Human Population Bottlenecks and Evolutionary Impact
An Overview of Human Population Bottlenecks and Evolutionary History
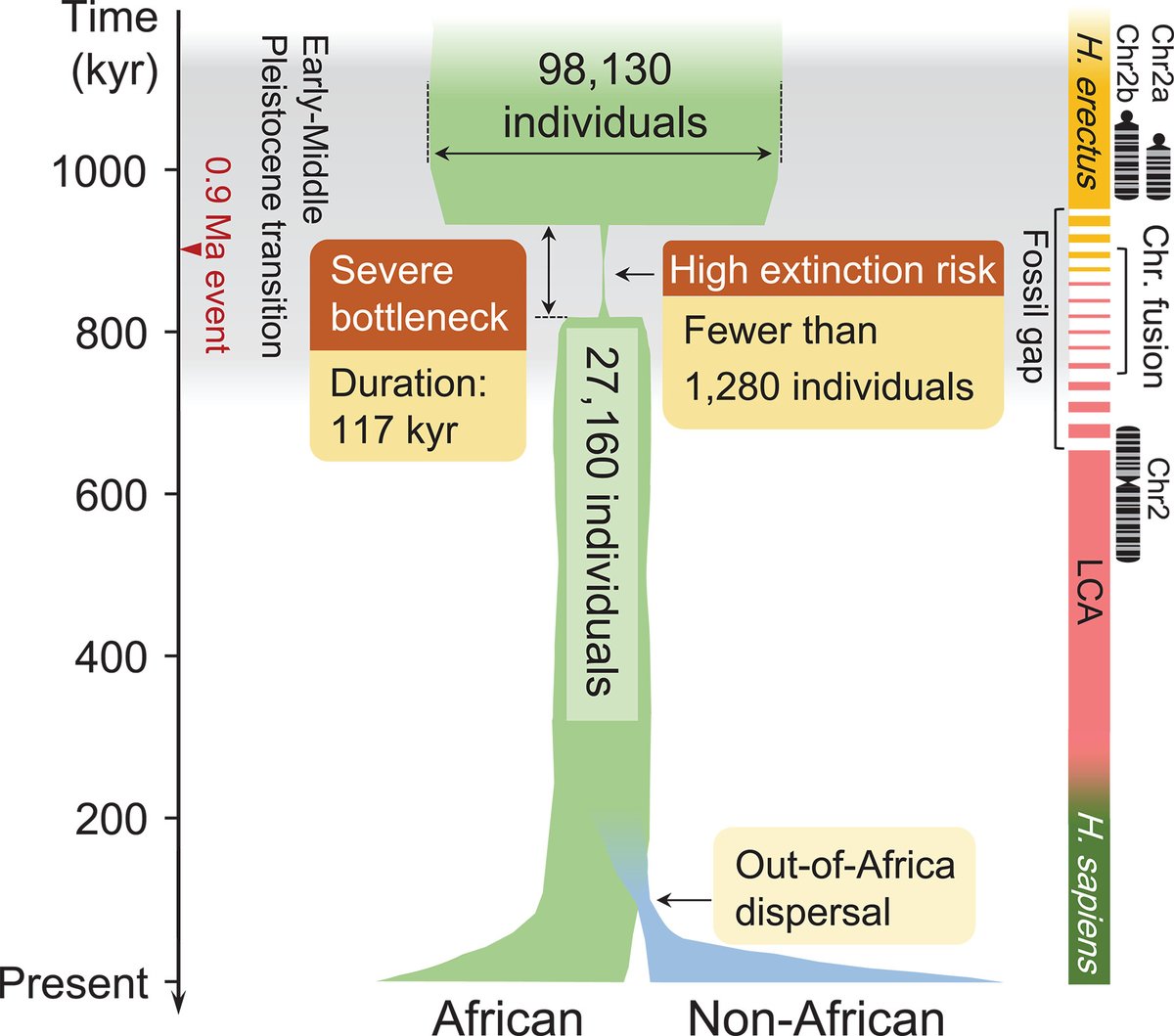
Severe Bottleneck and Population Size
-
Initial Population Size (Before Bottleneck):
- Around 98,130 individuals.
- This represents the estimated number of human ancestors during the early-middle Pleistocene transition before the bottleneck event.
-
Severe Bottleneck:
- Duration: 117 Kyr
- Population Size During Bottleneck:
- Decreased significantly to around 27,160 individuals.
- High Extinction Risk:
- Population declined to fewer than 1,280 individuals, posing a critical risk of extinction.
- The severe reduction and sustained low population size highlight the vulnerability of early human populations to environmental changes or other pressures.
Out-of-Africa Dispersal
- Following the bottleneck, the population diversified:
- African Population: Continues with the majority of the surviving individuals.
- Non-African Population: Represents the dispersal of humans out of Africa.
- This dispersal led to a divergence in genetic lines and the spread of humans across different continents.
Timeline and Evolutionary Events
-
0.9 Ma Event:
- Marked on the timeline at 900 Kyr.
- Indicates a significant climatic or environmental event coinciding with the bottleneck.
-
Early-Middle Pleistocene Transition:
- An important period in human evolution and climatic changes.
- The population bottle experienced during this time highlights evolutionary pressures that shaped modern human genetics.
Evolutionary Lineages
- H. erectus:
- Lineage split leading to the emergence of early humans.
- H. sapiens:
- Denotes the evolution and emergence of modern humans.
Genetic Insights
-
Chromosomal Fusion:
- Illustration of Chromosome 2 fusion event (Chr2a and Chr2b merging into Chr2), notable in human evolution.
- Highlights genetic evidence that supports these evolutionary processes.
-
Fossil Gap:
- Represents gaps in the fossil record, indicating periods with limited or no fossil evidence.
-
LCA (Last Common Ancestor):
- Represents the point of the last shared ancestor between modern humans and other hominins.
- Critical for understanding the divergence in the human lineage.
Key Phases Highlighted
- Pre-bottleneck: High population and early human diversity.
- Bottleneck and Low Population: Critical period of vulnerability and significant population reduction.
- Post-bottleneck Diversification: Recovery and eventual migration out of Africa, spreading globally.
Each of these phases provides valuable insights into the evolutionary history, genetic diversity, and survival challenges of early humans. The bottleneck event, in particular, underscores the importance of understanding environmental impacts on human evolution.
Reference:
reich.hms.harvard.edu
[PDF] Insights into human genetic variation and population history from ...
primo.lib.umn.edu
Admixture into and within sub-Saharan Africa - eLife
faculty.eeb.ucla.edu
[PDF] Spatial patterns of variation due to natural selection in humans