SQL Command Categories and Examples Cheat Sheet
SQL Cheatsheet
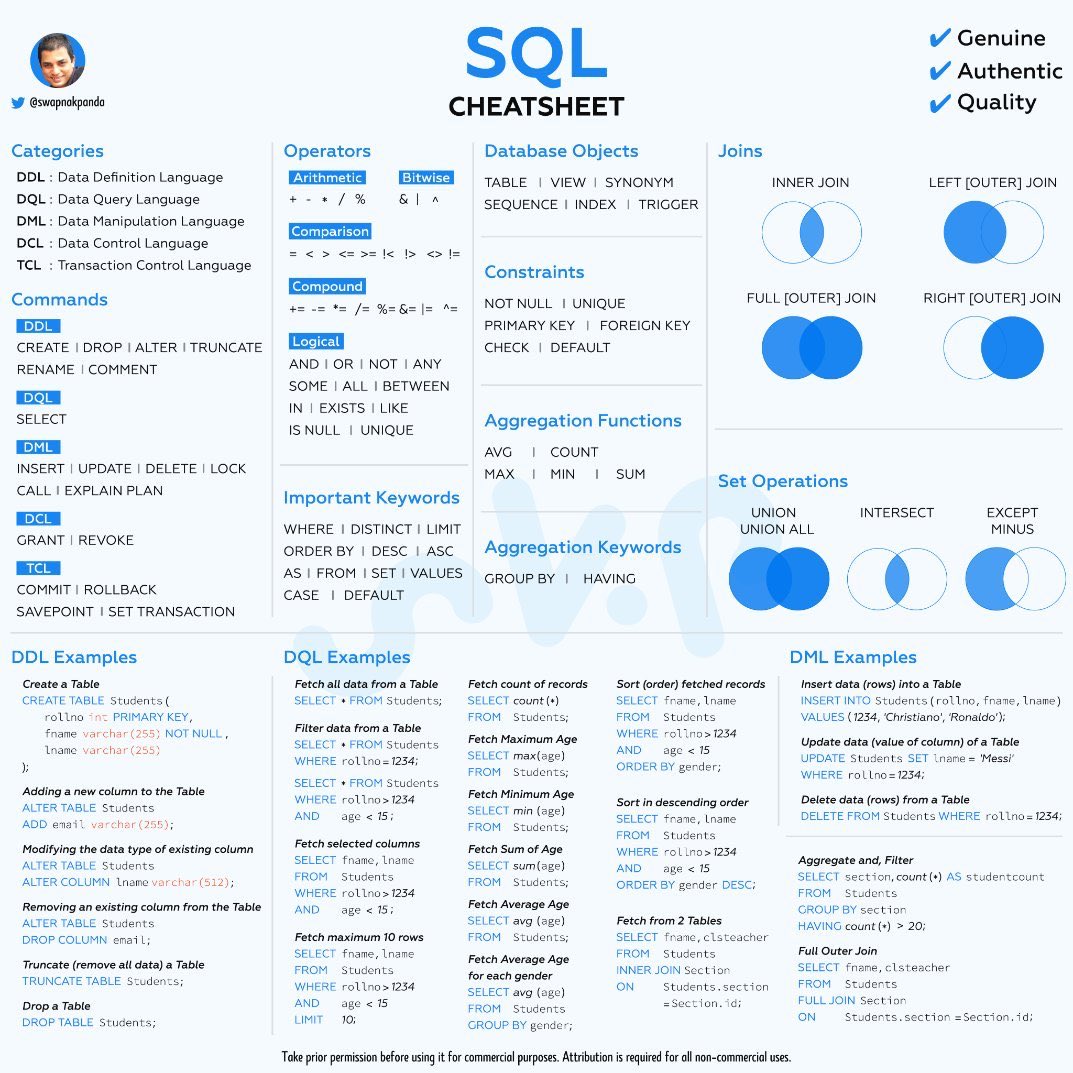
Categories
SQL commands are grouped into different categories based on their purpose:
-
DDL (Data Definition Language) :
- Used to define or alter database structures.
- Commands within DDL include:
CREATE,DROP,ALTER,TRUNCATE,RENAME,COMMENT.
-
DQL (Data Query Language) :
- Primarily focused on querying data within the database.
- Command:
SELECT.
-
DML (Data Manipulation Language) :
- Used to manipulate data stored in the database.
- Commands include:
INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE,LOCK,CALL,EXPLAIN PLAN.
-
DCL (Data Control Language) :
- Used to control access to data within the database.
- Commands:
GRANT,REVOKE.
-
TCL (Transaction Control Language) :
- Used to manage transactions within the database.
- Commands:
COMMIT,ROLLBACK,SAVEPOINT,SET TRANSACTION.
Commands
A quick overview of some of the commands and their uses:
-
DDL:
CREATE: Create a new table or object in the database.DROP: Delete objects from the database.ALTER: Modify an existing database object.TRUNCATE: Remove all records from a table.RENAME: Rename an existing database object.COMMENT: Add comments to the data dictionary.
-
DQL:
SELECT: Retrieve data from the database.
-
DML:
INSERT: Add new records to the table.UPDATE: Modify existing records.DELETE: Remove records.LOCK: Lock the table or object.CALL: Execute a PL/SQL or JAVA routine.EXPLAIN PLAN: Read the access path for a query.
-
DCL:
GRANT: Provide user access.REVOKE: Remove user access.
-
TCL:
COMMIT: Save transaction changes.ROLLBACK: Revert transaction changes.SAVEPOINT: Set a point within a transaction to which you can rollback.SET TRANSACTION: Change transaction settings like isolation level.
Operators
Different operators in SQL help perform various operations:
- Arithmetic:
+,-,*,/,%. - Bitwise:
&,|,^. - Comparison:
=,!=,<>,>,<,>=,<=. - Compound:
+,-,*,/,%. - Logical:
AND,OR,NOT,ANY,SOME,ALL,BETWEEN,IN,EXISTS,LIKE,IS NULL,UNIQUE.
Database Objects
Common objects in a database include:
- TABLE: Basic unit of data storage.
- VIEW: A virtual table based on a query.
- SYNONYM: An alias for a database object.
- SEQUENCE: Generates numeric values.
- INDEX: Provides quick access to rows.
- TRIGGER: Executes a predefined action.
Constraints
Constraints ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data within the database:
- NOT NULL
- UNIQUE
- PRIMARY KEY
- FOREIGN KEY
- CHECK
- DEFAULT
Aggregation Functions
These functions calculate statistics and summarize data:
AVG: Average value.COUNT: Number of values.MAX: Maximum value.MIN: Minimum value.SUM: Total sum of values.
Aggregation Keywords
GROUP BY: Groups rows sharing a property.HAVING: Filters grouped rows.
Joins
Joins combine rows from two or more tables:
- INNER JOIN: Returns records with matching values.
- LEFT (OUTER) JOIN: Returns all records from the left table and matched records from the right table.
- RIGHT (OUTER) JOIN: Returns all records from the right table and matched records from the left table.
- FULL (OUTER) JOIN: Returns all records from both tables.
Set Operations
Combine results from multiple queries:
- UNION: Combines results and eliminates duplicates.
- UNION ALL: Combines results without removing duplicates.
- INTERSECT: Returns records common to both queries.
- EXCEPT/MINUS: Returns records from the first query not found in the second.
Important Keywords
These keywords help refine SQL queries:
WHERE,DISTINCT,LIMIT,ORDER BY,DESC,ASC,AS,FROM,SET,VALUES,CASE,DEFAULT.
Examples of SQL Commands
1. DDL Examples
-
Create Table
CREATE TABLE Students (rollno int PRIMARY KEY,fname varchar(255) NOT NULL,lname varchar(255)); -
Adding a new column to the Table
ALTER TABLE StudentsADD email varchar(255); -
Modifying the data type of an existing column
ALTER TABLE StudentsALTER COLUMN lname varchar(512); -
Removing an existing column from the Table
ALTER TABLE StudentsDROP COLUMN lname; -
Truncate (remove all data) a Table
TRUNCATE TABLE Students; -
Drop a Table
DROP Table Students;
2. DQL Examples
-
Fetch all data from a Table
SELECT * FROM Students; -
Filter data from a Table
SELECT * FROM StudentsWHERE rollno = 1234; -
Fetch data containing specific records
SELECT * FROM StudentsWHERE gender = 'Female'; -
Fetch particular columns from Table and sort
SELECT fname, lnameFROM StudentsWHERE rollno = 1234AND gender = 'Female'ORDER BY fname; -
Fetch number of records
SELECT count(*)FROM Students; -
Fetch (order) fetched records
SELECT frame, lnameFROM StudentsWHERE rollno > 2345ORDER BY gender; -
Fetch Maximum Age
SELECT MAX(age)FROM Students; -
Fetch Minimum Age
SELECT MIN(age)FROM Students; -
Fetch Sum of record's Age
SELECT SUM(age)FROM Students; -
Fetch Average Age
SELECT AVG(age)FROM Students; -
Fetch Average Age grouped by section
SELECT section_id, AVG(age)FROM StudentsGROUP BY section_id;
3. DML Examples
-
Insert data (rows) into a Table
INSERT INTO Students (rollno, fname, lname)VALUES (1234, 'Christiano', 'Ronaldo'); -
Update data (value of column) of a Table
UPDATE StudentsSET lname = 'Messi'WHERE rollno = 1234; -
Delete data (rows) from a Table
DELETE FROM StudentsWHERE rollno = 1234; -
Aggregate, and Filter
SELECT section_id, COUNT(*)FROM StudentsGROUP BY section_idHAVING COUNT(*) > 20; -
Filter Inner Join
SELECT frame, classteacherFROM Students, SectionINNER JOIN SectionON Students.section_id=Section.id;
Reference: