"Exploring Effective Study Techniques and Mindsets"
how 2 study

General Description
- The image is an artistic sketch.
- It contains multiple sketched figures in various poses and activities.
- A large, bold title in the centre reads "how 2 study", suggesting a thematic focus on studying or learning.
- The artist's name, "dianats," is signed at the bottom.
Figures and Activities
- The figures are diverse in terms of poses and clothing styles.
- Some are sitting, some are standing, and others appear to be in motion, indicating different modes or methods of studying.
- The activities depicted include reading, writing, and collaborative work.
- There are both individual and group settings represented.
Artistic Style
- The sketch style is loose and dynamic, with an emphasis on movement and posture.
- The clothing and accessories depicted are contemporary, reflecting modern styles.
- The use of simple lines with minimal shading makes the figures stand out against the white background.
Concept and Theme
- The theme "how 2 study" suggests a guide or exploration of studying methods.
- The variety of poses and activities could symbolize different approaches to learning, such as solitary study, group projects, or interactive exercises.
- The light-hearted and casual nature of the sketches implies a message that studying can be approached in many different, flexible ways.
Additional Notes
- The lack of specific detail in the faces and backgrounds shifts focus to the poses and activities of the figures.
- The inclusion of different body types and styles promotes inclusivity and relatability, showing that studying is a universal activity.
Potential Applications
- Could be used as a visual aid in educational materials to illustrate various study techniques.
- May serve as inspiration for art students or artists interested in capturing dynamic human figures.
- Helpful for educators to demonstrate to students that studying and learning can be diverse in approach and not just limited to traditional methods.
Conclusion
- The image dynamically and artistically explores different methods and approaches to studying.
- The variety in figures and actions conveys a message of inclusivity and flexibility in educational practices.
Reference:
Understanding Efficient Study Techniques
-
Studying Misconceptions
- Illustration: Crossed-out image of a person struggling with study, depicted with a sad face.
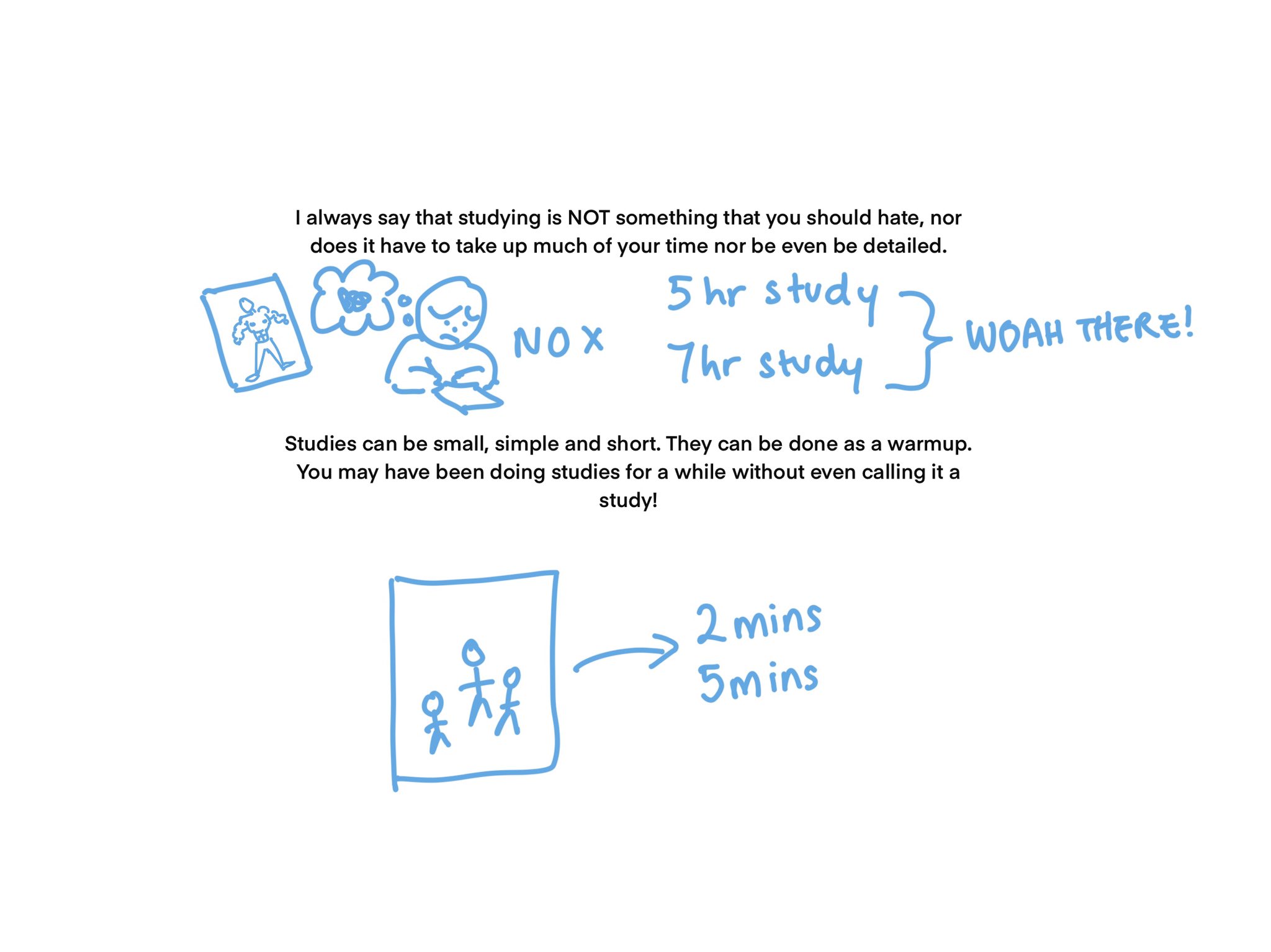
- Text: "I always say that studying is NOT something that you should hate, nor does it have to take up much of your time nor be even be detailed."
- Thoughts: Many people think that effective studying must be long and intensive, but this is not true.
- Additional Information: Introducing this point can help shift mindsets towards more balanced and enjoyable study methods.
-
Exaggerated Study Times
- Illustration: Text "5 hr study, 7 hr study" with the annotation "WOAH THERE!"
- Thoughts: Spending excessively long hours on studying is not sustainable or always necessary.
- Additional Information: Overdoing studying can lead to burnout and decreased productivity. It's more about studying smart rather than studying long.
-
Small, Simple, and Short Studies
- Illustration: Image of three stick figures, showing a small group activity.
- Text: "Studies can be small, simple, and short. They can be done as a warmup."
- Thoughts: Brief, focused study sessions can be highly effective and less overwhelming.
- Additional Information: Short study sessions can be more inclusive, helping those who may struggle with long periods of concentration to still study effectively.
-
Implication: Already Doing Studies
- Text: "You may have been doing studies for a while without even calling it a study!"
- Thoughts: Everyday activities and small practices can count as studying.
- Additional Information: Recognizing these small efforts can give a motivational boost, reinforcing the idea that progress might be happening without formal study sessions.
-
Recommended Short Study Durations
- Illustration: Study session depicted with a clock indicating "2 mins, 5 mins".
- Thoughts: Even a few minutes can be productive.
- Additional Information: Short bursts of study time can fit seamlessly into daily routines, making study sessions less daunting and more manageable.
General Theme:
- Shifting Study Mindsets: The main theme is about transforming the perception of studying from a burdensome task to an easy, integrated part of daily life.
- Encouraging Efficiency: Emphasis on the fact that the quality and consistency of studying often matter more than the total time spent.
Reference:
Understanding What a Study Is
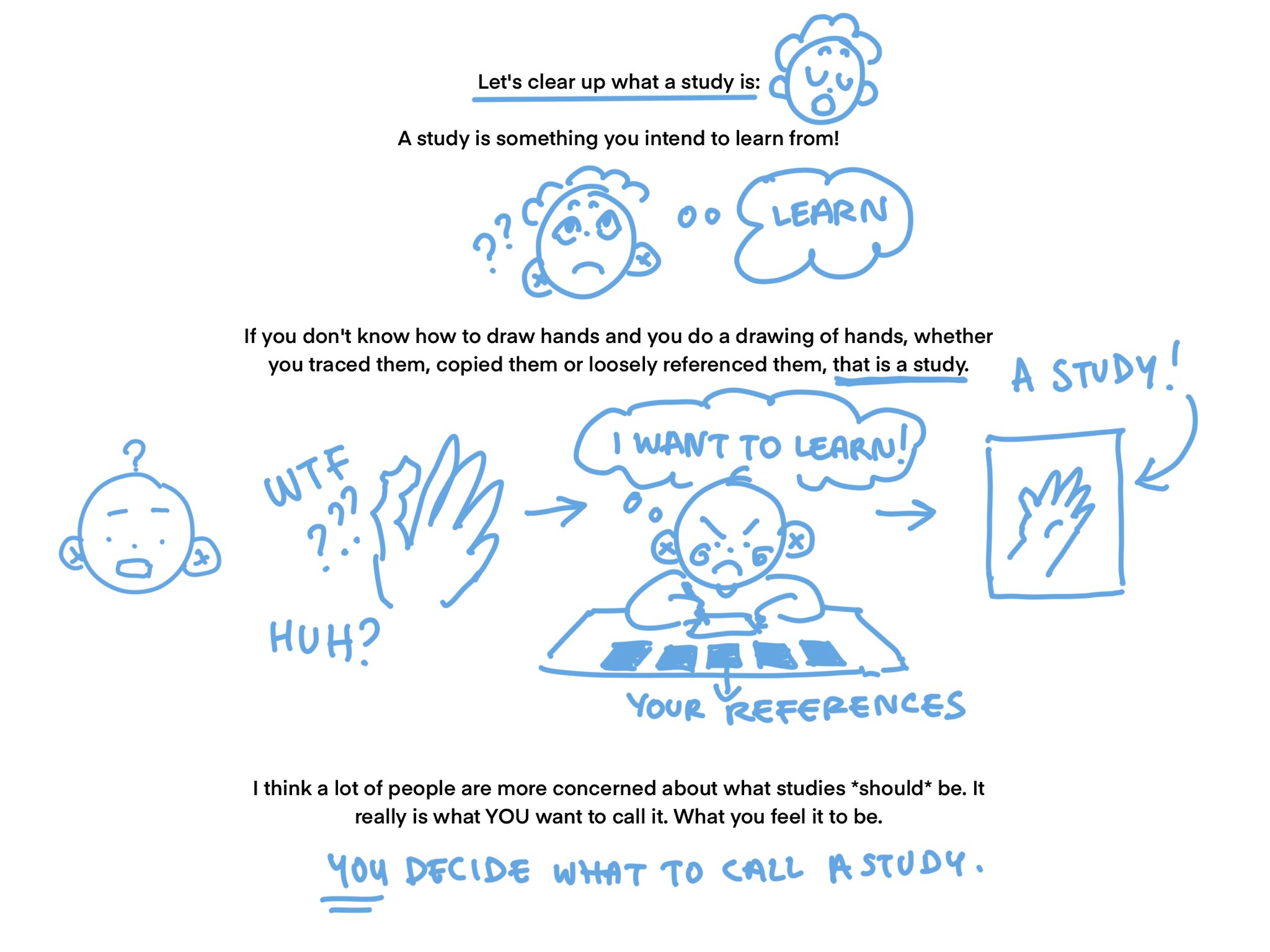
A Study Is What You Intend to Learn From
- Definition of Study:
- A study is an activity or a piece of work intended to help you learn something new.
- For example, if you don't know how to draw hands and you do a drawing of hands (whether you trace, copy, or loosely reference them), that process is considered a study.
- Process of Study:
- Confusion or Lack of Knowledge: Start with not knowing how to draw hands.
- Intent to Learn: Have a desire or intention to learn how to draw.
- References and Practice: Use references, trace, or copy hand drawings to understand the form and structure better.
- Result: The drawn hand or the practice sheet becomes the output of your study.
Perspective on Studies
-
Personal Definition:
- Many people worry about what a study 'should' be.
- The image emphasizes that a study is what you want it to be, what you feel it to be.
- The definition is subjective and is based on what you decide to call a study.
-
Encouragement:
- The message encourages artists or learners to define their own studies based on their learning needs and intentions.
Visual Elements in the Image
-
Expressive Illustrations:
- Confusion and desire to learn are depicted using expressive faces.
- The process from confusion to learning intention to drawing a study is shown with a series of simple, clear illustrations.
-
Learning Emphasis:
- Emphasizes that intention to learn (signified by “I WANT TO LEARN!”) turns any effort (including tracing, copying, etc.) into a valid study.
- Final drawing (whether a trace, copy, or referenced drawing) is considered a study if it helped in the learning process.
Conclusion
- Autonomy in Learning:
- You decide what to call a study, based on your own learning goals and processes.
- This note aims to provide clarity on what constitutes a study in art or any other learning activity.
Reference:
Diferencia entre estudiar y practicar
-
Definición de Estudio y Práctica:
-
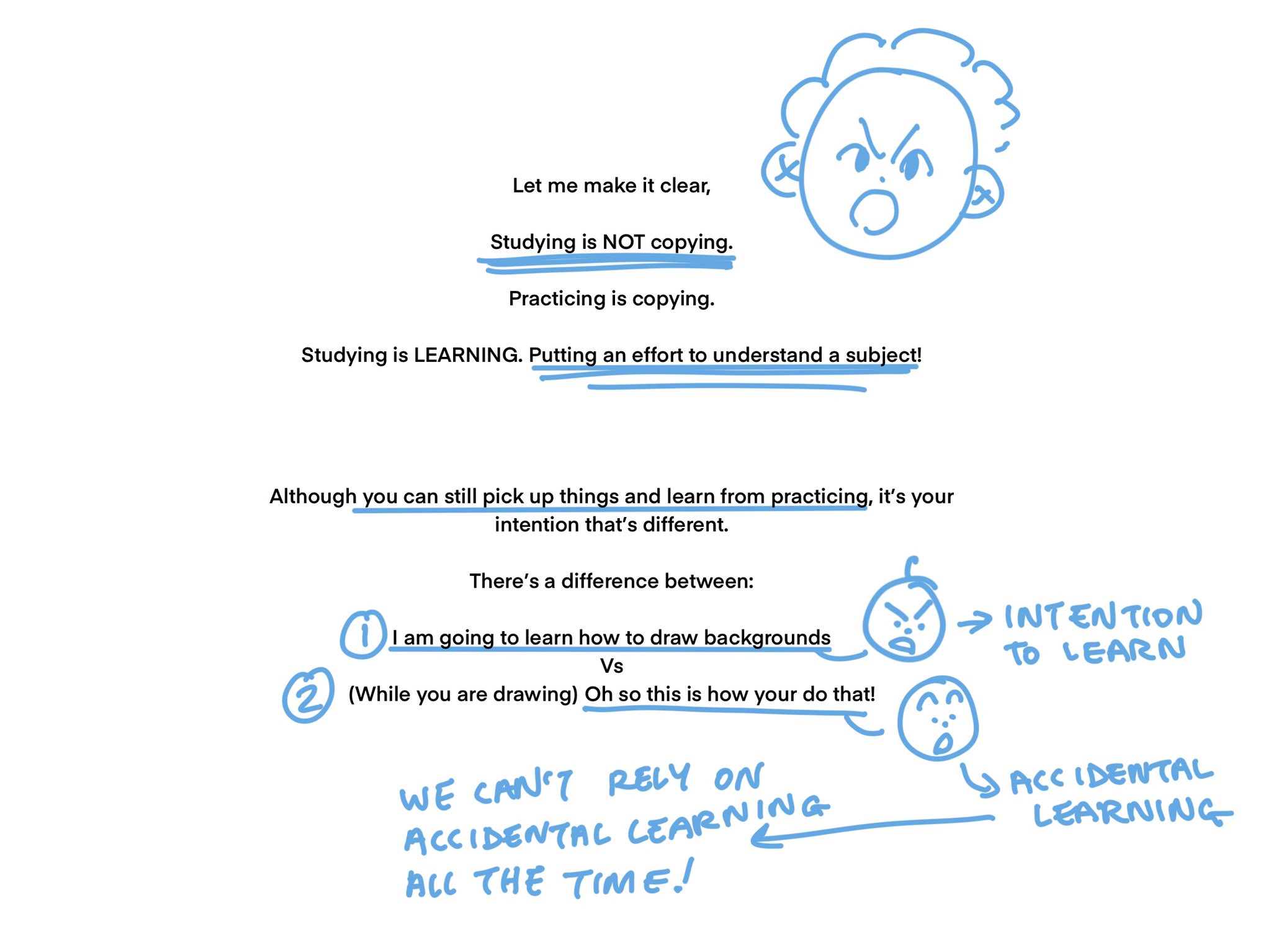
Estudiar NO es copiar: Estudiar implica un esfuerzo consciente para entender un tema.
-
Practicar es copiar: Practicar puede involucrar la repetición de acciones sin una guía consciente para el aprendizaje.
Pensamiento: El estudio se centra en la comprensión profunda, mientras que la práctica se puede centrar en la repetición automática de habilidades.
-
-
Intención en el Aprendizaje:
- Estudio (Intención Activa): "Voy a aprender cómo dibujar fondos."
- Se enfoca en aprender deliberadamente una habilidad específica.
- Práctica (Aprendizaje Accidental): (Mientras estás dibujando) "¡Ah, así es cómo haces eso!"
-
El aprendizaje ocurre de manera incidental sin intención previa.
-
Pensamiento: La intención activa impulsa el aprendizaje profundo, mientras que el aprendizaje accidental podría ser insuficiente a largo plazo.
- Estudio (Intención Activa): "Voy a aprender cómo dibujar fondos."
-
Importancia del Estudio Intencionado:
-
No se puede depender únicamente del aprendizaje accidental.
-
El aprendizaje intencionado asegura una comprensión y crecimiento consistentes y estructurados.
Ideas: Es beneficioso establecer metas claras de aprendizaje y enfocarse en la comprensión en lugar de depender solo del descubrimiento casual durante la práctica.
-
-
Diferencias Claves:
- Estudiar:
- Poner esfuerzo consciente.
- Focalización en entender.
- Practicar:
- Copiar y repetir.
- Aprender incidentalmente.
Actividad Característica Ejemplo Estudiar Intención de aprender "Voy a aprender cómo dibujar fondos" Practicar Accidental (Mientras dibuja) "¡Ah, así es cómo se hace eso!" Conclusión: Para un desarrollo eficaz y sostenido de habilidades, es esencial combinar la práctica con un estudio estructurado e intencional.
- Estudiar:
Reference: