"Key Anatomical Landmarks of the Female Body"
Anatomical Landmarks of the Human Body
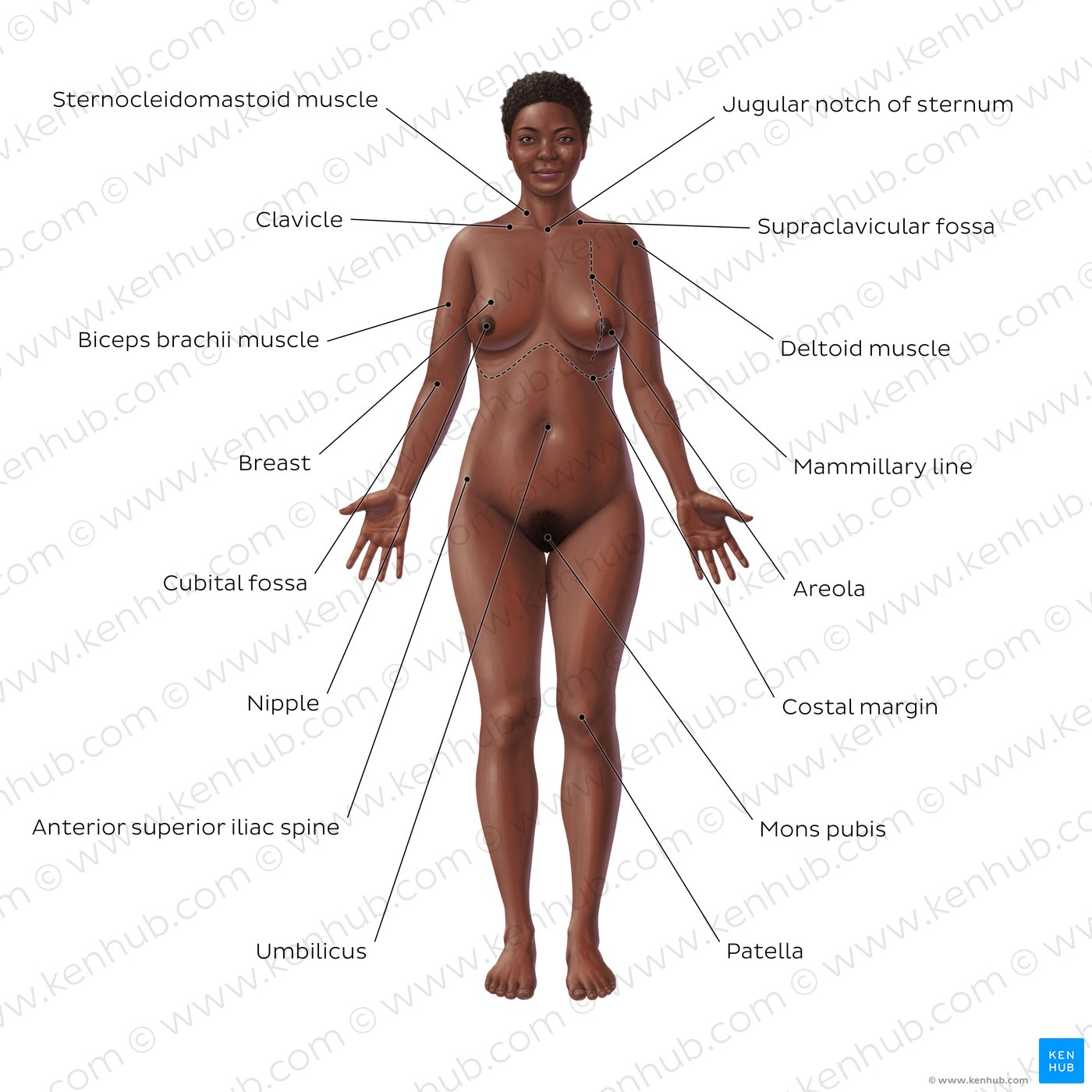
This image illustrates various anatomical landmarks on a female body. Below are notes elaborating on each identified structure.
Notes
-
Sternocleidomastoid Muscle
- Thoughts: This muscle plays a crucial role in neck movement.
- Additional Information: It helps in turning the head and bending the neck and is commonly used in activities involving head rotation.
-
Clavicle
- Thoughts: The collarbone connects the arm to the body.
- Additional Information: It is a key structure in shoulder mechanics and serves as a strut that stabilizes the shoulder.
-
Biceps Brachii Muscle
- Thoughts: A vital muscle for arm movement.
- Additional Information: It's responsible for flexing the elbow and rotating the forearm, making it essential for many upper body actions.
-
Cubital Fossa
- Thoughts: This triangular region is important clinically.
- Additional Information: It's where the medical professional can palpate the brachial artery and median nerve; often used for venipuncture.
-
Breast
- Thoughts: A primary feature of female anatomy.
- Additional Information: Breasts contain glandular tissue for milk production and are also a secondary sex characteristic.
-
Nipple
- Thoughts: Central to breast function.
- Additional Information: The nipple contains openings for milk ducts, allowing for breastfeeding.
-
Areola
- Thoughts: The circular pigmented area around the nipple.
- Additional Information: It contains small glands that provide lubrication during breastfeeding.
-
Jugular Notch of Sternum
- Thoughts: A landmark for the jugular vein.
- Additional Information: Useful for locating central veins during medical procedures.
-
Supraclavicular Fossa
- Thoughts: This hollow area above the clavicle is significant in physical examinations.
- Additional Information: It can indicate possible health issues if swollen.
-
Deltoid Muscle
- Thoughts: The prime mover for shoulder abduction.
- Additional Information: Essential for lifting and raising the arm, commonly targeted in exercise.
-
Mamillary Line
- Thoughts: An important landmark for breast anatomy.
- Additional Information: It runs horizontally around the body and is significant in breast surgery.
-
Costal Margin
- Thoughts: Important for the protection of internal organs.
- Additional Information: The lower border of the rib cage, important for identifying organs during physical examinations.
-
Mons Pubis
- Thoughts: The fatty area located above the pubic bone.
- Additional Information: Provides protection to the underlying bone and contains pubic hair after puberty.
-
Patella
- Thoughts: Commonly known as the kneecap.
- Additional Information: It protects the knee joint and improves leverage for thigh muscles during leg movements.
-
Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
- Thoughts: A bony prominence of the ilium.
- Additional Information: Often used as a landmark for assessment of pelvic alignment and anatomy.
-
Umbilicus
- Thoughts: Commonly referred to as the navel or belly button.
- Additional Information: It marks the spot where the umbilical cord was attached during fetal development, indicating a vital connection to maternal nutrients and oxygen.
Reference:
www.medicalnewstoday.com
Female anatomy: Body parts, their functions, and diagram
www.gettyimages.com
602 Female Anatomy Diagram Stock Photos & High-Res Pictures
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis: Female Internal Genitals - NCBI