Use-inspired Workflows in AI Development and Community Engagement
Use-inspired (Developmental) Workflows: A General Schematic
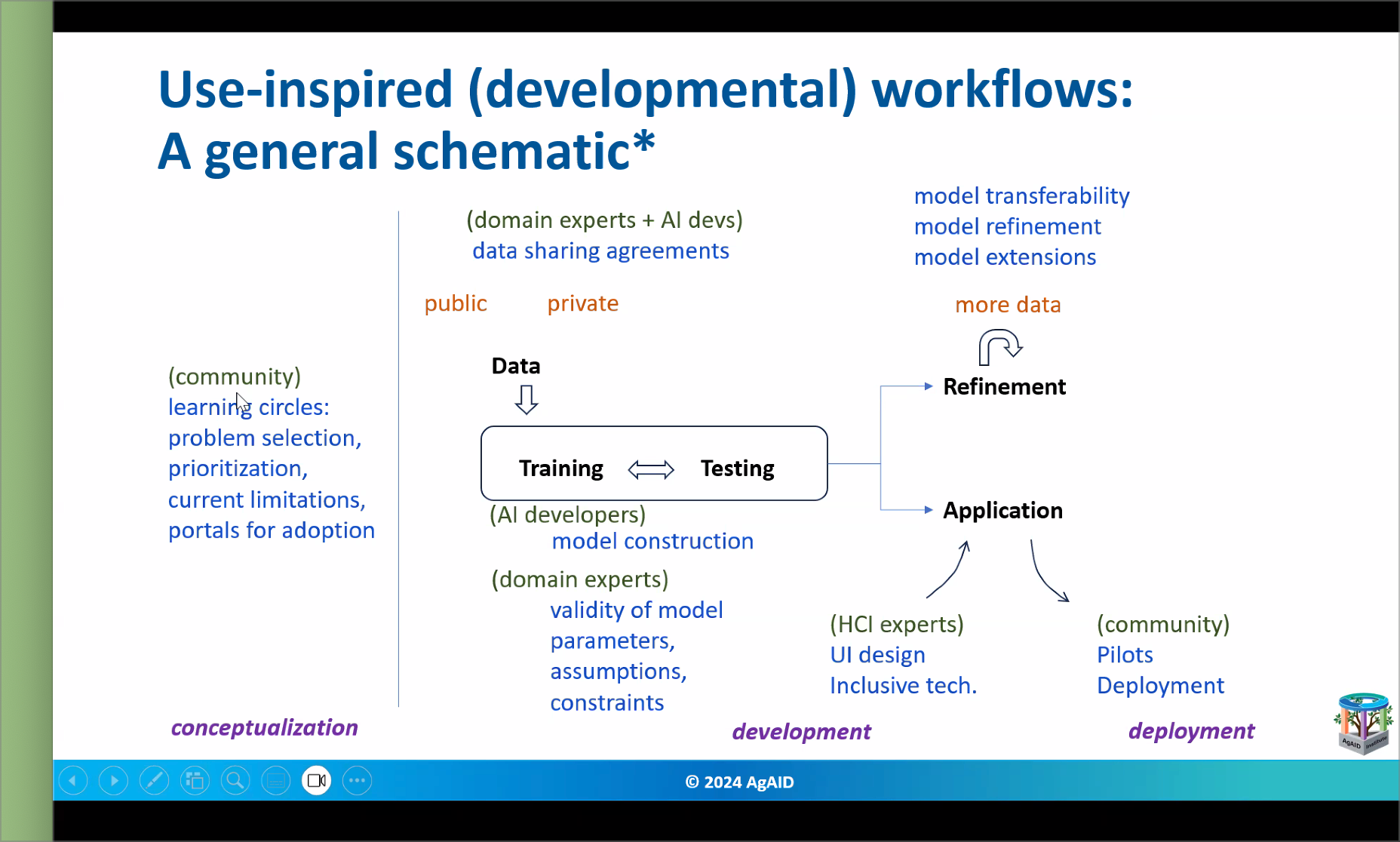
Key Components of the Workflow
-
Community Involvement
- Emphasizes the role of community in shaping AI projects.
- Learning Circles: Groups that collaboratively select problems, prioritize them, acknowledge current limitations, and provide portals for adoption to ensure inclusivity and practical problem-solving.
-
Data Management
- Public vs. Private Data: Highlights the importance of data sharing agreements between domain experts and AI developers, facilitating the use of both public and private datasets in training and testing phases.
-
Development Stages
- Training and Testing: An iterative process where data is fed into models for both training and testing, ensuring the validity and effectiveness of the model.
- AI Developers focus on model construction.
- Domain Experts verify the validity of model parameters, assumptions, and constraints.
- Training and Testing: An iterative process where data is fed into models for both training and testing, ensuring the validity and effectiveness of the model.
-
Model Refinement
- Feedback loop for continuous improvement of the models through:
- Model Transferability: Ensuring models can be applied to different datasets or scenarios.
- Model Refinement: Enhancing model accuracy over time.
- Model Extensions: Adapting models to incorporate new features or data sources.
- Feedback loop for continuous improvement of the models through:
-
Application
- Ultimately, refined models are applied in real-world scenarios. This includes considerations for:
- HCI Experts: Focus on user interface design and inclusive technology to ensure accessibility.
- Community: Involvement in pilots and deployment of applications to guarantee they meet user needs.
- Ultimately, refined models are applied in real-world scenarios. This includes considerations for:
Process Overview
The schematic illustrates a workflow that follows a circular path:
- Conceptualization: Initial problem identification and community engagement.
- Development: The main phase involving data handling, model training, and testing.
- Deployment: Final implementation and community feedback loops to refine further based on real-world usage.
This workflow emphasizes collaboration across various stakeholders—from domain experts and AI developers to community members—to create holistic and effective AI solutions.
Reference:
AI Apps: Ship of Theseus Paradox

-
Thought Experiment: The Ship of Theseus paradox raises the question of identity in objects. It asks whether an object remains the same if all its components are replaced over time.
- Implication: This paradox can be applied to AI as components of AI systems, such as algorithms, datasets, and infrastructure, may undergo constant changes while the system aims to retain its identity and purpose.
-
AI Components Similarity: Just as the planks of a ship need to be replaced, AI components (like algorithms or data) also require frequent updates and replacements.
- Consideration: This necessitates a strategic approach to manage these changes, ensuring that the overall functionality and objectives of the AI system remain intact despite the ongoing modifications.
-
Strategic Management: Projects in AI must devise strategies for component management that address replacement in a way that maintains continuity and effectiveness.
- Framework Suggestion: Implementing a systematic approach that includes tracking changes, assessing impact, and maintaining quality control can help manage the “replacement” process effectively.
-
Broader Application: The Ship of Theseus can relate to various fields where systems evolve over time, prompting discussions about identity and continuity in long-term projects.
- Discussion Points: This can lead to inquiries about how organizations evolve, the relevance of legacy technologies, and the importance of maintaining operational coherence through transitions.
These notes serve as a foundational exploration of the image's themes, linking philosophical concepts to practical AI project management.
Reference:
Notes on Universal Screening and Intervention Framework
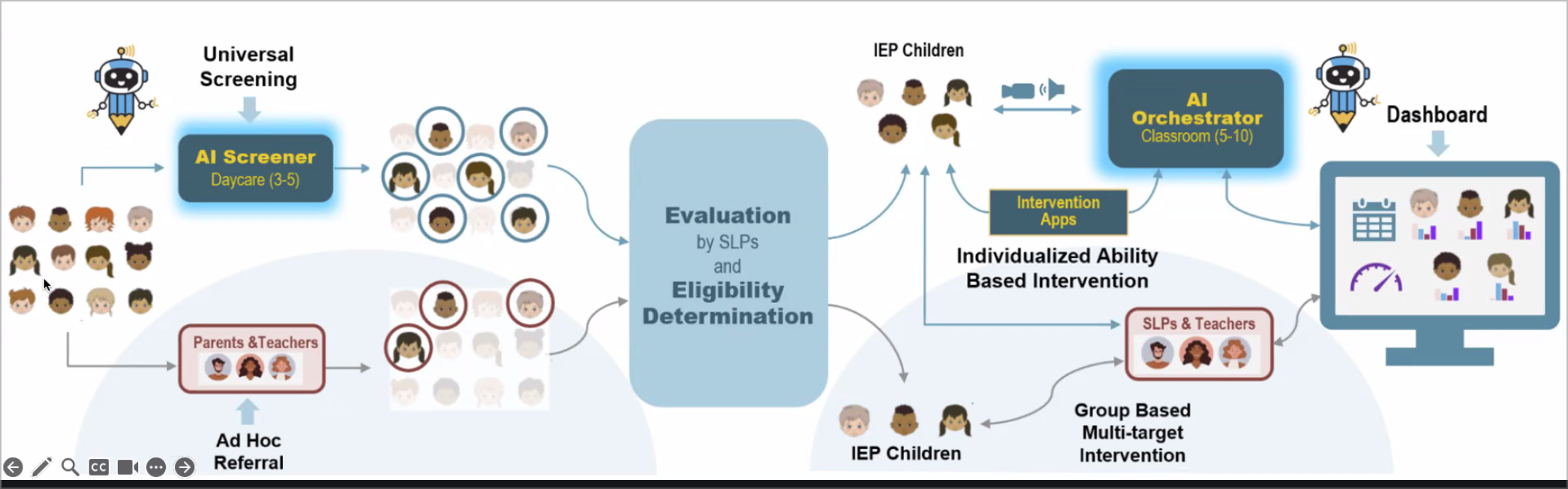
Universal Screening
- Purpose: The process initiates with a universal screening designed to identify children aged 3-5 in daycare settings who may require further evaluation.
- Thoughts: This early identification can significantly aid in addressing developmental delays and behavioral issues before they become more pronounced.
AI Screener
- Function: An AI-driven tool assesses children's developmental progress.
- Idea: Utilizing AI can streamline the screening process, making it more efficient and potentially more accurate than traditional methods.
Parental and Teacher Involvement
- Connection: Parents and teachers are integral to the screening process, as their insights can lead to ad hoc referrals for additional assessment.
- Additional Information: Engaging families and educators ensures a comprehensive understanding of a child’s needs and behavior in different environments.
Evaluation and Eligibility Determination
- Process: Following screening, qualified Speech Language Pathologists (SLPs) evaluate children to determine eligibility for interventions.
- Thoughts: This step is critical in ensuring that children who require support receive the appropriate services tailored to their needs.
Interventions
- Individualized Ability-Based Intervention: Tailored strategies utilizing intervention apps focus on the specific abilities and requirements of each child.
- Reflection: Personalization in interventions enhances engagement and effectiveness, supporting diverse learning needs.
AI Orchestrator
- Role: For children aged 5-10, an AI orchestrator manages the classroom environment to facilitate targeted interventions.
- Consideration: Integrating tech into classroom management can improve engagement and allow for real-time adjustment of educational strategies.
Dashboard for Monitoring
- Functionality: A dashboard compiles data for SLPs and teachers to monitor progress and refine strategies.
- Insight: Visual data representation can assist educators in making informed decisions regarding instructional adjustments and interventions.
Group-Based Multi-Target Interventions
- Approach: IEP (Individualized Education Program) children may benefit from group-based interventions, allowing for collaborative learning experiences.
- Benefit: This fosters social skills and peer interactions while addressing academic needs in a supportive environment.
Summary
The image outlines a comprehensive framework for early intervention in educational settings, emphasizing the integration of AI technology, parental engagement, and tailored intervention strategies to address the needs of young children effectively. Such structured approaches can help in identifying and supporting children with diverse developmental needs efficiently.
Reference: