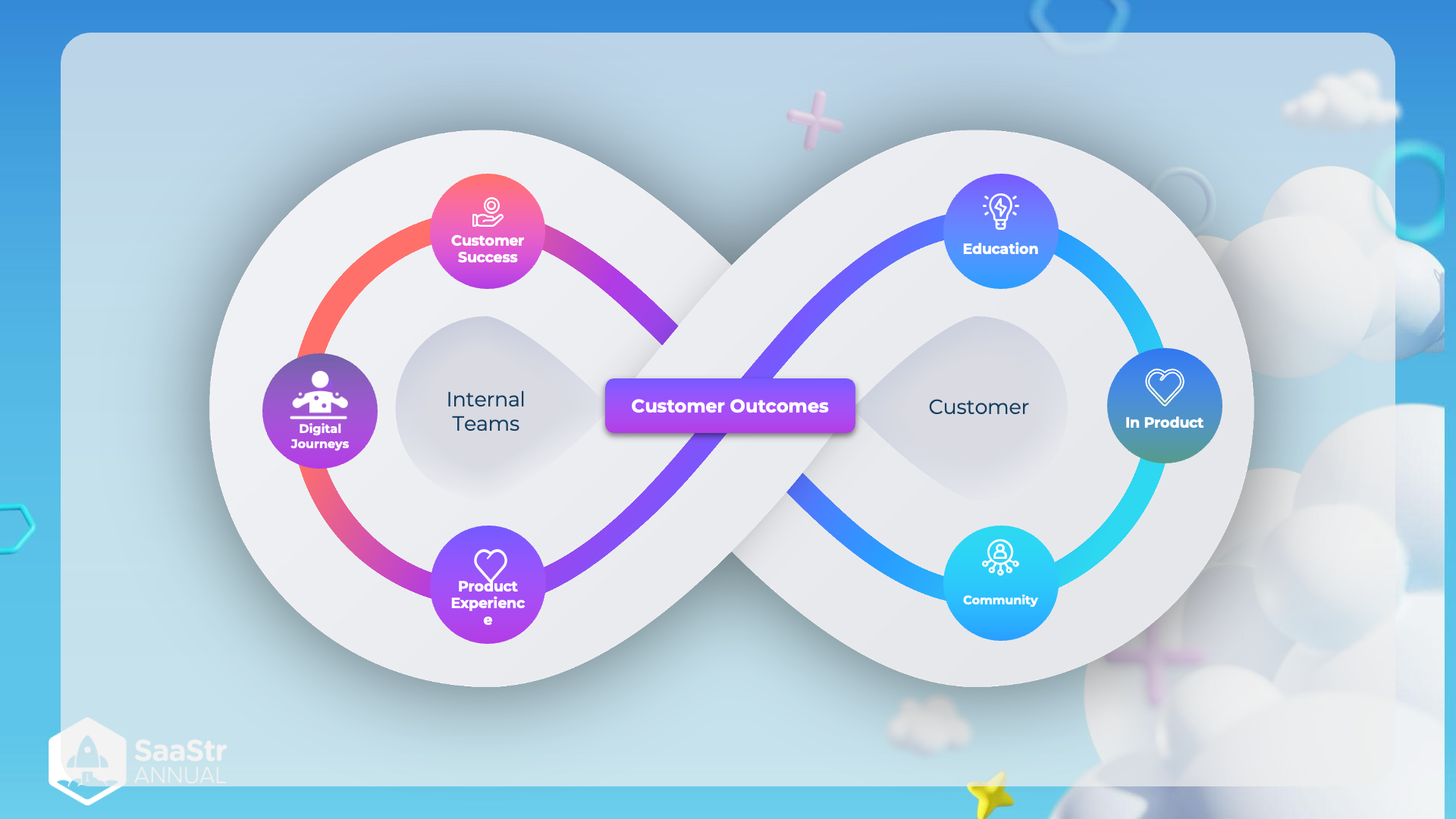
Overview
This image illustrates the interconnected and continuous journey between internal teams and customers in the SaaS (Software as a Service) industry. The focus is on achieving positive customer outcomes through coordinated efforts between different functions within a company and customer interactions.
Internal Teams
-
Customer Success
- Role: Ensures customers achieve their desired outcomes while using the product.
- Importance: Vital for customer retention and satisfaction. Customer Success teams often act as liaisons between the customer and the company.
-
Digital Journeys
- Role: Manages the digital experience of the customer journey.
- Importance: Enhances customer engagement through digital touchpoints, ensuring a seamless and effective interaction with the product.
-
Product Experience
- Role: Focuses on the usability and satisfaction derived from the product.
- Importance: A critical determinant of customer loyalty and product adoption. A positive product experience is often a result of responsive and intuitive product design.
Customer
-
Education
- Role: Provides knowledge and resources to help customers use the product effectively.
- Importance: Empowers customers, reduces support costs, and boosts customer satisfaction by enabling users to fully utilize the product features.
-
In Product
- Role: In-app guidance, support, and feedback mechanisms.
- Importance: Directly impacts user experience by offering help and making the product more user-friendly.
-
Community
- Role: Encourages interaction among users to share experiences and solutions.
- Importance: Builds a sense of belonging and loyalty among customers. Users can learn from each other, thereby enhancing their overall experience.
Central Concept: Customer Outcomes
- The ultimate goal of both internal teams and customer-facing efforts is to drive positive outcomes for customers, which, in turn, benefits the company through sustained engagement and loyalty.
Summary
The image uses an infinity loop to represent the ongoing and symbiotic relationship between a company's internal teams and its customers. Each team and each customer-facing component continuously feed into achieving desirable customer outcomes, emphasizing an ongoing cycle of improvement, engagement, and satisfaction.
Human-First AI Playbook

For Your Team
-
Eliminate Blind Spots
- Identifying and addressing areas where information is missing or underutilized.
- This can help in making better decisions and improving overall productivity.
-
Remove Grunt Work To Make Time For What Matters
- Automating or outsourcing repetitive and mundane tasks.
- Allows team members to focus on higher-value activities, leading to increased job satisfaction and efficiency.
-
Turn Every Teammate into Your Best Teammate
- Leveraging AI to enhance the capabilities of each team member.
- Ensuring that all team members can contribute at their highest potential, fostering a collaborative and high-performance work environment.
For Your Customers
-
Make Self-Service Not Suck
- Improving self-service options to be user-friendly and effective.
- Enables customers to resolve their issues efficiently, improving their experience and satisfaction.
-
Transform Novices into Gurus
- Providing tools and resources that help customers become experts in using the product.
- Enhances customer empowerment and retention.
-
Help Customers Find Their Work Besties
- Facilitating connections between customers to build a supportive community.
- Encourages knowledge sharing and collaboration among users, enhancing their experience with the product.
This playbook focuses on leveraging AI to enhance both team and customer experiences by addressing key areas that improve productivity, satisfaction, and community building.
Reference:
Neuron X Customer Dashboard
Overview Section
- Tier: 3
- Indicates the level or classification of the customer. In this case, Neuron X is classified as a Tier 3 customer.
- Renewal Date: 1.8.2024
- The date when the contract or subscription with the customer is set to renew. Useful for preparing renewal strategies.
- Revenue: $48,763
- Total revenue generated from Neuron X. This gives an idea of the customer's monetary contribution.
- Journey Phase: Adoption
- Current phase in the customer journey. Indicates that Neuron X is in the adoption phase.
- Owner: John Barry
- Employee responsible for managing the relationship with Neuron X.
Last 14 Days Section
- Engagement: Average (Trend: 9% ↗)
- Engagement level with the customer. It's showing an average rating with an increasing trend of 9%.
- Sentiment: Low (Trend: -30% ↓)
- Customer sentiment towards the company is low with a decreasing trend of 30%.
- Open Items: Medium (Trend: -30% ↘)
- Number of unresolved or pending tasks. It is currently medium but the trend is decreasing by 30%.
- Response Time: 9 hours (Trend: 9% ↗)
- Average response time to customer queries or issues. Currently 9 hours with an improving trend of 9%.
Activity Section
- Activity Categories:
- Events:
- Major milestones like Acquisition, Onboarding, and Adoption.
- Events Timeline:
- Acquisition: April 2022
- Onboarding: June 2022
- Adoption: Starting from June 2022 to ongoing.
- Events Timeline Visualization:
- Shows specific activities such as Transition meetings, Onboarding, and mentions of renewals.
- Activity (Bar Chart) :
- Tracks different types of activities over time (Emails, Hourglass, Chats, Meetings, Tickets).
- Activity Date Range:
- March 28
- April 28
- May 28
- June 28
- July 28
- August 28
- September 28
- October 28
- Events:
Navigation Menu
- Icons (from top to bottom):
- Home
- Customers
- Relationships
- Reports
- Settings
User Information
- Group: US market sector
- Group classification which the user is part of. In this case, it's the US market sector.
- User Profile: Acme Inc.
- Indicates the organization the user is associated with.
- Invite Button: For inviting other users to the platform.
Visual Design
- UI Elements:
- The interface uses a clean and minimal design with pastel colors and straightforward navigation.
- Background:
- Features a sky with clouds and animated elements, adding a playful element to the design.
Additional Metrics
- Trend Indicators:
- Engagement (9% ↗)
- Sentiment (-30% ↓)
- Open Items (-30% ↘)
- Response Time (9% ↗)
These notes capture the essential information and offer insights into the customer relationship management platform's usability and purpose.
My Hopes for You

-
Being Mediocre and Making Mistakes is OK
- It's important to embrace imperfection and understand that making mistakes is a natural part of growth. Don’t aim for constant perfection; instead, focus on learning from every experience.
-
Keep Grinding
- Persistence and hard work are key to achieving success. Even on tough days, maintain your efforts towards your goals.
-
Take Some Time for Yourself
- Self-care is crucial for maintaining overall well-being. Schedule some personal time to relax and recharge.
-
Refill Your Oxygen Tank
- Analogous to the oxygen mask on an airplane, take care of your needs first so you can be better equipped to help others.
-
Be Proud - at Work and at Home
- Celebrate your achievements in all aspects of your life. Acknowledge your efforts and be proud of what you accomplish both professionally and personally.
-
Embrace Your Scars
- View your scars as symbols of your strength and resilience. They are a testament to the challenges you’ve faced and overcome.
This image from SaaStr Annual conveys a motivational message about self-acceptance, perseverance, self-care, and pride in personal and professional life.
Reference: