**Title: Therapeutic Insights from Multi-Omics in TNBC Subtypes**
Multi-omics Analysis Identifies Therapeutic Vulnerabilities in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Subtypes
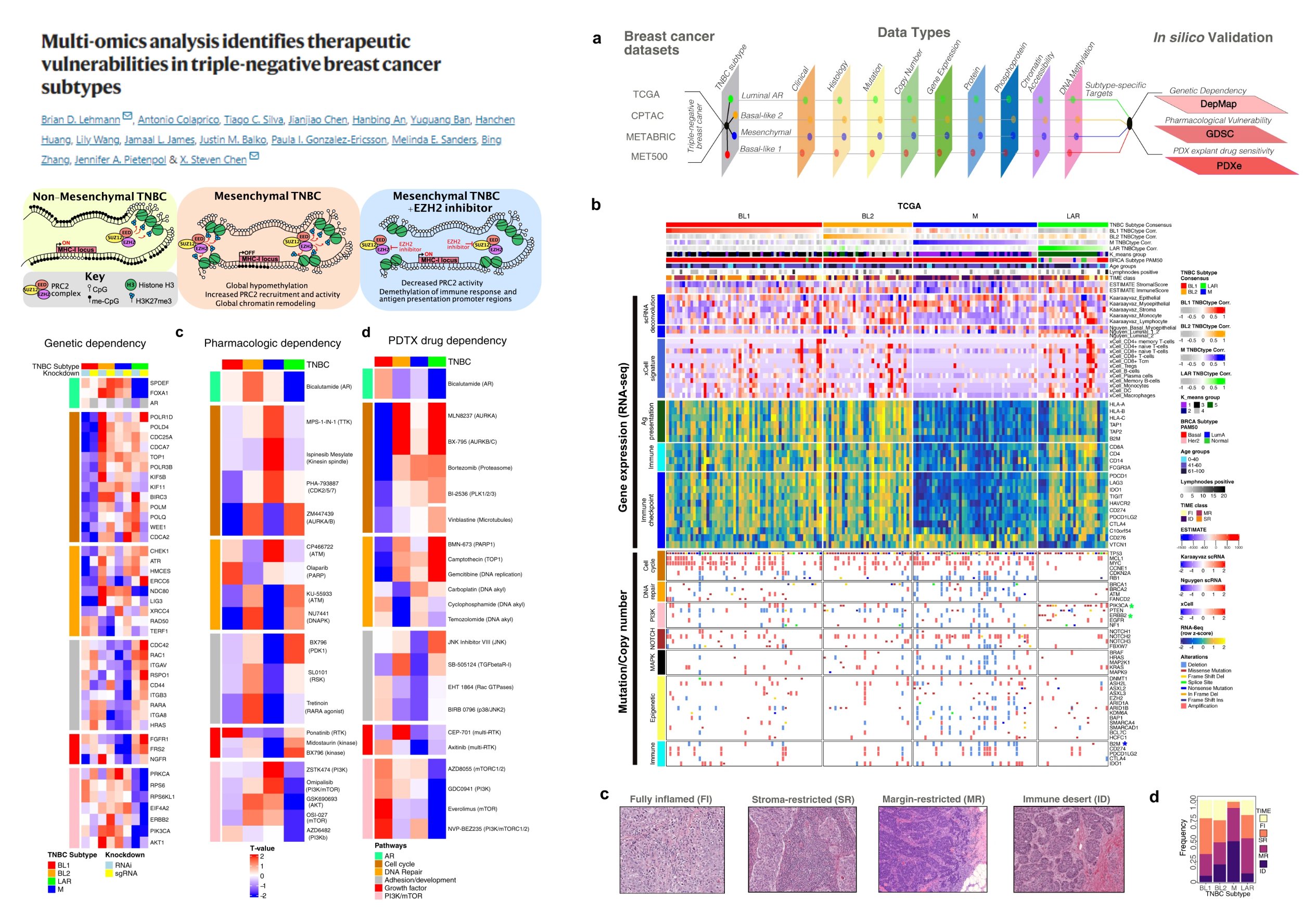
Overview
This image presents a multi-omics analysis to identify therapeutic vulnerabilities in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) subtypes.
Key Points
-
TNBC Subtypes Identification:
- Non-Mesenchymal TNBC
- Mesenchymal TNBC
- Mesenchymal TNBC + EZH2 Inhibitor Treatment
-
Methods and Data Types (a) :
- Breast Cancer Datasets:
- TCGA
- CPTAC
- METABRIC
- MET500
- Data Types:
- Transcriptomic
- Proteomic
- Clinical
- Metabolic
- Mutation
- RPPA
- Phosphoproteomic
- DNA Methylation
- This multi-omics approach allows comprehensive analysis spanning various biological layers, helping in identifying subtype-specific targets.
- Breast Cancer Datasets:
-
In silico Validation:
- Genetic Dependency
- Pharmacological Vulnerability
- PDXE (Patient-Derived Xenograft) Drug Sensitivity
Genetic Dependency Data (b)
Extracted Highlights:
| PDCX Genes | Dependency |
|---|---|
| SF3B1 | High |
| ACly | Moderate |
| PLK1 | Moderate |
| CCDN2 | Low |
- Genetic dependencies are visualized across various TNBC subtypes, aiding in spotting potential therapeutic targets for specific TNBC subtypes.
Pharmacologic Dependency Data (c)
Analyzed drugs and their efficacy:
| Drug Name | Pathway Targeted |
|---|---|
| Bicalutamide | AR |
| Nilotinib | ABL/PDGFR |
| BX-795 | PDK1 |
| Bortezomib | Proteasome |
| Vinblastine | Microtubules |
- This helps in understanding which drugs are more effective for different TNBC subtypes, guiding personalized treatment strategies.
PDXT Drug Dependency Data (d)
Analyzed drugs and their TNBC subtype-specific dependency:
| Drug Name | Pathway Targeted |
|---|---|
| Bicalutamide | AR |
| Nilotinib | ABL/PDGFR |
| BX-795 | PDK1 |
| Bortezomib | Proteasome |
| Vinblastine | Microtubules |
| SN38 | TOP1 |
| Gemcitabine | DNA Replication |
| Cyclophosphamide | DNA Alkylation |
- Provides insights into drug efficacy for patient-derived TNBC subtypes, promoting a personalized medicine approach based on individual tumor characteristics.
Tumor Microenvironments (c)
-
Tumour Samples:
- Fully Inflamed (FI)
- Stroma-Restricted (SR)
- Margin-Restricted (MR)
- Immune Desert (ID)
-
Depicts various histopathological appearances and immune contexts, crucial for understanding the tumor-immune microenvironment interactions, which can influence treatment responses.
Fraction of Tumor Types (d)
Bar graph showing distribution across TNBC subtypes (BL1, BL2, LAR, M):
-
BL1: Most tumors fall in this subtype.
-
BL2: Moderate number of samples.
-
LAR and M: Fewer samples.
-
Distribution helps visualize and quantify the prevalence of each subtype in the total sample studied, beneficial for identifying statistically significant patterns.
Conclusion
The multi-omics approach combined with in silico validation provides a comprehensive understanding of the TNBC landscape, guiding precise therapeutic interventions based on distinct molecular vulnerabilities across subtypes.
Reference: