Linux File Permissions: Overview and Representation Guide
LINUX FILE PERMISSIONS OVERVIEW
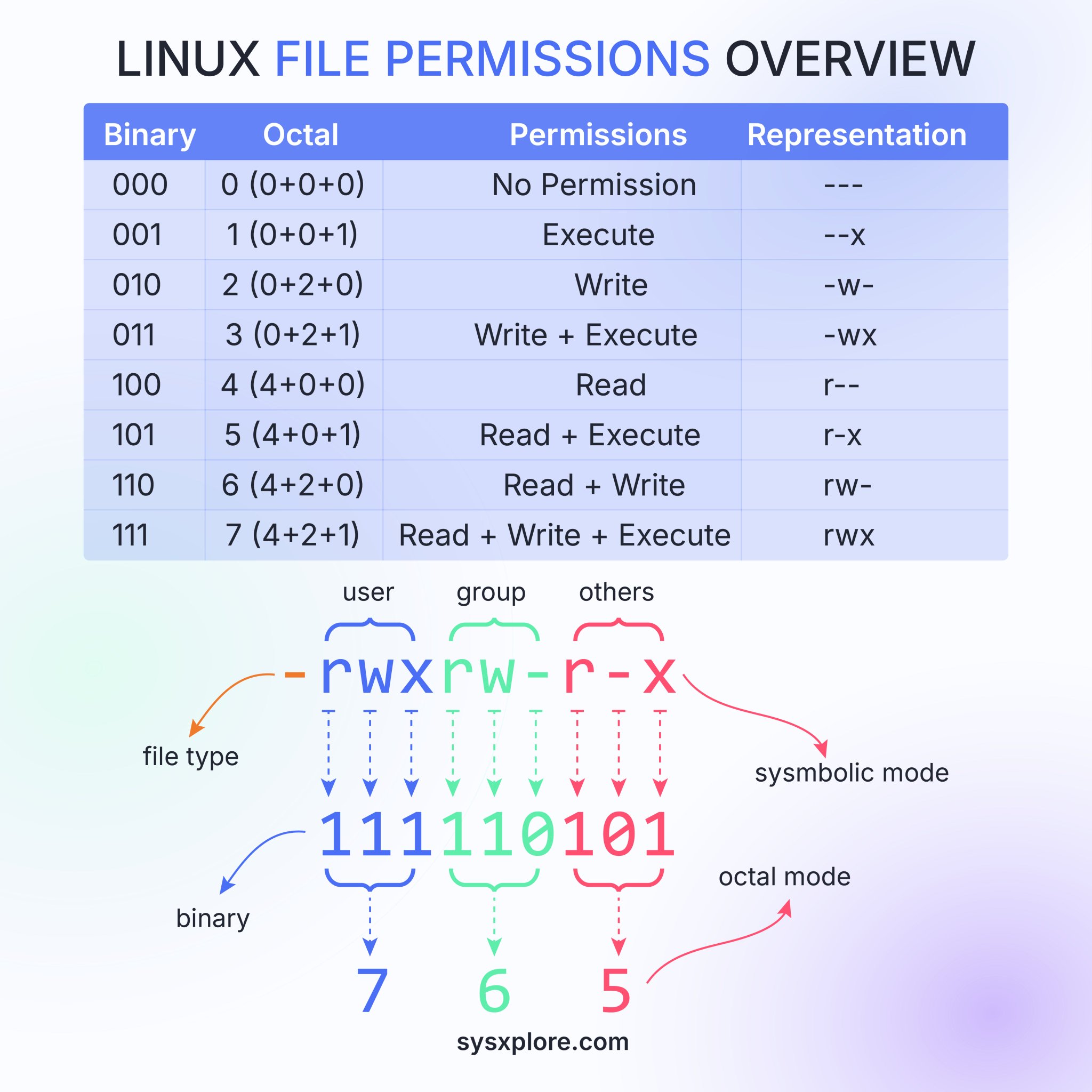
Table of Permissions
| Binary | Octal | Permissions | Representation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 000 | 0 | No Permission | --- |
| 001 | 1 | Execute | --x |
| 010 | 2 | Write | -w- |
| 011 | 3 | Write + Execute | -wx |
| 100 | 4 | Read | r-- |
| 101 | 5 | Read + Execute | r-x |
| 110 | 6 | Read + Write | rw- |
| 111 | 7 | Read + Write + Execute | rwx |
Thoughts and Additional Information:
- Binary and Octal Representation: Each permission set is represented in both binary and octal format. This dual representation is essential for understanding different ways of setting file permissions.
- Permissions Explanation: The permissions range from having no permissions (000) to having all permissions (read, write, and execute - 111). This organizer helps in understanding the exact level of access provided.
Permissions Representation Breakdown
- User: The first set of permissions is for the user who owns the file.
- Group: The second set of permissions is for the group that the file belongs to.
- Others: The last set of permissions is for everyone else.
Thoughts and Additional Information:
- Order of Permissions: User, group, and others are the standardized order for permissions. The distinction ensures clarity in specifying access control.
Modes of Permissions
- Symbolic Mode: Uses letters (r, w, x) to represent read, write, and execute permissions.
- Octal Mode: Uses octal numbers (0-7) to succinctly represent all possible permission combinations for user, group, and others.
Thoughts and Additional Information:
- Ease of Use: Symbolic mode is more human-readable, while octal mode is more concise and compact. Understanding both is crucial for efficient system use.
Diagram Breakdown
- File Type: Imagined as a prefix in the diagram (not explicitly showcased in the table).
- User (rwX) : Full set of permissions for the user (read, write, execute).
- Group (rW-) : Permissions set for the group.
- Others (r-X) : Permissions set for others.
Thoughts and Additional Information:
- Visual Representation: Using a visual guide helps in understanding how binary and octal permissions translate into symbolic form and vice versa.
- Practical Application: This visual representation is foundational for using commands like
chmodin the terminal to set permissions accurately.
Reference:
www.redhat.com
Linux file permissions explained | Enable Sysadmin - Red Hat
docs.nersc.gov
Unix File Permissions - NERSC Documentation
www.geeksforgeeks.org
How to Set File Permissions in Linux? - GeeksforGeeks