SaaS Resilience in Japan's Depopulating Landscape
SaaS as Infrastructure for a Depopulating Society

Growth and Stability in SaaS
-
Continued Growth: Despite declining stock prices, SaaS businesses are expanding, with major companies in Japan exceeding JPY 30 billion in ARR by 2024.
- Insight: SaaS has transitioned from a start-up phase to a mature industry, showing resilience and adaptability.
-
Market Drivers: Expansion to large enterprises and SMEs through multi-product strategies and M&A activities hit a record high in 2023.
- Additional Info: Multi-product strategies involve offering a range of solutions, enabling SaaS companies to capture diverse market needs.
Trends in Vertical SaaS
-
Focus on Social Issues: Increasingly, vertical SaaS in Japan addresses social challenges, using models unique to the Japanese context, such as "time-machine management."
- Insight: This adaptation highlights SaaS’s potential to innovate beyond traditional IT solutions.
-
Labor Shortage Challenges: Japan's declining population and labor shortages in key industries necessitate improved productivity via vertical SaaS.
- Additional Info: Vertical SaaS solutions are tailored to specific industries, enhancing efficiency and addressing niche problems.
Report Breakdown
- Overview: Latest data and trends in the SaaS market.
- Vertical SaaS: Analysis of growth drivers within this segment.
- Depopulating Society: Examination of the impact on productivity and societal challenges.
Macro-Economic Divergences
- U.S. vs Japan Trends: Different economic conditions, demographic shifts, and interest rate gaps influence startup paths in both countries.
- Insight: Such differences may lead to innovative solutions unique to the Japanese context.
Opportunities in Population Decline
- Innovative Potential: Japan’s experience with population decline creates opportunities for disruptive innovations in SaaS.
- Insight: Addressing depopulation may lead to technological and operational breakthroughs, serving as a model for other nations.
Industry Maturity
- SaaS Maturity: The industry must harness its maturity to address large-scale societal issues like depopulation.
- Insight: The success of SaaS in this context will demonstrate its true value and sustainability.
Osamu Iwasawa's Role
- Leadership: Osamu Iwasawa of UB Ventures leads efforts focusing on innovation amidst a depopulating society, with an extensive background in finance and management.
- Additional Info: His expertise could be pivotal in driving SaaS solutions to tackle societal challenges effectively.
SaaS Industry in Japan: ARR Insights
Overview
- The report focuses on the Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) performance of listed SaaS companies in Japan.
- Major players have reached up to JPY 30 billion in ARR.
- Growth is sustained by diversifying products and strategic pricing.
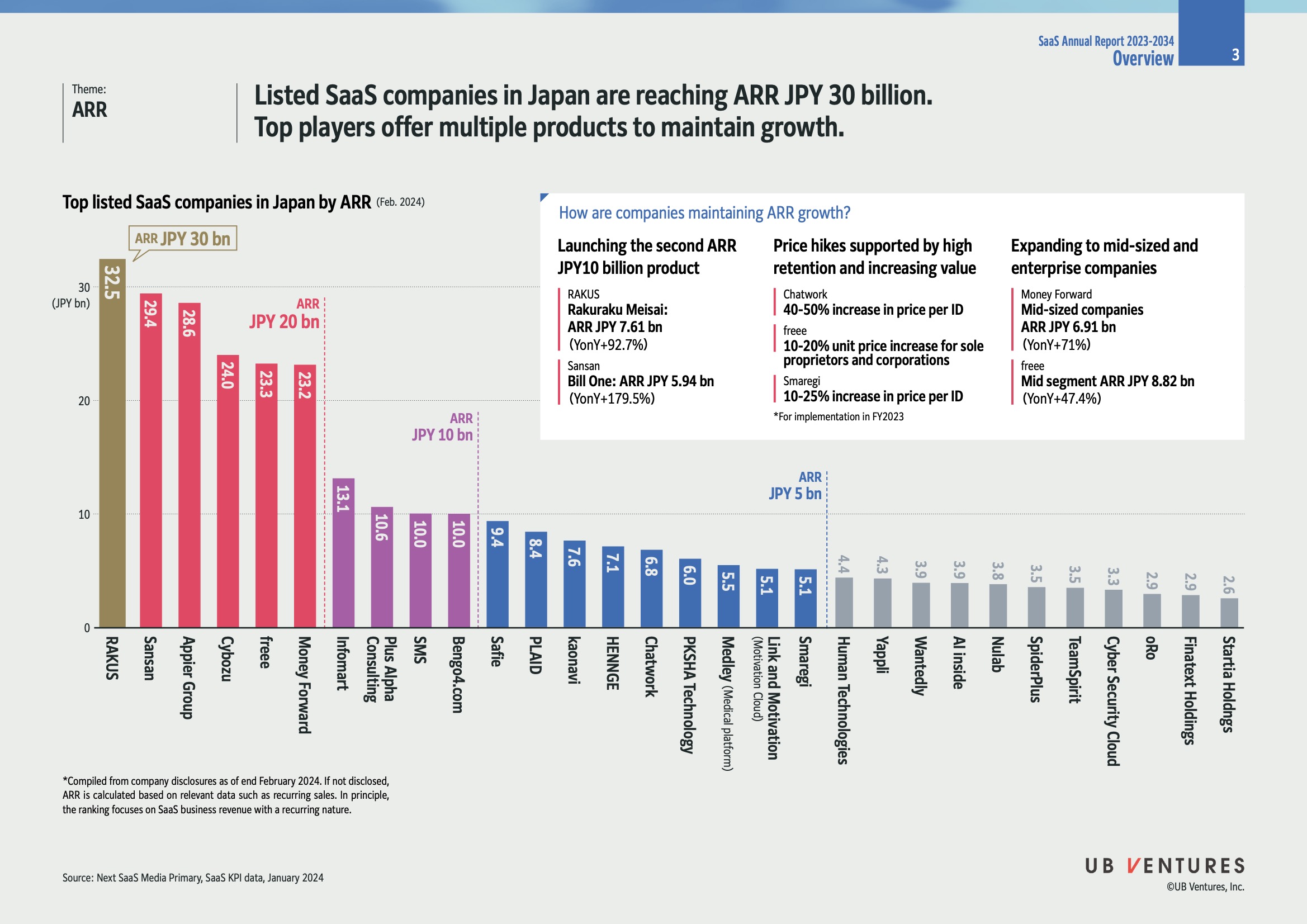
Top SaaS Companies by ARR (as of February 2024)
| Company | ARR (JPY bn) |
|---|---|
| RAKUS | 32.5 |
| Sansan | 29.4 |
| Appier Group | 28.6 |
| Cybozu | 24.0 |
| freee | 23.3 |
| Money Forward | 23.2 |
Insight: RAKUS leads the market, nearing the JPY 30 billion mark. Companies like Sansan and Appier Group also show strong ARR, indicating a competitive landscape in Japan’s SaaS sector.
Strategies for ARR Growth
-
Launching New Products:
- RAKUS: Introduced RakuRaku Meisai with ARR of JPY 7.61bn (YoY+92.7%).
- Sansan: Launched Bill One achieving JPY 5.94bn ARR (YoY+179.5%).
Explanation: Introducing new high-demand products allows companies to tap into new market segments and broaden revenue streams.
-
Price Hikes with Value Increase:
- Chatwork: Increased prices per ID by 40-50%.
- freee: Implemented a 10-20% price rise for sole proprietors and corporates.
- Smaregi: Raised prices per ID by 10-25%.
Explanation: Strategic pricing adjustments help maintain profitability amidst rising customer value offerings and service demands.
-
Expanding to Mid-sized and Enterprise Companies:
- Money Forward: Targeted mid-sized companies, achieving ARR of JPY 6.91bn (YoY+71%).
- freee: Expanded ARR in the mid-segment to JPY 8.82bn (YoY+47.4%).
Explanation: Targeting enterprise clients helps secure larger contracts and potentially higher ARR due to extended service offerings.
Additional Companies and ARR
| Company | ARR (JPY bn) |
|---|---|
| Morisawa | 13.1 |
| Plus Alpha Consulting | 10.6 |
| Bengo4.com | 10.0 |
| SMS | 10.0 |
| Safie | 9.4 |
Insight: Companies with ARR ranging from JPY 5 to 10 billion indicate a strong mid-tier presence, collectively uplifting the SaaS market stability.
Key Takeaways
- Product Diversification: Crucial for sustaining competitive advantage and maintaining steady ARR growth.
- Market Insight: Understanding market demands and customer value perception can guide effective pricing strategies.
- Expansion: Scaling into different company sizes can increase market share and ARR.
Conclusion: Japan's SaaS industry shows robust growth with strategic innovations and market expansions playing integral roles in achieving high ARR figures.
Extended readings:
Product Portfolios of Top Listed SaaS Companies in Japan

Overview
SaaS Companies with ARR Over JPY 10 Billion
This section outlines the annual recurring revenue (ARR) breakdown for leading SaaS companies in Japan, each surpassing JPY 10 billion.
| Company | Total ARR | Significant Products and ARR (bn) | Growth Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| RAKUS | JPY 32.47 | Meisai: JPY 7.61<br>Seisan: JPY 15.19<br>Mail Dealer: JPY 5.94 | -92.7%<br>-42.4%<br>+57.3% |
| Sansan | JPY 29.43 | Sansan: JPY 21.14<br>BillOne: JPY 5.94 | +179.5% |
| Cybozu | JPY 24.01 | Office: JPY 4.74<br>kintone: JPY 13.31 | - |
| freee | JPY 23.25 | freee: JPY 17.53 | +36.6% |
| Money Forward | JPY 23.15 | Money Forward ME: JPY 2.69<br>Cloud: JPY 1.66 | +46% |
| infomart | JPY 13.14 | B2B: JPY 8.01 | +58.6% |
| Plus Alpha Consulting | JPY 10.62 | Talent Palette: JPY 6.98 | +37.6% |
Key Notes
-
Growth Not Driven by First Product: Companies are leveraging the “Compound Strategy” by launching multiple products in specific domains, allowing for diversified revenue streams and sustained growth.
-
Diversification Strategy: By expanding into fields like HR, labor, contract, and SaaS ID management, companies mitigate risks associated with relying on a single product. This mirrors trends in tech industries where diversification supports resilience.
-
Post-IPO Growth: Products like RAKUS’ Rakuraku series, Cybozu’s kintone, and Plus Alpha Consulting's Talent Palette have become significant post-IPO growth drivers. Post-IPO strategies often include expanding product lines to leverage existing resources.
-
Future Trends: The shift from organic growth to strategic mergers and acquisitions (M&A) could indicate increasing market consolidation. Companies will likely focus on maximizing the number of products achieving JPY 10 billion in ARR.
Insights
-
Product-Specific ARR: Understanding ARR per product allows companies to identify key revenue generators and strategically invest in those areas.
-
Growth Rate Impact: Exponential growth rates, such as Sansan’s BillOne, indicate successful market penetration and potential for scaling.
Strategic Implications
-
Revenue Diversification: Businesses should consider developing multiple products early to diversify risk, even if it requires increased initial R&D investment.
-
Adoption of M&A: With a shift towards inorganic growth, firms might need to develop robust integration processes to ensure smooth transitions during mergers and acquisitions.
This summary provides a snapshot of current strategies and future directions in Japan’s SaaS sector, emphasizing the importance of ARR diversification and strategic expansion.
Extended readings:
SaaS Valuation and PSR Trends
Overview
-
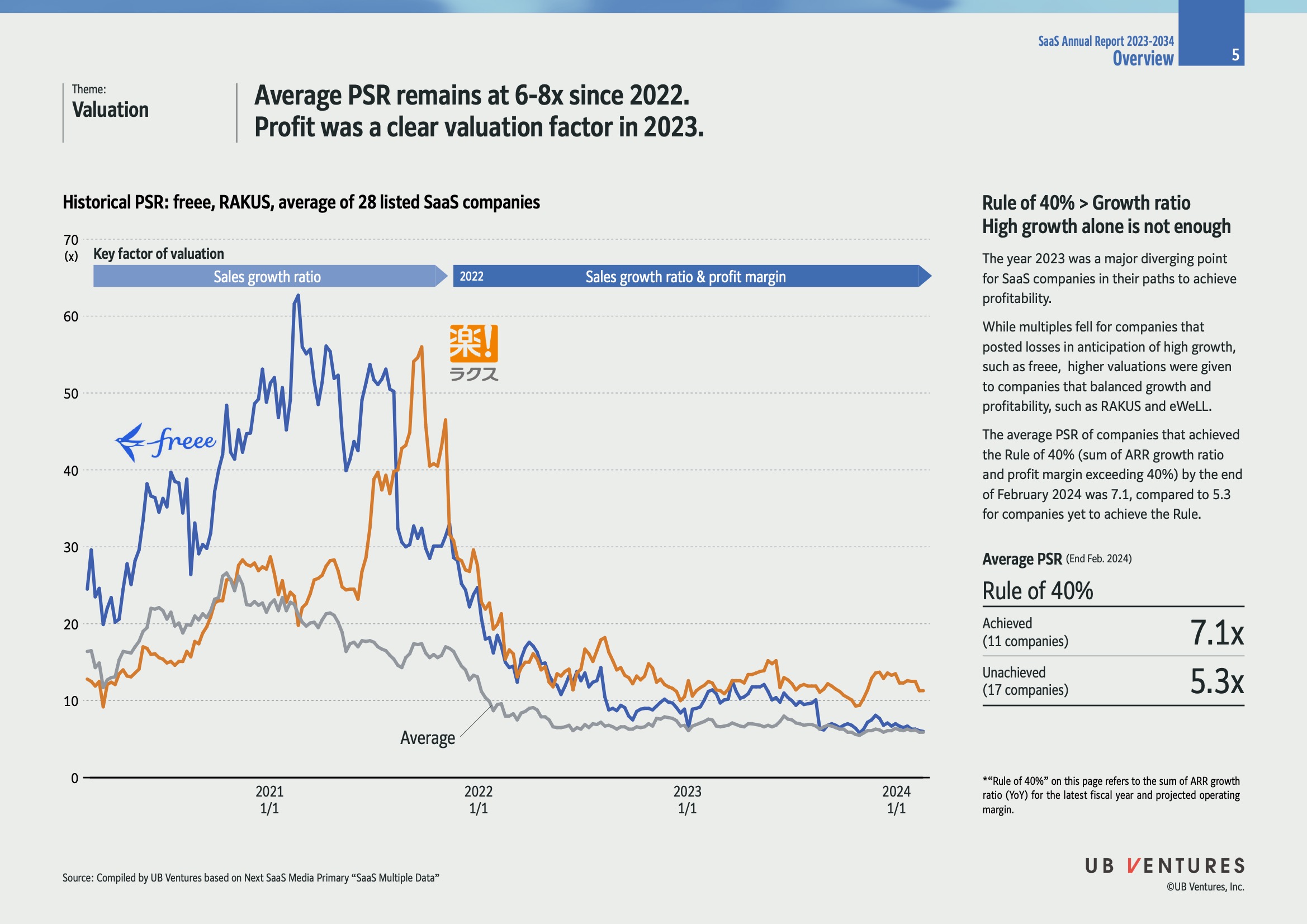
Average PSR Stability: The Price-to-Sales Ratio (PSR) for SaaS companies has remained between 6-8x since 2022. This suggests a consistent valuation approach in the market.
-
Profit as a Valuation Factor: In 2023, profitability became a more significant factor in determining company valuations, indicating a shift in investor focus from just growth to sustainable profitability.
Key Factors of Valuation
-
2022-2023 Shift: The primary valuation factor shifted from sales growth ratio in 2022 to a combination of sales growth and profit margin by 2023. This reflects the changing investor priorities towards profitability alongside growth.
-
Rule of 40% : This rule is a benchmark that adds a company's ARR growth rate and profit margin to evaluate performance. A total exceeding 40% indicates a balanced growth and profitability strategy.
Historical PSR Data
-
Companies Tracked: Data includes 28 listed SaaS companies, with notable examples like "freee" and "RAKUS."
-
Trends:
- Freee: Showed high PSR in early 2021, suggesting initial investor enthusiasm.
- RAKUS: Similar early peak but a more balanced decline over time.
-
Analysis by Company:
- Companies achieving balanced growth (Rule of 40%) have seen higher valuations.
- Freee's high early valuation versus later decline shows investor reassessment based on profitability.
2024 PSR Insights
| Rule of 40% | End Feb. 2024 Average PSR |
|---|---|
| Achieved | 7.1x |
| Unachieved | 5.3x |
-
Achieved Companies: Companies that met the Rule of 40% saw a higher average PSR of 7.1, indicating investor preference for balanced growth and profitability.
-
Unachieved Companies: Those that did not meet this rule had a lower average PSR, highlighting market penalties for companies with an imbalanced growth-profit strategy.
Insights
-
Investor Behavior: The data reflects a market trend where investors are rewarding companies that show both growth and profitability. This emphasizes the importance of strategic financial management in SaaS companies.
-
Market Dynamics: As growth alone becomes insufficient for valuation, companies need to focus on operational efficiency and profitability to maintain and enhance valuations.
Conclusion
The SaaS market is experiencing a paradigm shift from a growth-centric to a more balanced approach that incorporates profitability as a crucial metric for valuation. The Rule of 40% serves as a pivotal benchmark in this environment.
Extended readings:
Overview of Japanese SaaS Companies Relative to the Rule of 40
Key Themes
The Rule of 40
- Definition: The Rule of 40 is a performance metric in the SaaS industry, which suggests that a company's growth rate and profit margin should sum to 40% or more for robust valuation.
- Importance: Achieving the Rule of 40 indicates strong business health, balancing growth and profitability.
Shift in Focus
- Profitability Over Growth: Companies are transitioning from focusing solely on growth to emphasizing profitability. This alignment is necessary for higher valuations as per investor expectations.
Valuation Metrics
- Current Trends: SaaS companies are increasingly evaluated based on their profit margins in response to investor emphasis on profitability.
Data Analysis
Scatter Plot Overview
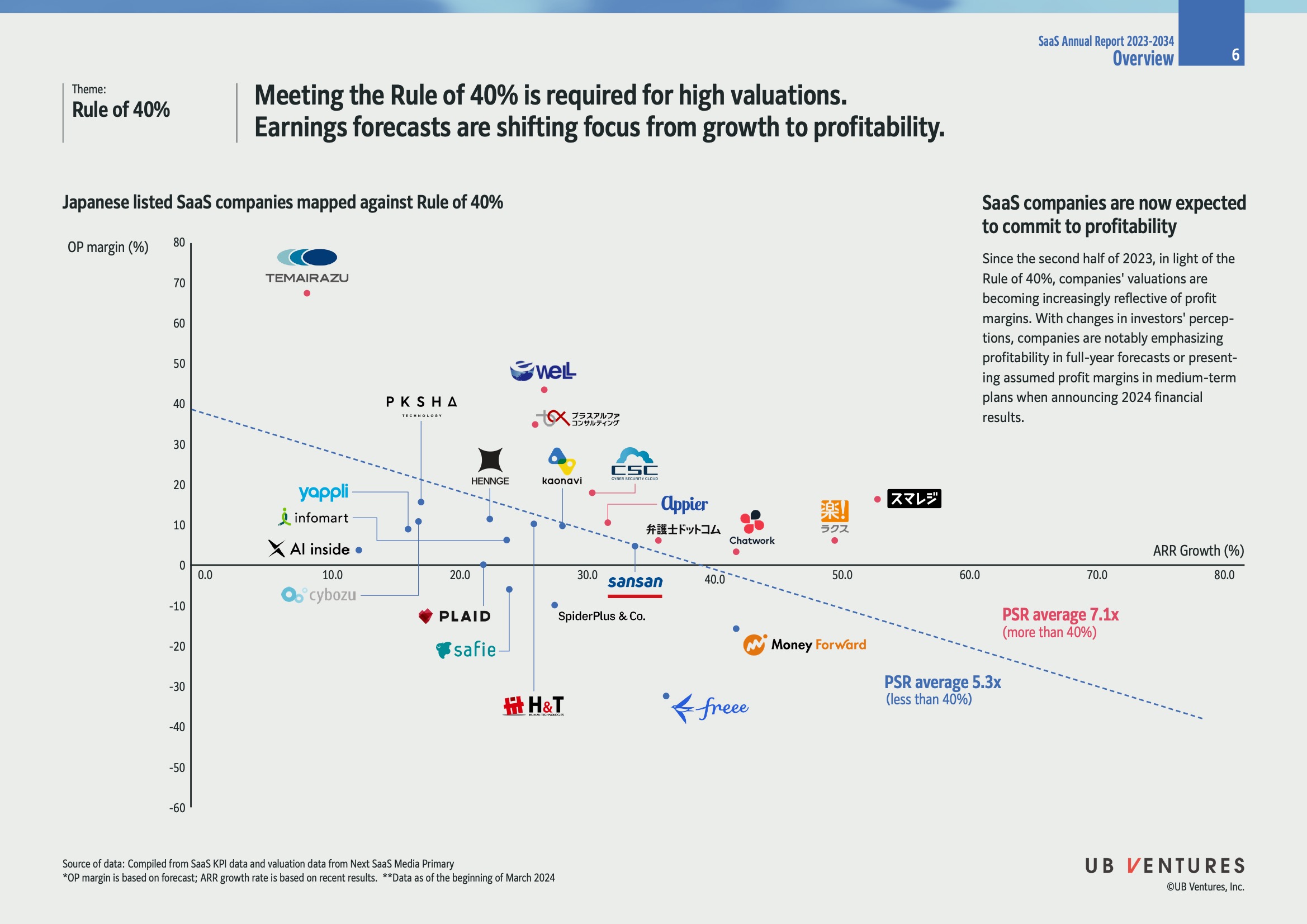
- Axes:
- Vertical Axis (Y-Axis) : Operating Profit Margin (%)
- Horizontal Axis (X-Axis) : ARR (Annual Recurring Revenue) Growth (%)
- Insight: Companies meeting the Rule of 40 are above the diagonal line, indicating better valuation positions.
Companies Mapped
- Quadrants: Companies are scattered across different performance quadrants:
- High Margin & Growth: Companies like Temairazu and Wel demonstrate strong positions.
- Low Margin & High Growth: Companies like Money Forward and Freee focus more on growth.
- Other Observations: Some companies, such as Cybozu and PLAID, fall into negative margins and growth, highlighting the need for strategic shifts.
Comparative Values
- PSR (Price-to-Sales Ratio) Averages:
- More than 40% : PSR average of 7.1x.
- Less than 40% : PSR average of 5.3x.
- Implication: Higher PSR for companies meeting the Rule of 40 stresses the investor preference for balanced growth and profitability.
Strategic Implications
Company Strategies
- Profit Margin Focus: Many companies are incorporating profit margins in their financial forecasts to meet investor demands.
- Long-term Planning: Emphasis on profitability in medium-term plans signals a strategic pivot and commitment to financial sustainability.
Conclusion
- Investor Sentiment: There is a notable shift towards evaluating SaaS companies with a lens on profitability, not just aggressive growth rates.
- Future Outlook: Companies are expected to maintain this dual focus on growth and profitability to enhance their market valuations.
Source
- Data Compilation: Derived from SaaS KPI data and valuation data by Next SaaS Media Primary. Data reflects forecasts and recent results as of March 2024.
Extended readings:
Overview of SaaS IPOs in 2023
General Insights
-
Trend in SaaS IPOs:
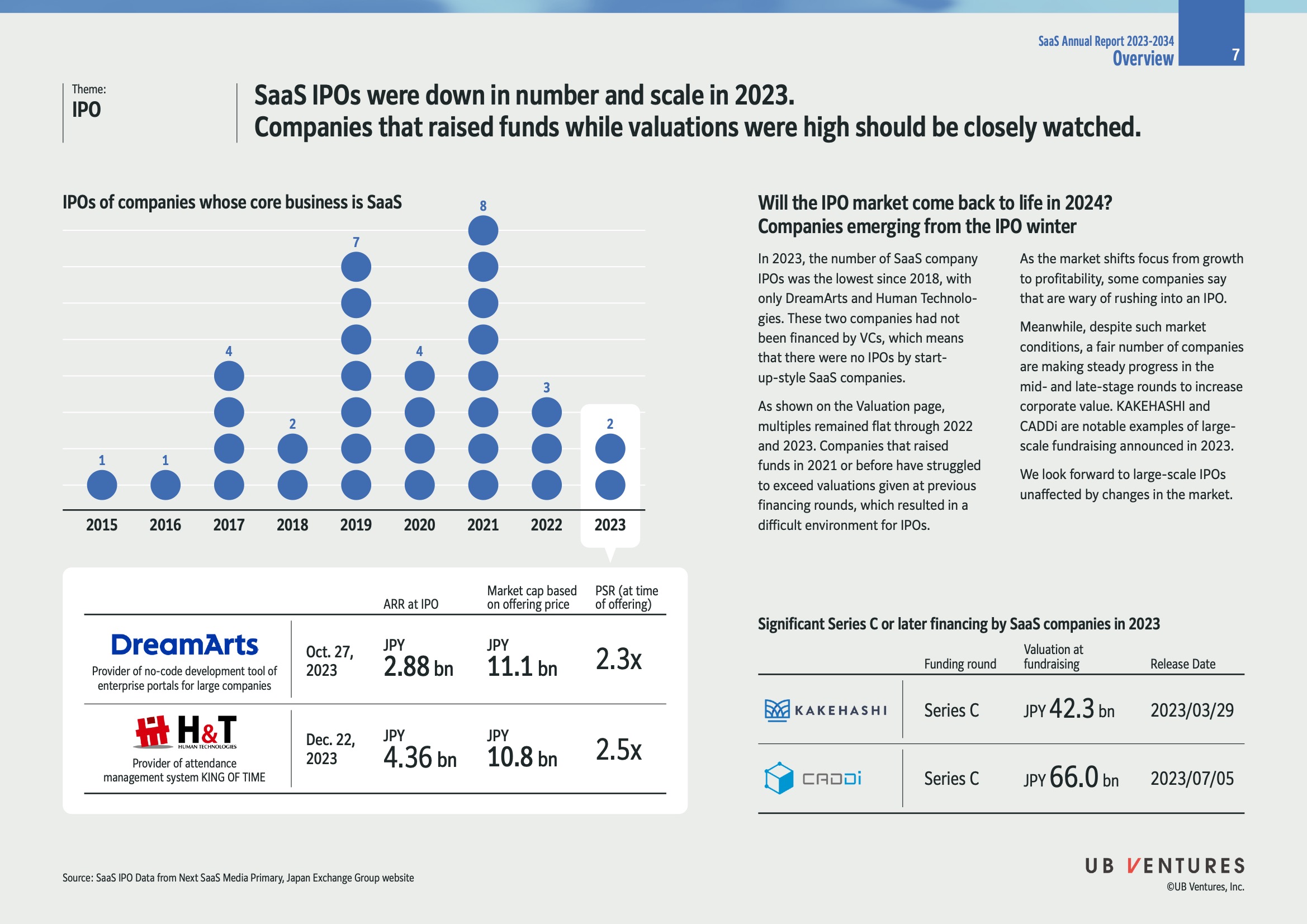
- In 2023, the number and scale of SaaS IPOs declined significantly, marking the lowest point since 2018.
- Only two companies, DreamArts and Human Technologies, went public, indicating a challenging environment for start-up SaaS companies.
-
Market Observation:
- Companies that raised funds in 2021 or earlier are facing difficulties meeting previous valuation expectations.
- The market is shifting focus from growth to profitability, influencing IPO activities.
Specific Company Data
Companies with IPOs in 2023
| Company | IPO Date | ARR at IPO | Market Cap | PSR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DreamArts | Oct. 27, 2023 | JPY 2.88 bn | JPY 11.1 bn | 2.3x |
| Human Technologies | Dec. 22, 2023 | JPY 4.36 bn | JPY 10.8 bn | 2.5x |
- DreamArts: Specializes in no-code development tools for enterprise portals.
- Human Technologies: Offers an attendance management system, KING OF TIME.
Key Terms
- ARR (Annual Recurring Revenue) : A metric that shows the predictable revenue expected over the course of a year.
- PSR (Price to Sales Ratio) : A valuation metric for companies indicating how much investors are willing to pay per dollar of sales.
Future Prospects
-
2024 Expectations:
- There might be potential for a revival in the IPO market as companies continue to adapt their strategies.
- Some companies are hurrying to join IPOs despite uncertain market conditions.
-
Prominent Fundraising Examples:
- Companies like KAKEHASHI and CADDi have shown strong fundraising in 2023, with valuations at JPY 42.3 bn and JPY 66.0 bn respectively. Both are significant for maintaining growth during a difficult period.
Conclusion
The SaaS IPO landscape in 2023 reflects the broader economic pressures, with a shift towards profitability. Companies holding onto previous valuations face challenges, while some larger firms manage to thrive through strategic fundraising. Looking ahead to 2024, the market may see renewed activity as conditions evolve.
Extended readings:
2023 M&A Trends in SaaS Startups
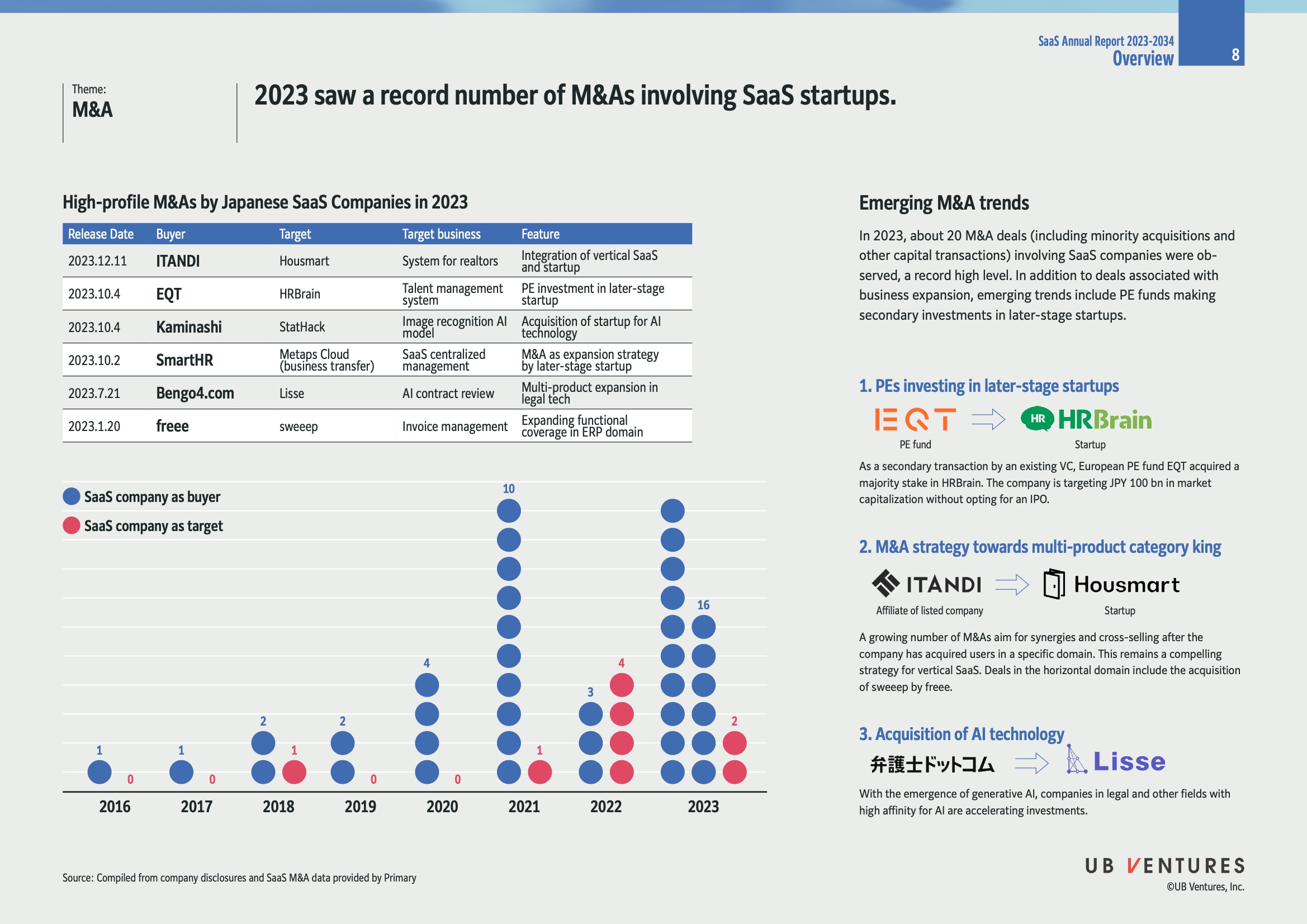
Overview
- Record M&A Activity: In 2023, approximately 20 merger and acquisition (M&A) deals involving SaaS startups were recorded, marking a significant increase in activity.
- Emerging Trends: Key trends include private equity (PE) funds investing in later-stage startups and strategic expansions by acquiring companies in the same or complementary sectors.
High-Profile M&As by Japanese SaaS Companies
| Release Date | Buyer | Target | Target Business | Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023.12.11 | ITANDI | Housmart | System for realtors | Integration of vertical SaaS and startup |
| 2023.10.4 | EQT | HRBrain | Talent management system | PE investment in later-stage startup |
| 2023.10.4 | Kaminashi | StatHack | Image recognition AI model | Acquisition of startup for AI technology |
| 2023.10.2 | SmartHR | Metaps Cloud | SaaS centralized management | M&A as expansion strategy by later-stage startup |
| 2023.7.21 | Bengo4.com | Lisse | AI contract review | Multi-product expansion in legal tech |
| 2023.1.20 | freee | sweeep | Invoice management | Expanding functional coverage in ERP domain |
Insights:
- The diversification strategy focuses on gaining expertise in complementary technologies and broadening service offerings (e.g., AI and legal tech integrations).
M&A Trends Analysis
-
PE Funds in Later-Stage Startups
- Companies like EQT acquire stakes in startups such as HRBrain as a strategic move to scale without the need for an initial public offering (IPO).
- This trend indicates a shift towards securing investments for established startups to enhance market capitalization.
-
M&A for Multi-Product Expansion
- ITANDI’s acquisition of Housmart represents efforts to dominate specific verticals in the SaaS domain by consolidating related technologies and services.
- The goal is to create synergetic benefits that enhance resource optimization.
-
AI Technology Acquisition
- The legal sector sees investments like Bengo4.com's acquisition of Lisse, emphasizing the growing importance of AI in optimizing operations and delivering new services.
M&A Activity Chart (2016-2023)
- SaaS as Buyers (Blue Dots):
- Strong upward trend since 2021, peaking at 16 deals in 2023.
- SaaS as Targets (Red Dots):
- Lower activity compared to buyers but showing an increase, with 2 deals in 2023.
Insights:
- The increase in SaaS as buyers underscores a strategic movement towards growth through acquisition.
- As targets, these SaaS companies are seen as valuable assets for capabilities that complement or augment the acquirer’s offerings.
Conclusion
- The M&A landscape for SaaS companies in 2023 reveals an aggressive expansion and strategic investment focus, particularly in areas like AI, talent management, and legal tech. The pattern shows a blend of tactical innovation and market consolidation to secure competitive advantages without the immediate necessity for public listings.
Extended readings:
Japanese SaaS Startup Fundraising Overview (2023)
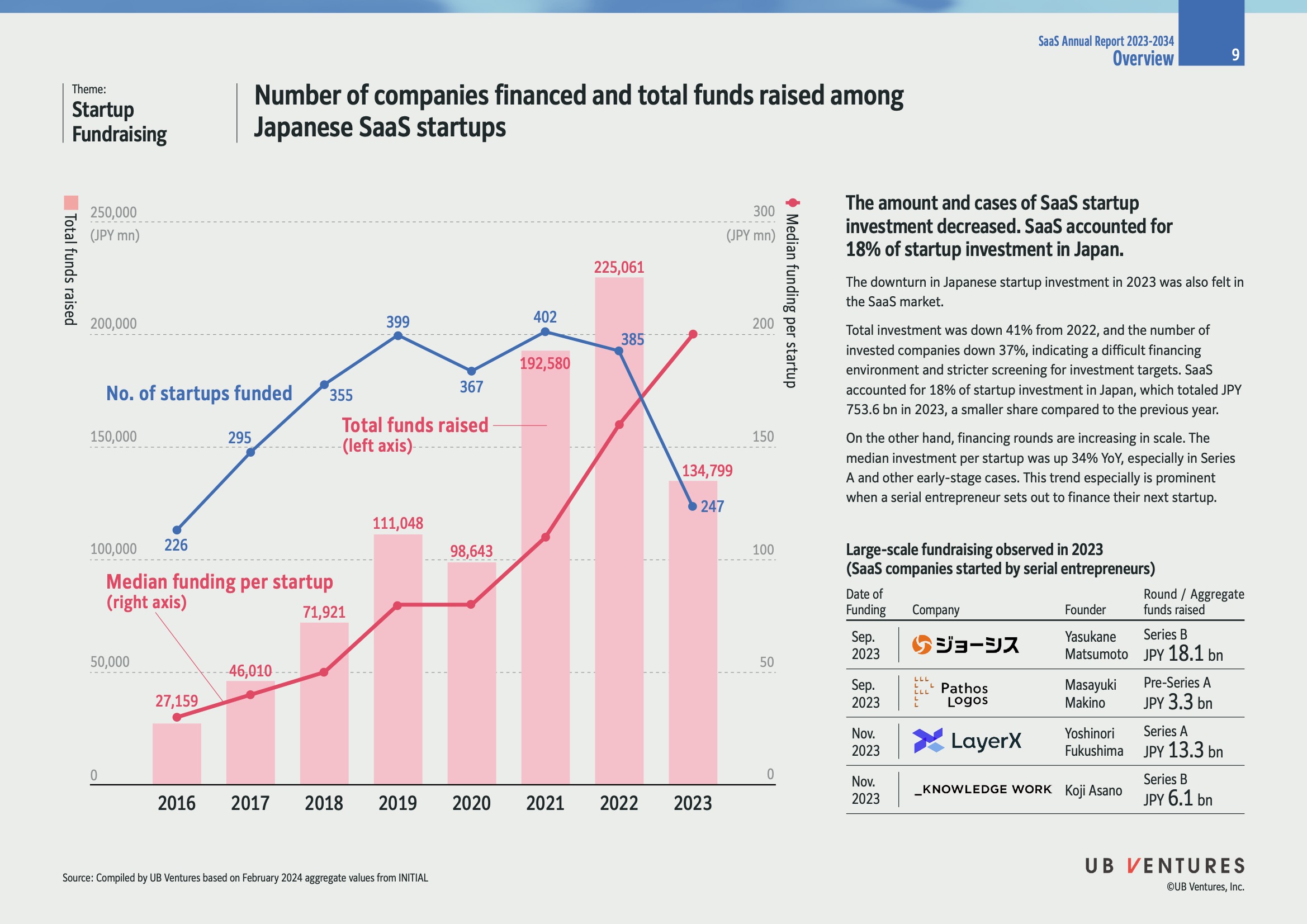
Overview
-
Decline in Investment: In 2023, the total investment in Japanese SaaS startups decreased by 41% from 2022, indicating a challenging financing environment with stricter investor screening. The number of invested companies fell by 37%.
-
Share in Startup Investment: SaaS startups accounted for 18% of total startup investment in Japan, totaling JPY 753.6 billion in 2023.
Trends
- Median Funding Increase: Despite the overall decline, the median investment per startup increased by 34% year-over-year, particularly in Series A and other early-stage financings. This growth is notably seen when serial entrepreneurs finance new startups.
Graph Analysis
- Funding and Number of Startups:
-
Total Funds Raised (JPY mn) :
- 2016: 27,159
- 2017: 46,010
- 2018: 71,921
- 2019: 111,048
- 2020: 98,643
- 2021: 192,580
- 2022: 225,061
- 2023: 134,799
-
Number of Startups Funded:
- 2016: 226
- 2017: 295
- 2018: 355
- 2019: 367
- 2020: 399
- 2021: 402
- 2022: 385
- 2023: 247
-
Median Funding per Startup (JPY mn) :
- 2016: Data unavailable
- 2023: 134,799
-
The graph reflects a decline in both the total funds raised and the number of funded startups in 2023, yet an increase in median funding per startup.
Large-scale Fundraising (2023)
| Date of Funding | Company | Founder | Round | Aggregate Funds Raised (JPY bn) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sep. 2023 | Company S | Yasukane Matsumoto | Series B | 18.1 |
| Sep. 2023 | Pathos Logos | Masayuki Makino | Pre-Series A | 3.3 |
| Nov. 2023 | LayerX | Yoshiro Fukushima | Series A | 13.3 |
| Nov. 2023 | Knowledge Work | Koji Asano | Series B | 6.1 |
Insights
-
Serial Entrepreneurs: Companies founded by serial entrepreneurs attracted large-scale funding, reflecting trust and confidence in seasoned founders.
-
Investment Stages: Significant investments were made in both early stages (e.g., Pre-Series A) and later stages (e.g., Series B), showing varied investor interests.
Conclusion
Despite the downturn in total investments and the number of startups funded in 2023, there is an upward trend in median funding per startup, driven by larger financing rounds and the presence of serial entrepreneurs. This indicates a selectivity in investment toward potentially more secure or promising ventures.
Extended readings:
ARR Acquisition Efficiency in SaaS Companies
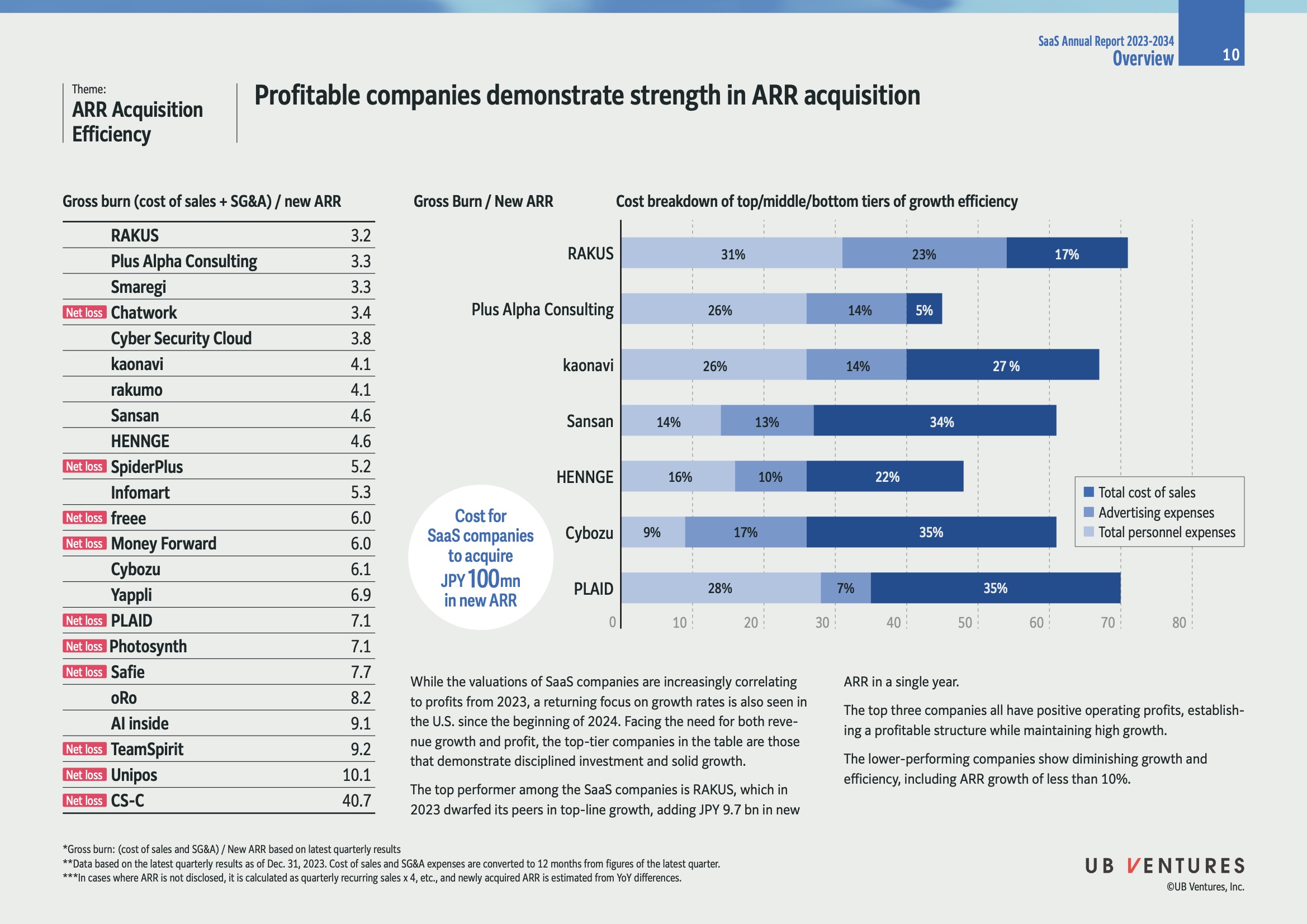
Overview
- The focus of this analysis is on Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) acquisition efficiency among SaaS companies, highlighting those that are profitable and demonstrate strong growth.
Key Findings
- Top Performer: RAKUS stands out as the leading company, acquiring JPY 9.7 billion in new ARR in 2023.
- Insight: Efficient ARR acquisition is critical for sustaining growth and profitability in the SaaS market.
- Profitability and Efficiency: The top three companies in the list exhibit both positive operating profits and high growth efficiency.
- Explanation: This balance is vital as it indicates a sustainable business model that can adapt to market demands.
Company Efficiency Data
| Company | Gross Burn / New ARR | Cost of Sales (%) | Advertising Expenses (%) | Personnel Expenses (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAKUS | 3.2 | 31 | 23 | 17 |
| Plus Alpha Consulting | 3.3 | 26 | 14 | 5 |
| Smaregi | 3.3 | - | - | - |
| Chatwork (Net Loss) | 3.4 | - | - | - |
| Cyber Security Cloud | 3.8 | - | - | - |
| kaonavi | 4.1 | 26 | 14 | 27 |
| rakumo | 4.1 | - | - | - |
| Sansan | 4.6 | 14 | 13 | 34 |
| HENNGE | 4.6 | 16 | 10 | 22 |
| SpiderPlus (Net Loss) | 5.2 | - | - | - |
| Infomart | 5.3 | - | - | - |
| freee (Net Loss) | 6.0 | - | - | - |
| Money Forward (Net Loss) | 6.0 | - | - | - |
| Cybozu | 6.1 | 9 | 17 | 35 |
| Yappli (Net Loss) | 6.9 | - | - | - |
| PLAID (Net Loss) | 7.1 | 28 | 7 | 35 |
| Photosynth (Net Loss) | 7.1 | - | - | - |
| Safie | 7.7 | - | - | - |
| oRo | 8.2 | - | - | - |
| AI inside | 9.1 | - | - | - |
| TeamSpirit (Net Loss) | 9.2 | - | - | - |
| Unipos (Net Loss) | 10.1 | - | - | - |
| CS-C (Net Loss) | 40.7 | - | - | - |
- Note: Companies marked with "Net Loss" show higher Gross Burn / New ARR ratios, indicating less efficiency.
Insights
-
Cost Structure: The cost breakdown among companies reveals varied emphasis on sales, advertising, and personnel, highlighting different strategic focuses.
- Idea: Analyzing which cost components are optimized can provide insights into strategic priorities and market positioning.
-
Market Focus Shift: Starting 2023, a crucial shift toward profit-correlated valuations has been observed in the SaaS market.
- Explanation: This aligns with global trends where profitability is increasingly important to investors, especially during economic downturns.
Conclusion
- SaaS Market Strategy: To thrive, companies must balance growth with efficiency, indicating disciplined investment and strategic planning. The data underscores the importance of agile business models adapting to changing economic landscapes.
Extended readings:
Top Vertical SaaS Startups in Japan by Valuation
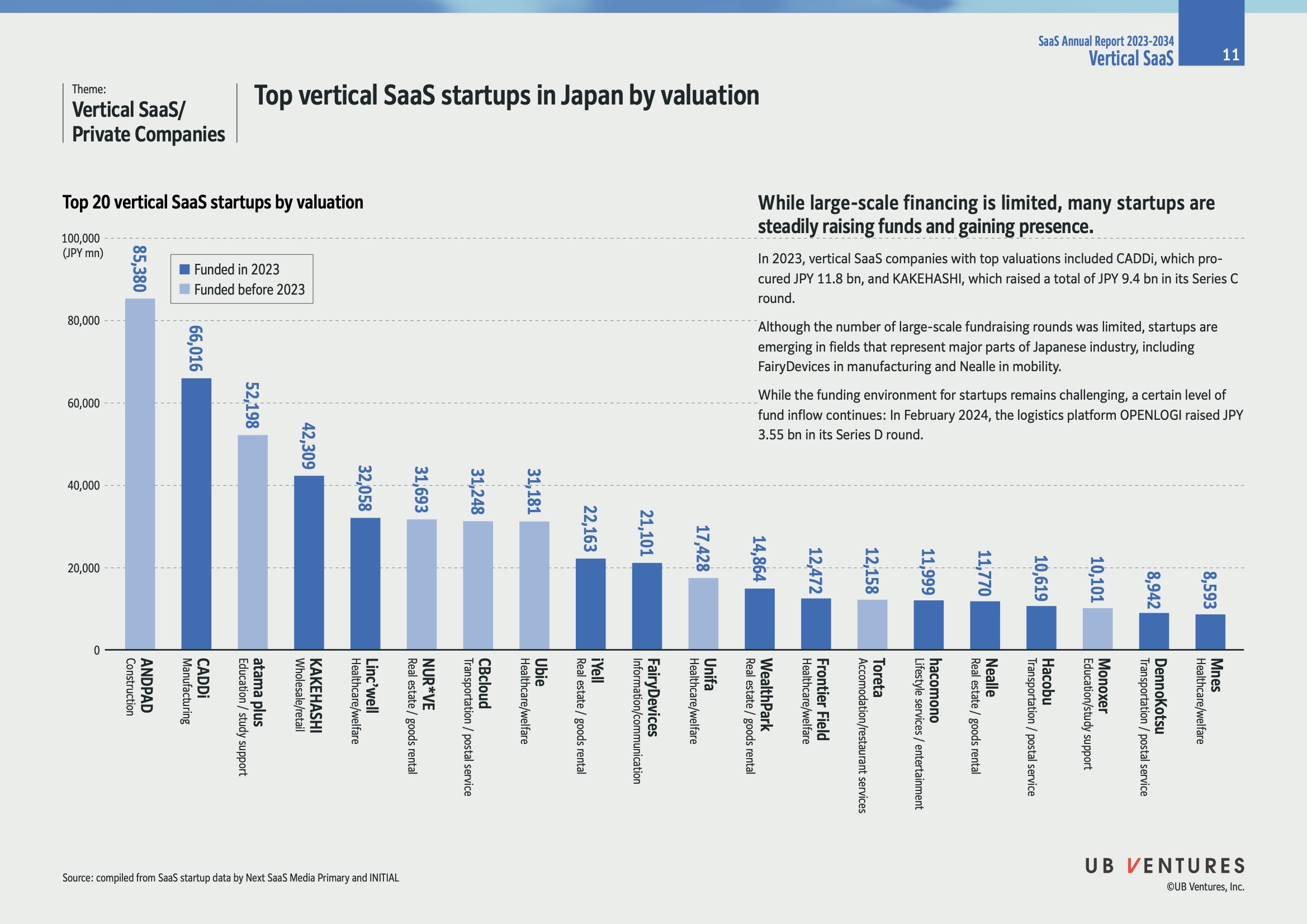
Overview
The image provides insights into the top 20 vertical SaaS (Software as a Service) startups in Japan, arranged by their valuations in Japanese Yen (JPY) as of 2023. It highlights trends in funding and the challenges faced by these startups in the current financial climate.
Key Data
| Rank | Startup Name | Industry | Valuation (JPY mn) | Funding Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ANDPAD | Construction | 85,380 | Funded before 2023 |
| 2 | CADDi | Manufacturing | 69,106 | Funded in 2023 |
| 3 | Atama Plus | Education/Study Support | 52,198 | Funded before 2023 |
| 4 | LinkWiz | Wholesale/Retail | 42,090 | Funded before 2023 |
| 5 | KAKEHASHI | Healthcare/Welfare | 32,058 | Funded in 2023 |
| 6 | NURVE | Real Estate Goods Rental | 31,693 | Funded before 2023 |
| 7 | CBcloud | Transportation/Postal Service | 31,148 | Funded before 2023 |
| 8 | Ubie | Healthcare/Welfare | 31,181 | Funded before 2023 |
| 9 | Nealle | Real Estate Goods Rental | 21,163 | Funded before 2023 |
| 10 | FairyDevices | Information/Communication | 21,101 | Funded before 2023 |
| 11 | Unifa | Healthcare/Welfare | 17,428 | Funded before 2023 |
| 12 | WealthPark | Real Estate Goods Rental | 14,864 | Funded before 2023 |
| 13 | Frontier Field | Information/Communication | 12,472 | Funded before 2023 |
| 14 | Toreta | Food/Restaurant Services | 12,158 | Funded before 2023 |
| 15 | Itamono | Lifestyle Services/Enrichment | 11,999 | Funded before 2023 |
| 16 | Nealle | Real Estate Goods Rental | 11,770 | Funded before 2023 |
| 17 | Hatoku | Transportation/Postal Service | 10,619 | Funded before 2023 |
| 18 | Monoxer | Education/Study Support | 10,101 | Funded before 2023 |
| 19 | DemoKOTSU | Transportation/Postal Service | 8,942 | Funded before 2023 |
| 20 | Mebius | Healthcare/Welfare | 8,553 | Funded before 2023 |
Insights from Trends
-
Limited Large-scale Financing: While large-scale financing is scarce, startups are strategically raising funds to gain presence and continue operations.
-
Significant Fundings in 2023: Notable fundraisings in 2023 include CADDi securing JPY 11.8 billion in the manufacturing sector, and KAKEHASHI raising JPY 9.4 billion in healthcare/welfare.
-
Sector-Specific Growth: Startups are finding opportunities in key Japanese industries like manufacturing and mobility. For instance, FairyDevices and Nealle are notable companies in these sectors.
-
Emerging Challenges and Continuity: The logistics platform OPENLOGI raised JPY 3.55 billion in a Series D round, showing ongoing interest despite challenging conditions.
Contextual and Additional Information
-
Valuation Measures: Startup valuations provide an estimate of potential market size, growth rate, and risk factors, based on numerous financial metrics and projections.
-
Vertical SaaS: These are SaaS companies focusing on niche markets, providing highly specialized services tailored to particular industries.
-
Funding Rounds Explained: Series C and Series D rounds are stages in the funding lifecycle, often indicating scaling to new markets or refining a business model.
By understanding the positioning and strategies of these startups, stakeholders can track developments in Japan’s dynamic SaaS environment.
Extended readings:
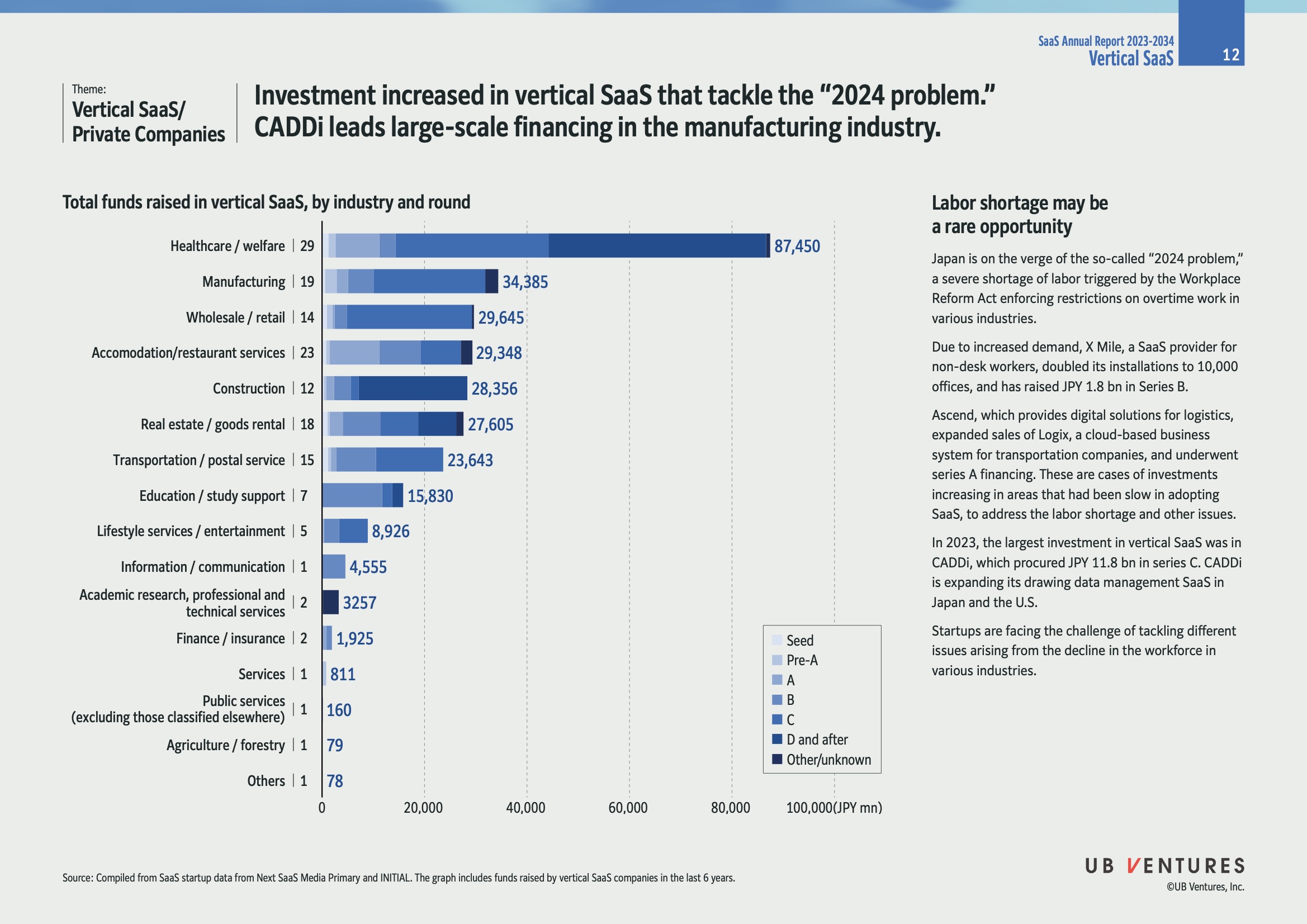
Investment in Vertical SaaS & Tackling the 2024 Problem
Key Insights
-
Increased Investment in Vertical SaaS:
- Investments have surged in vertical SaaS addressing the "2024 problem."
- Vertical SaaS refers to software solutions tailored for specific industries.
-
Leading Industry in SaaS Investment:
- The Healthcare/Welfare industry leads with ¥87,450 million.
- Investments target specific needs and regulations, enhancing industry-specific solutions.
-
Manufacturing Industry:
- Acquired significant funding, ranking second with ¥34,385 million.
- CADDi is highlighted as a major player, acquiring ¥11.8 billion in Series C funding.
2024 Problem
-
Labor Shortage:
- Predicted due to the Workplace Reform Act, enforcing overtime limits.
- Affects various industries, creating demand for efficiency through technology.
-
Opportunities:
- X Mile: A SaaS provider for non-desk workers, indicates growth by doubling installations and raising ¥1.8 billion.
- Ascend: Offers logistics solutions and a cloud-based system for transportation; raised Series A funding.
Detailed Funding Breakdown
| Industry | Total Funding (JPY mn) | Number of Rounds |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare / Welfare | 87,450 | 29 |
| Manufacturing | 34,385 | 19 |
| Wholesale / Retail | 29,645 | 14 |
| Accommodation / Restaurant Services | 29,348 | 23 |
| Construction | 28,356 | 12 |
| Real Estate / Goods Rental | 27,605 | 18 |
| Transportation / Postal Service | 23,643 | 15 |
| Education / Study Support | 15,830 | 7 |
| Lifestyle Services / Entertainment | 8,926 | 5 |
| Information / Communication | 4,555 | 1 |
| Academic Research, Professional & Technical | 3,257 | 2 |
| Finance / Insurance | 1,925 | 2 |
| Services | 811 | 1 |
| Public Services | 160 | 1 |
| Agriculture / Forestry | 79 | 1 |
| Others | 78 | 1 |
Strategic Implications
-
Adoption of SaaS Solutions:
- Address labor shortages with digital solutions, increasing demand for industry-specific SaaS.
- Encourage investments in slow-adopting areas to boost efficiency and compliance.
-
Future Trends:
- Continued integration of SaaS platforms in traditional industries.
- Potential rise of startups solving industry-specific challenges via SaaS.
Conclusion
Vertical SaaS investment highlights the shift towards specialized, tech-driven solutions in response to regulatory challenges and labor shortages. The sectors benefiting most from these investments are those under pressure from regulatory frameworks and seeking efficiencies.
Extended readings:
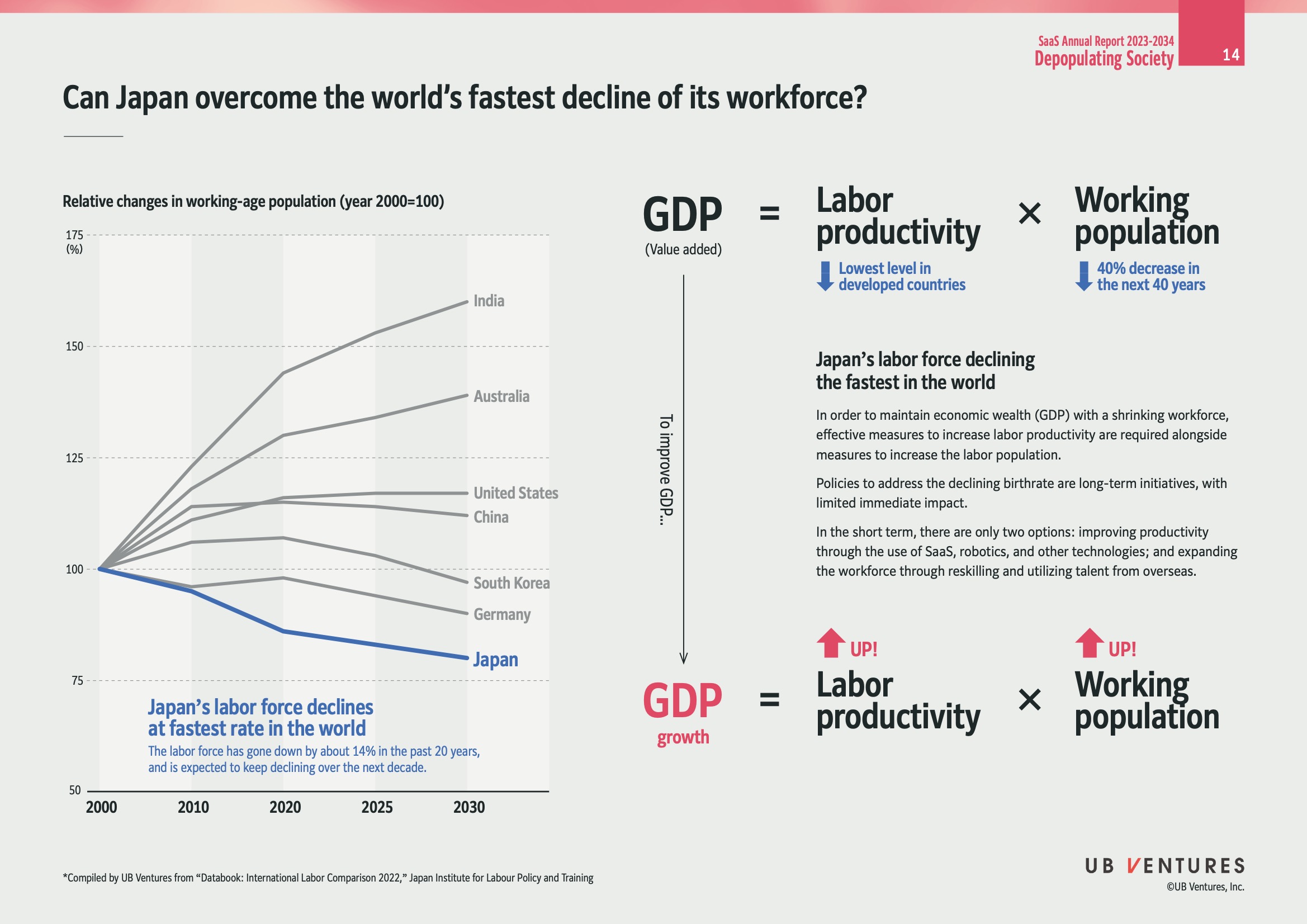
Can Japan Overcome the World's Fastest Decline of Its Workforce?
Overview
Japan is experiencing the fastest decline in its workforce among developed countries. The infographic highlights the challenge faced by Japan in maintaining economic growth with a shrinking working-age population.
Workforce Changes
Relative Changes in Working-Age Population (2000-2030)
| Country | Change Percentage (2000-2030) |
|---|---|
| India | Increasing |
| Australia | Increasing |
| United States | Slightly Increasing |
| China | Slightly Increasing |
| South Korea | Slightly Increasing |
| Germany | Declining |
| Japan | Fastest Declining |
- Insight: Japan's labor force has decreased by about 14% in the past 20 years and is projected to continue declining. This trend poses severe economic challenges and necessitates strategic interventions.
Economic Impact
Formula for GDP
-
Labor Productivity: Currently, Japan has the lowest level of productivity among developed countries. Increasing productivity is crucial to counter the declining workforce.
-
Working Population: A projected 40% decrease over the next 40 years suggests significant economic implications unless countered by technological and workforce strategies.
-
Insight: To sustain GDP growth, Japan must focus on boosting labor productivity, alongside strategies to stabilize or grow its workforce.
Strategic Solutions
Short-Term Strategies
-
Improving Productivity
- Leveraging SaaS, robotics, and other technology-driven solutions to enhance efficiency.
- Insight: Technological advancements can help maintain output levels even with a smaller workforce.
-
Expanding Workforce
- Emphasizing reskilling of existing workers and utilizing talent from overseas.
- Insight: Encouraging immigration and enhancing domestic skills can mitigate the workforce decline.
Long-Term Solutions
- Addressing Birthrate Decline
- Policies aimed at increasing birthrate are crucial but have limited immediate impact.
- Insight: Social policies supporting family growth and childcare can have future benefits.
Conclusion
Japan's economic future depends significantly on its ability to innovate and adapt to the challenges posed by a declining working-age population. Immediate steps must be taken to enhance labor productivity and consider international workforce integration to sustain economic growth.
Extended readings:
Key Themes to Tackle Population Decline

Labor Productivity
Measures to increase labor productivity per capita.
Tech-Driven Productivity Improvement
- Objective: Enhance work efficiency through technology.
- Methods: Utilize vertical SaaS, automation, robotics, and AI.
- Insight: Integrating these technologies can streamline processes and reduce manual labor, leading to cost savings and higher productivity.
Age Tech to Support a Super-Aging Society
- Objective: Maintain productivity in an aging population.
- Services: Focus on elderly care, inheritance, and post-death procedures.
- Insight: Investing in technology that supports elder care can free up the working-age population, reducing caregiver burnout and maintaining economic stability.
Well-being Tech to Improve Worker Satisfaction
- Objective: Increase fulfillment and productivity among workers.
- Methods: Enhance quality of life through tech solutions.
- Insight: Employee satisfaction is directly linked to productivity. Providing tools that enhance well-being can lead to more engaged and efficient workers.
HR and Payroll Infrastructure Toward Improving Wages
- Objective: Enable fair wage negotiations.
- Systems: Use of HR/payroll databases and matching platforms.
- Insight: Transparent and accessible systems ensure fair labor practices, reducing conflicts and improving morale.
Labor Population
Measures to expand the workforce.
Reception and Support of Foreign Workers
- Objective: Expand workforce with skilled foreign labor.
- Strategies: Implement shared services and multilingual support.
- Insight: A diverse workforce can drive innovation and fill labor gaps, especially in industries facing skill shortages.
Reskilling of Senior Generation
- Objective: Broaden workload capabilities of older workers.
- Methods: Training programs for new job options.
- Insight: Providing opportunities for the senior generation to acquire new skills can keep them economically active longer, combating workforce shrinkage.
Women's Empowerment in the Workforce and Femtech
- Objective: Increase workplace diversity and gender inclusion.
- Focus: Support social change and technology to prevent career sacrifices due to gender.
- Insight: Gender diversity leads to broader perspectives and drives organizational success. Supporting women through Femtech can remove barriers to career progression.
Sustainable Energy and Raising Food Self-Sufficiency
- Objective: Enhance energy and food security sustainably.
- Methods: Employ renewable energy and agri-tech.
- Insight: Sustainable practices contribute to long-term stability and can alleviate pressures related to population decline by creating self-sufficient communities.
Summary
Addressing population decline involves enhancing productivity through technology and infrastructure, expanding the labor pool through worker diversity and re-skilling, and investing in sustainable practices to ensure long-term societal resilience.
Extended readings:
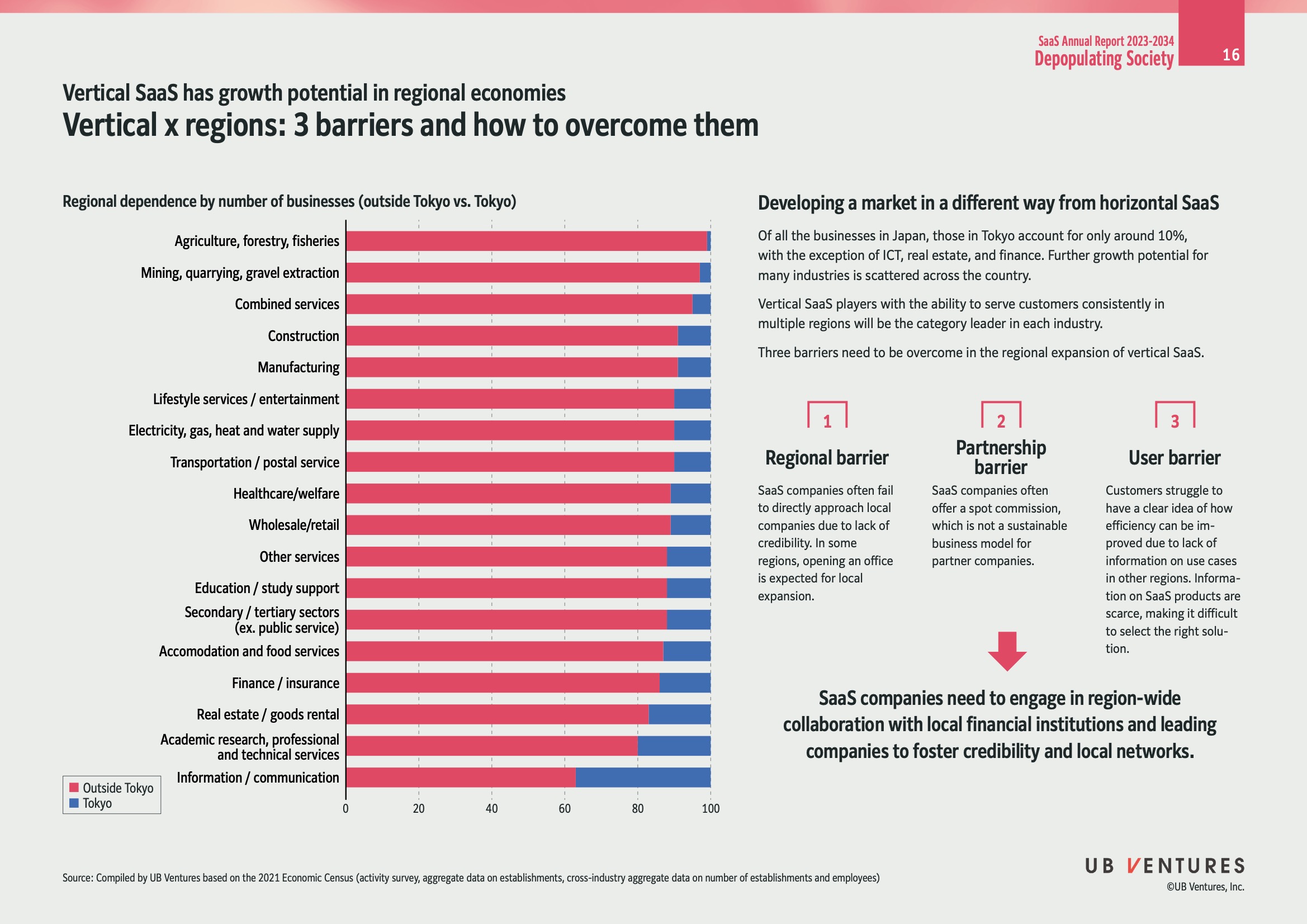
Vertical SaaS Growth Potential in Regional Economies
Overview
Vertical SaaS (Software as a Service) has significant growth potential in regional economies across Japan. Unlike horizontal SaaS, which offers a broad range of services, vertical SaaS targets specific industry needs, making it crucial in serving diverse markets outside of Tokyo.
Regional Dependence by Industry
A comparison by the number of businesses outside Tokyo versus within Tokyo. This highlights market dispersion and potential opportunities for Vertical SaaS:
| Industry | Outside Tokyo | Tokyo |
|---|---|---|
| Agriculture, Forestry, Fisheries | High | Low |
| Mining, Quarrying, Gravel Extraction | High | Low |
| Combined Services | High | Low |
| Construction | High | Low |
| Manufacturing | High | Low |
| Lifestyle Services/Entertainment | High | Low |
| Electricity, Gas, Heat and Water Supply | High | Low |
| Transportation/Postal Service | High | Low |
| Healthcare/Welfare | High | Low |
| Wholesale/Retail | High | Low |
| Other Services | High | Low |
| Education/Study Support | High | Low |
| Secondary/Tertiary Sectors (Ex. Public Service) | High | Low |
| Accommodation and Food Services | High | Low |
| Finance/Insurance | High | Low |
| Real Estate/Goods Rental | High | Low |
| Academic Research, Professional and Technical Services | High | Low |
| Information/Communication | Low | High |
Market Development Insights
-
Unique Approach: Unlike horizontal SaaS, developing a market for vertical SaaS often requires addressing specialized needs within specific industries.
-
Region-Specific Opportunities: With only roughly 10% of businesses located in Tokyo (excluding some fields), there's immense potential for regional expansion.
Key Barriers to Overcome
1. Regional Barrier
- Challenge: Establishing credibility and accessing local companies.
- Insight: Opening local offices can foster trust and facilitate easier market entry.
- Additional Info: Having a local presence may reassure clients about service quality and support.
2. Partnership Barrier
- Challenge: Offering unsustainable business models like spot commissions.
- Insight: Establishing solid, sustainable partnerships is crucial for long-term success.
- Additional Info: Long-term partnerships can provide ongoing support and market stability.
3. User Barrier
- Challenge: Limited information on SaaS product efficiency hinders adoption.
- Insight: Clear communication and demonstrations of product capabilities can enhance user acceptance.
- Additional Info: Producing case studies and testimonials may aid in illustrating product viability.
Strategy for Growth
- Collaboration: Engage in region-wide collaboration with local financial institutions and leading companies.
- Goal: Foster credibility and robust local networks, ensuring consistent and widespread SaaS integration.
Source
Information is compiled by UB Ventures based on the 2021 Economic Census, providing valuable insights into establishment activities and regional business dynamics.
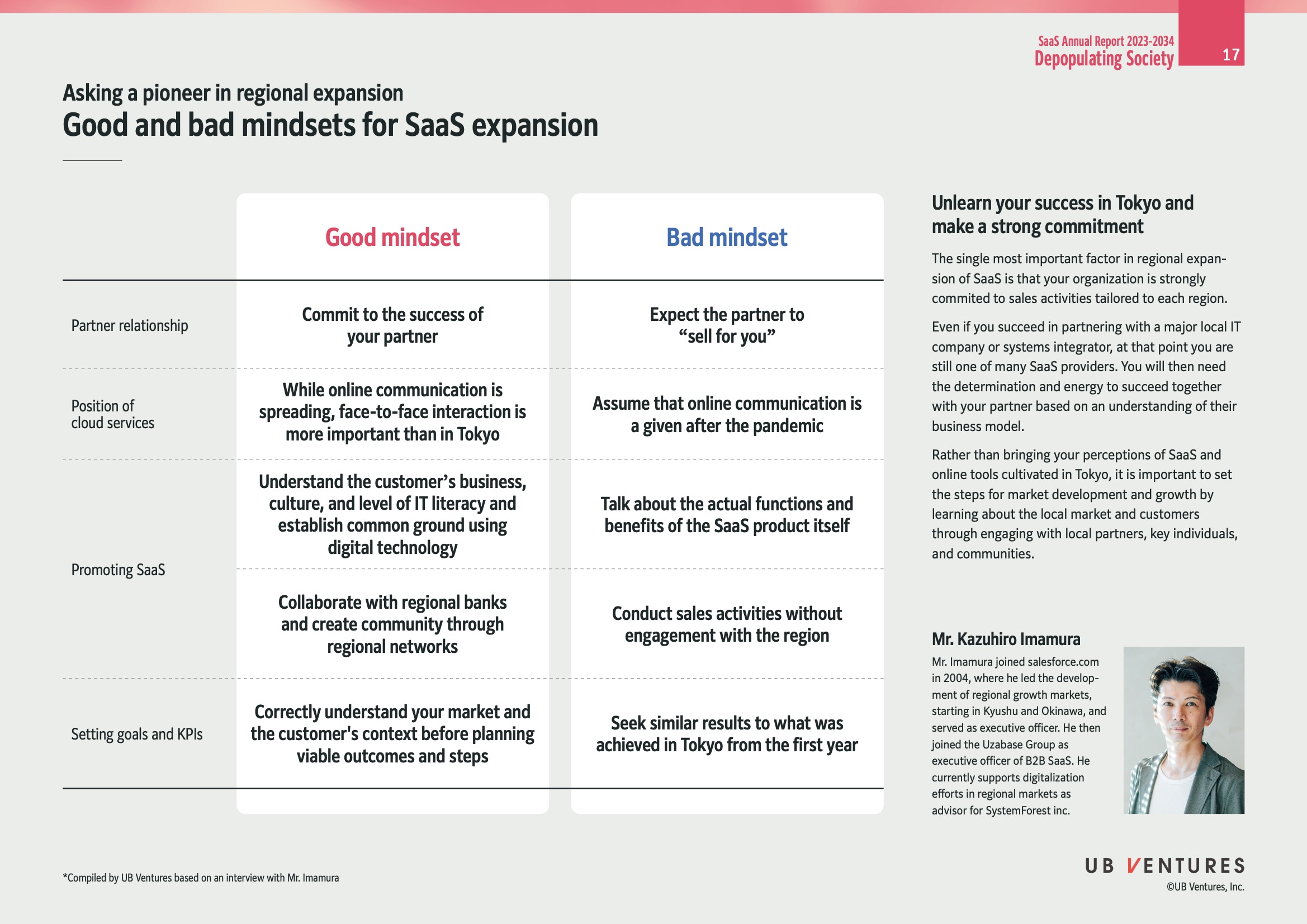
Good and Bad Mindsets for SaaS Expansion
Partner Relationship
Good Mindset
- Commit to the success of your partner
- Building a strong partnership involves mutual commitment and sharing goals.
- Long-term success relies on collaboration and joint efforts.
Bad Mindset
- Expect the partner to "sell for you"
- Over-reliance on partners can lead to lack of engagement and understanding of the target market.
- Selling should be a joint effort.
Position of Cloud Services
Good Mindset
- Face-to-face interaction is crucial
- While online communication is convenient, personal interactions help build trust and better relationships, especially outside major tech hubs like Tokyo.
Bad Mindset
- Assume online communication is sufficient
- Relying solely on digital communication can overlook cultural nuances and personal connections important in business development.
Promoting SaaS
Good Mindset
-
Understand the customer’s business
- Knowledge of the customer’s needs, culture, and IT literacy is essential for effective promotion.
- Use digital technologies to find common ground.
-
Collaborate with regional banks
- Regional networks can offer valuable market insights and support.
- Building local communities strengthens brand presence and reliability.
Bad Mindset
-
Focus only on product features
- Mere emphasis on product benefits without contextual understanding may not resonate with potential clients.
-
Conducting sales without regional engagement
- Ignoring local networks and cultural context can lead to missed opportunities and weaker market position.
Setting Goals and KPIs
Good Mindset
- Understand market and customer context
- Successful planning requires in-depth market research and clear goals aligned with customer needs.
Bad Mindset
- Seek results similar to Tokyo immediately
- Each market has unique traits, and expecting similar outcomes without adaptation can lead to disappointment.
Additional Insights
-
Unlearn Success in Tokyo
- Expanding SaaS requires adapting to the regional nuances and not relying solely on past successful strategies from metropolitan cities like Tokyo.
-
Commitment and Adaptation
- It's crucial for organizations to commit to tailored sales activities and fully integrate into the local business model and market dynamics.
Expert Insight
- Mr. Kazuhiro Imamura
- Background: Key role in regional market development for Salesforce and other SaaS platforms.
- Current Work: Supports digitalization in regional markets, advising on strategic market growth and engagement.
Conclusion
- Effective SaaS expansion requires a deep understanding and commitment to local markets.
- Balancing digital communication with personal interactions and fostering regional partnerships are key strategies for success.
24 Startups Tackling the Challenges of a Depopulating Society
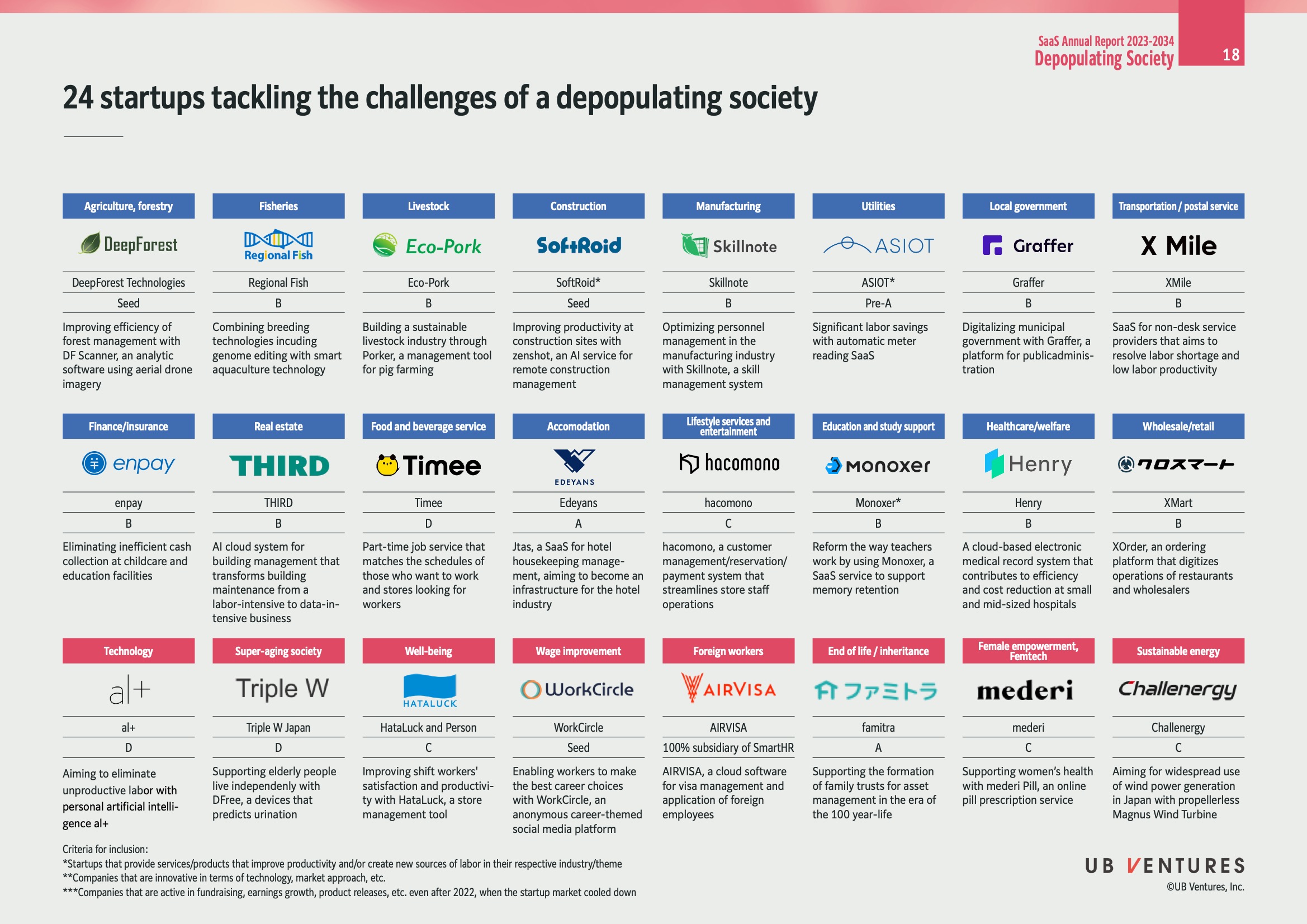
The image showcases various startups addressing issues arising from societal depopulation across different sectors. Each startup provides innovative solutions for enhancing productivity and tackling specific challenges within their respective industries. Here's a detailed breakdown:
Agriculture, Forestry
- DeepForest Technologies
- Stage: Seed
- Focus: Enhances the efficiency of forest management using "DF Scanner," an analytic software employing aerial drone imagery.
- Insight: Leveraging drones can significantly increase data accuracy and reduce labor costs in forestry.
Fisheries
- Regional Fish
- Stage: B
- Focus: Uses breeding technologies, combining genome editing with smart aquaculture.
- Insight: This modernizes the aquaculture industry, promising sustainability and increased yields.
Livestock
- Eco-Pork
- Stage: B
- Focus: Builds a sustainable livestock industry with "Porker," a management tool for pig farming.
- Insight: Such tools can optimize livestock management, potentially leading to better animal care and resource efficiency.
Construction
- SoftRoid
- Stage: Seed
- Focus: Boosts productivity at construction sites using "zenshot," an AI-based remote construction management service.
- Insight: This could minimize human error and streamline project management, crucial for large-scale constructions.
Manufacturing
- Skillnote
- Stage: B
- Focus: Optimizes personnel management in manufacturing through "Skillnote," a skill management system.
- Insight: Tracking skill development can enhance workforce productivity and reduce skill gaps.
Utilities
- ASIOT
- Stage: Pre-A
- Focus: Offers significant labor savings with an automatic meter reading SaaS.
- Insight: Automation in utilities can lead to both cost savings and enhanced operational efficiencies.
Local Government
- Graffer
- Stage: B
- Focus: A digital platform for government administration, aimed at enhancing public service efficiency.
- Insight: Streamlining government operations can significantly improve public service delivery.
Transportation/Postal Service
- XMile
- Stage: B
- Focus: Provides SaaS for operations aiding labor shortage resolution and boosting productivity.
- Insight: Technology can bridge gaps in labor-intensive industries, making them more efficient.
Finance/Insurance
- enpay
- Stage: B
- Focus: Facilitates efficient cash collection in childcare and educational facilities.
- Insight: This can lead to significant time and resource savings for institutions.
Real Estate
- THIRD
- Stage: B
- Focus: AI-based system transforming building maintenance from labor-intensive to data-intensive.
- Insight: AI can automate and predict maintenance needs, reducing downtime and cost.
Food and Beverage Service
- Timee
- Stage: D
- Focus: Matches work schedules with job seekers in stores and other locations.
- Insight: Flexible job matching can cater to non-standard work hours, improving employment rates.
Accommodation
- Edeyans
- Stage: A
- Focus: A SaaS for hotel housekeeping management, evolving the industry infrastructure.
- Insight: Automation in hospitality can enhance guest experience and reduce operational costs.
Lifestyle Services and Entertainment
- hacomo
- Stage: C
- Focus: A management system for customer relations and staff operations.
- Insight: Streamlining operations can improve service delivery and customer satisfaction.
Education and Study Support
- Monoxer
- Stage: C
- Focus: A SaaS tool enhancing teachers' work habits and supporting memory retention.
- Insight: EdTech can play a crucial role in improving educational standards and methodologies.
Healthcare/Welfare
- Henry
- Stage: B
- Focus: An electronic medical record system that aids efficiency in medical practices.
- Insight: Digitizing health records leads to better patient data management and care.
Wholesale/Retail
- XMart
- Stage: B
- Focus: Ordering platform digitizing restaurant and wholesale operations.
- Insight: E-commerce solutions can streamline supply chains and enhance B2B transactions.
Technology
- aI+
- Stage: D
- Focus: Personal artificial intelligence aimed at eliminating unproductive labor.
- Insight: AI deployment in task automation could vastly increase productivity across industries.
Super-Aging Society
- Triple W Japan
- Stage: D
- Focus: Devices aiding elderly independence, predicting urination needs.
- Insight: Innovative health tech can improve quality of life in aging populations.
Well-being
- HataLuck and Person
- Stage: C
- Focus: Enhancing shift workers' satisfaction and productivity with management tools.
- Insight: Addressing worker satisfaction can lower turnover rates and increase morale.
Wage Improvement
- WorkCircle
- Stage: Seed
- Focus: Career enhancement through a social media platform for job opportunities.
- Insight: Networking can open up pathways to better career prospects and wage improvements.
Foreign Workers
- AIRVISA
- Stage: 100% subsidiary of SmartHR
- Focus: Facilitates visa management and foreign employee application processing.
- Insight: Streamlining these processes can ease transitions for international workers.
End of Life/Inheritance
- famitra
- Stage: A
- Focus: Supports family trust formation for asset management over long-term life spans.
- Insight: Estate planning tools can provide peace of mind and financial security.
Female Empowerment, Femtech
- mederi
- Stage: C
- Focus: Digital solutions for women's health, like online pill prescriptions.
- Insight: Femtech is pivotal in addressing specific women's health issues efficiently.
Sustainable Energy
- Challenergy
- Stage: C
- Focus: Promotes wind power generation using "Magnus Wind Turbine."
- Insight: Renewable energy technologies are essential for sustainable development and reducing carbon footprints.
These startups highlight how technological innovations can address demographic challenges by increasing efficiency, reducing labor reliance, and enhancing overall quality of life.
Extended readings:
Issues and Solutions in the Construction Industry
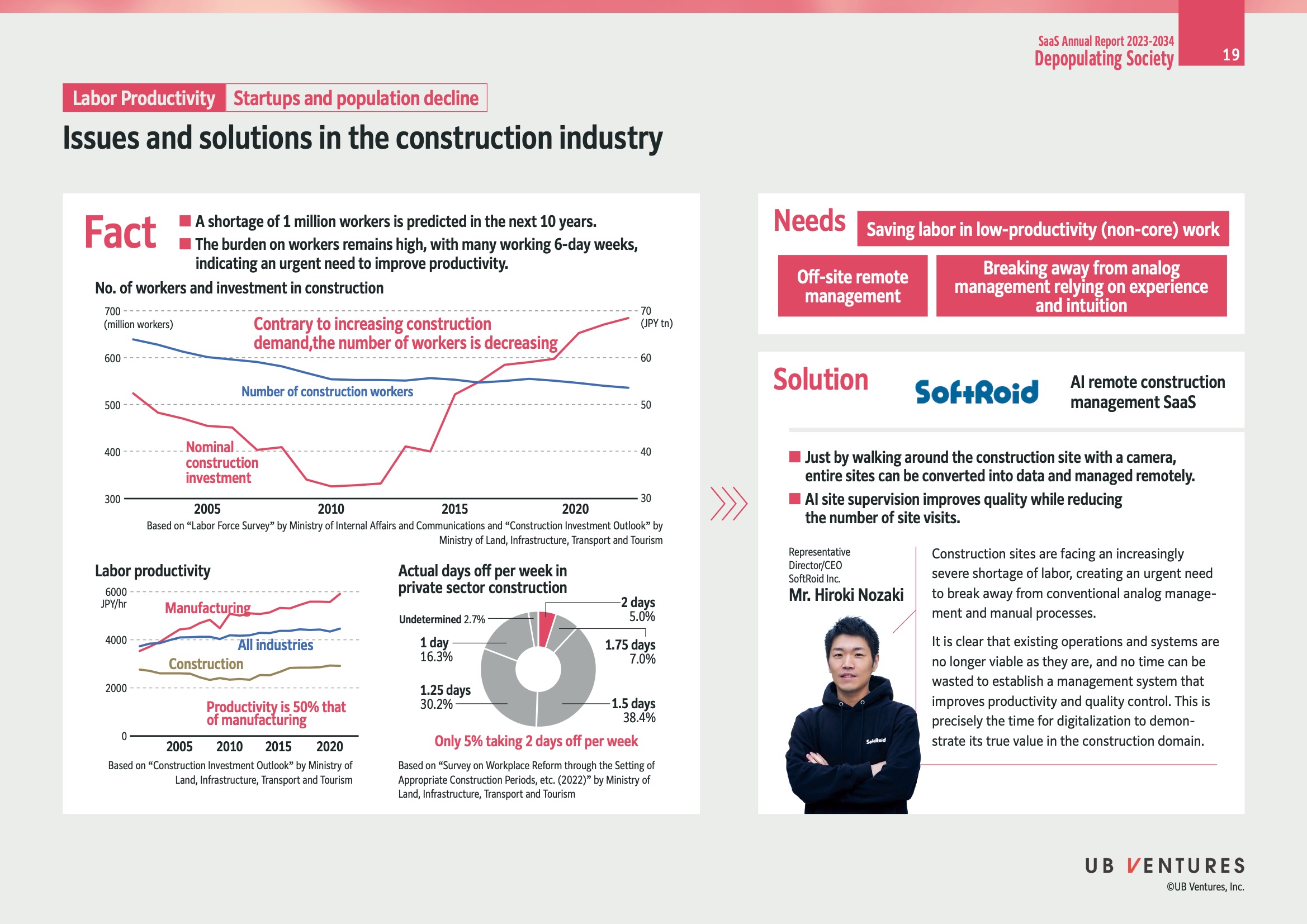
Facts
-
Worker Shortage Prediction:
- A shortage of 1 million workers is anticipated in the next 10 years.
- Implication: There's a critical need to improve productivity to manage the decreasing workforce.
-
Burden on Workers:
- Many are working 6-day weeks, highlighting the necessity to enhance efficiency.
- Insight: Productivity improvements can help balance work-life dynamics and reduce burnout.
Data Insights
-
Number of Workers and Investment in Construction:
- Increasing demand for construction, but the workforce is declining.
- Chart Details:
- Workers (in million): Dropped from around 600 in 2005 to below 500 in 2015, slightly recovering by 2020.
- Nominal construction investment (in JPY trillion): Showing a rising trend after 2015.
- Importance: Balancing investment vs. workforce can optimize resource allocation.
-
Labor Productivity:
- Construction productivity is 50% that of manufacturing.
-
Actual Days Off per Week:
- Only 5% take 2 days off per week.
- Breakdown:
- 1 day: 16.3%
- 1.25 days: 30.2%
- 1.5 days: 38.4%
- 1.75 days: 7.0%
- 2 days: 5.0%
- Undetermined: 2.7%
- Insight: More balanced time-off policies may improve morale and retention.
Needs
- Labor Saving in Non-Core Work:
- Importance: Automating or outsourcing non-core tasks can allow workers to focus on critical activities.
- Off-Site Remote Management:
- Relevance: Enables flexibility and reduces the necessity of being physically present.
- Breaking from Analog Management:
- Transition from experience/intuition to data-driven management.
Solution: SoftRoid - AI Remote Construction Management SaaS
- Features:
- Site data conversion and management via camera walkthrough.
- AI supervision for quality and site visit reduction.
- Benefits:
- Addressing labor shortages by optimizing existing resources.
- Accelerating transition to digital management techniques.
- Strategic Ideas:
- Emphasizing digital innovation to demonstrate value in construction.
- Immediate restructuring of management systems for productivity boosts.
Representative
- Mr. Hiroki Nozaki:
- Position: Representative Director/CEO of SoftRoid Inc.
- Perspective: Urgency in adopting digital tools for improving construction management.
Issues and Solutions in Employment of Foreign Workers
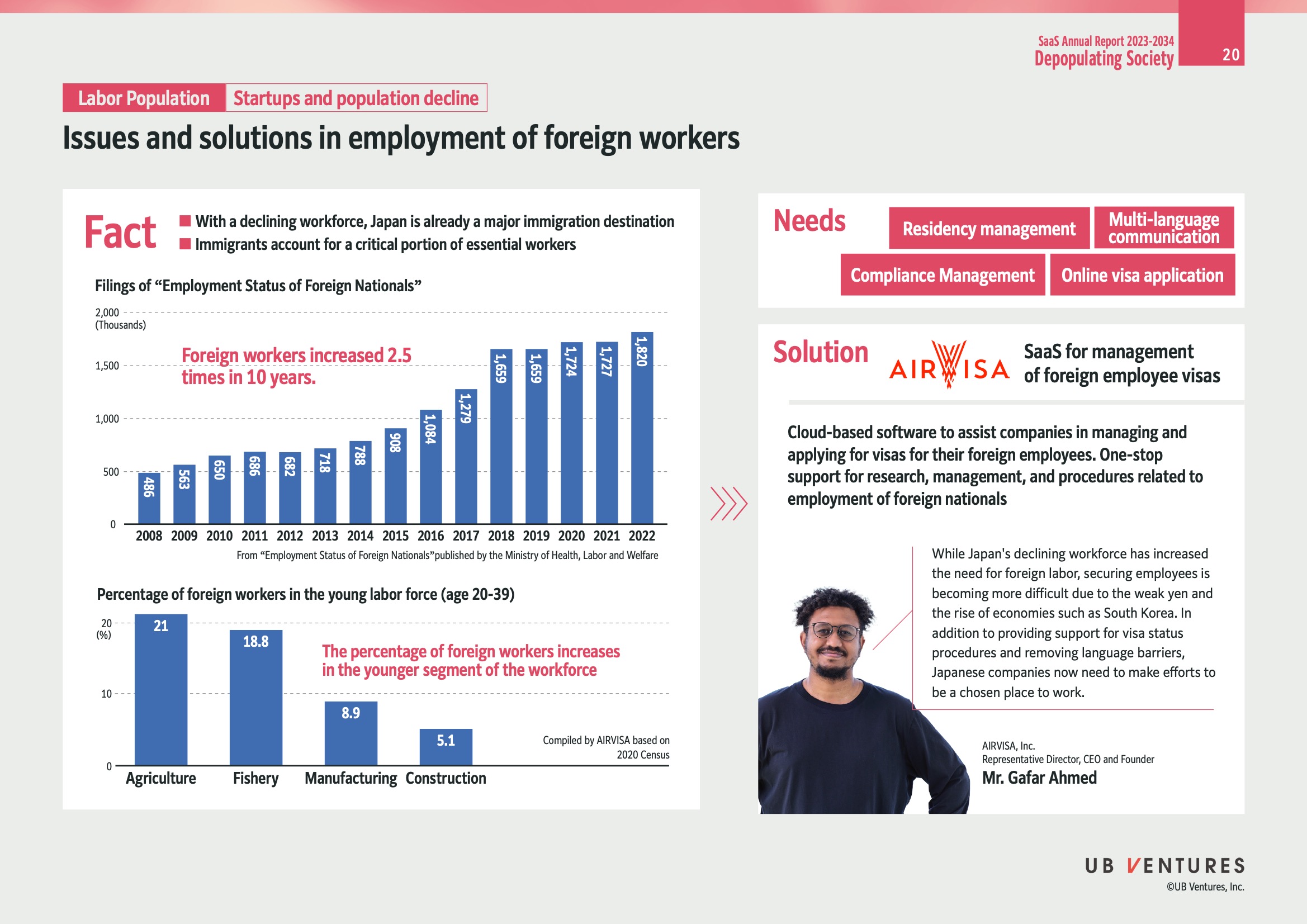
Overview
Japan is facing a shortage in its workforce, making it a major destination for immigration. Foreign workers play a crucial role, especially in essential sectors.
Key Facts
- Workforce Increase: Foreign workers have increased 2.5 times over the past decade.
- Essential Workers: Immigrants are vital in sectors like agriculture, fishery, manufacturing, and construction.
Chart Data
Filings of “Employment Status of Foreign Nationals”
| Year | Filings (Thousands) |
|---|---|
| 2008 | 486 |
| 2009 | 565 |
| 2010 | 650 |
| 2011 | 686 |
| 2012 | 682 |
| 2013 | 717 |
| 2014 | 788 |
| 2015 | 908 |
| 2016 | 1,083 |
| 2017 | 1,279 |
| 2018 | 1,460 |
| 2019 | 1,662 |
| 2020 | 1,724 |
| 2021 | 1,727 |
| 2022 | 1,820 |
Percentage of Foreign Workers (Age 20-39) in Young Labor Force
| Sector | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|
| Agriculture | 21 |
| Fishery | 18.8 |
| Manufacturing | 8.9 |
| Construction | 5.1 |
- Trend: The percentage of foreign workers is increasing, especially in younger segments of the workforce.
Needs Identified
Companies in Japan require effective management in the following areas:
- Residency Management
- Multi-language Communication
- Compliance Management
- Online Visa Application
Solution by AirVisa
Description
AirVisa offers cloud-based software to assist companies with:
- Managing and applying for visas for foreign employees.
- Providing a one-stop solution for research, management, and procedures related to employing foreign nationals.
Benefits
- Streamlined Process: Simplifies visa applications and compliance.
- Communication Support: Breaks down language barriers, making the workplace more inclusive.
Challenges
- Economic Competition: The declining workforce necessitates foreign labor, yet competition from rising economies like South Korea impacts recruitment.
- Workplace Choice: Japanese companies must distinguish themselves to attract talent.
Representative
- Company: AirVisa, Inc.
- Founder & CEO: Mr. Gafar Ahmed
Insight
With ongoing demographic challenges, integrating foreign workers efficiently is essential for sustaining economic growth in Japan. Solutions like AirVisa can address logistical barriers, but cultural and competitive factors remain significant obstacles.
Extended readings: