Introduction to Design Thinking Principles and Applications
An Introduction to World of Design Thinking

Overview
- Title: An Introduction to World of Design Thinking
- Presented by: Dr. B.S.C. Ranjan
Key Concepts
What is Design Thinking?
- Definition: Design Thinking is a human-centered approach to innovation that integrates the needs of people, the possibilities of technology, and the requirements for business success.
- Purpose: It aims to solve complex problems and find desirable solutions for clients.
Core Principles
-
Empathy: Understanding the user’s needs and experiences.
- Involves direct interaction and observation of users.
- Important for creating customer-centric products.
-
Ideation: Generating a wide range of ideas.
- Encourages free thinking and creativity.
- Utilizes brainstorming sessions to explore multiple solutions.
-
Prototyping: Building tangible models of ideas.
- Helps in visualizing potential solutions.
- Allows for experimentation and testing.
-
Testing: Evaluating prototypes for feedback.
- Provides insights into user preferences and behaviors.
- Iterative process to refine solutions.
Benefits of Design Thinking
- Promotes innovation and creative problem-solving.
- Enhances user satisfaction and product usability.
- Facilitates cross-disciplinary collaboration.
Applications
- Widely used in business strategy, product development, and customer experience design.
- Can be applied to any field that requires problem-solving and creativity.
Additional Resources
- Books:
- "Change by Design" by Tim Brown
- "The Design of Everyday Things" by Don Norman
- Courses:
- IDEO U Design Thinking Course
- Stanford d.school online resources
Conclusion
Design Thinking is a valuable framework for teams aiming to deliver innovative solutions that truly meet user needs. By integrating user feedback and iterative processes, it ensures that solutions are not only creative but also practical and sustainable.
Extended readings:
New Product Development

Key Points
-
Importance of Product Innovation
- Product innovation involves developing new and improved products and services.
- It is crucial for the survival and prosperity of modern corporations.
- Insight: Innovation drives competitive advantage and helps companies adapt to market changes.
-
Impact of New Products
- Products launched in the last three years account for:
- 27% of company sales
- 25% of company profits
- Source: Buffoni et al. 2017
- Insight: New products significantly contribute to a company's revenue and profitability, emphasizing the importance of continuous innovation.
- Products launched in the last three years account for:
-
Failure Rates of New Products
- Approximately 40% of launched products fail.
- This contrasts with the commonly cited, but exaggerated, failure rates of 80-90%.
- Source: Castellion and Markham 2013
- Insight: Understanding realistic failure rates can help businesses set more accurate expectations and develop better risk management strategies.
Additional Information
-
Product Innovation Definition
- Refers to the creation and introduction of goods and services that are either entirely new or significantly improved.
- Includes improvements in technical specifications, components, materials, or software in the products.
-
Challenges in Product Development
- High failure rates can be due to inadequate market research, poor product-market fit, or lack of unique value propositions.
-
Strategies for Successful Product Development
- Conduct thorough market research to understand consumer needs.
- Implement design thinking principles to iterate based on user feedback.
- Focus on creating a unique value proposition to stand out in the market.
Understanding the dynamics of new product development can greatly benefit businesses aiming for growth and innovation.
Extended readings:
High Failure Rates in New Product Development

Key Statistics and Insights
-
Low Commercial Success Rate
- Out of every 7 to 10 new product (NP) concepts, only one typically becomes a commercial success (Barczak et al., 2009).
- Insight: This highlights the inherent challenges and risks associated with product development. It's crucial for companies to have robust evaluation and selection processes to identify viable product ideas early on.
-
Financial and Timely Launch Challenges
- Only 53% of NP projects meet their financial objectives.
- 44% of projects are launched on time (Cooper and Edgett, 2012; Edgett, 2011).
- Insight: Achieving financial goals and timely launches are significant hurdles. Companies may benefit from agile methodologies and effective project management practices to improve these metrics.
-
Low Profit Objective Achievement
- Merely 13% of firms achieve their annual profit objectives with new products (Cooper, 2019).
- Insight: This indicates a need for better alignment of product strategies with market demands and cost management. Market research and forecasting can play pivotal roles here.
-
Performance Variances Among Firms
- There is a broad variance in performance metrics, with the top 20% of firms significantly outperforming others in NP development.
- Insight: Studying these top-performing firms can provide valuable insights into best practices and strategies that lead to successful product development and commercialization.
Additional Considerations
-
Importance of Monitoring and Adjustment
- Regular assessment and flexibility in the NP process can help in making timely adjustments, boosting the likelihood of success.
- Leveraging feedback loops during development phases ensures alignment with customer expectations and market conditions.
-
Strategic Resource Allocation
- Efficient use of resources, including time, money, and talent, is critical. Prioritizing projects with the highest potential can improve overall success rates.
-
Adopting Innovative Methodologies
- Incorporating design thinking and other innovative methodologies can foster creativity and user-centered design, leading to better product-market fit.
Understanding these dynamics is essential for businesses aiming to sustain growth and competitive advantage through new product development.
Extended readings:
Design Thinking

Overview
- Definition: Design Thinking is a human-centered approach to problem-solving and innovation. It involves understanding user needs, exploring creative solutions, and iteratively testing ideas to develop products or services that effectively meet user demands.
Key Phases of Design Thinking
-
Empathize: Understand the users and their needs.
- Insight: Engage with users through interviews and observations. Develop empathy maps to visualize user experiences.
- Additional Info: Techniques such as user personas and journey mapping can help in this phase.
-
Define: Clearly articulate the problem to be solved.
- Insight: Frame the problem statement in a user-centered manner.
- Additional Info: The "How Might We" questions are often used to open up creative thinking.
-
Ideate: Generate a wide range of ideas.
- Insight: Encourage brainstorming sessions to explore innovative solutions. Aim for quantity over quality initially.
- Additional Info: Use techniques like mind mapping and SCAMPER (Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, Reverse) to expand thinking.
-
Prototype: Build tangible versions of ideas.
- Insight: Create simple and low-cost versions of products (paper prototypes, role-playing).
- Additional Info: Prototypes are tools for learning and should be iterated upon quickly.
-
Test: Validate the prototypes with users.
- Insight: Gather feedback and refine solutions based on user interactions.
- Additional Info: Testing is not the end but often the beginning of a new iteration cycle.
Benefits of Design Thinking
- Innovation: Encourages out-of-the-box thinking and novel solutions.
- User Satisfaction: Aligns products and services closely with user needs.
- Collaboration: Fosters cross-disciplinary collaboration and team creativity.
Applications
- Business Strategy: Helps in formulating strategies that are user-focused and innovative.
- Product Development: Employed to ensure products meet market needs and expectations.
- Customer Experience Design: Enhances overall customer interactions and satisfaction.
Challenges
- High Failure Rates: Approximately 40% of new products fail.
- Insight: Effective problem definition and thorough user research can mitigate this risk.
Conclusion
Design Thinking is essential for developing innovative solutions that truly address user needs. It is a structured approach that aids in navigating complex challenges through empathy, creativity, and strategic iteration.
Additional Resources
- Books, online courses, and workshops for deeper understanding and practical application of Design Thinking.
Extended readings:
What is a Product?
Definition and Function
- Products as Systems
- Products are systems consisting of artefacts or processes. They are conceived, produced, transacted, and used due to their properties and functions. This perspective is attributed to Roozenburg.
- Insight: Viewing products as systems emphasizes their complexity and functional roles. This perspective helps in designing and managing products effectively.
- Additional Info: In design and engineering, systems thinking is crucial for managing complexities and ensuring product effectiveness.
Understanding Systems
-
Components of a System
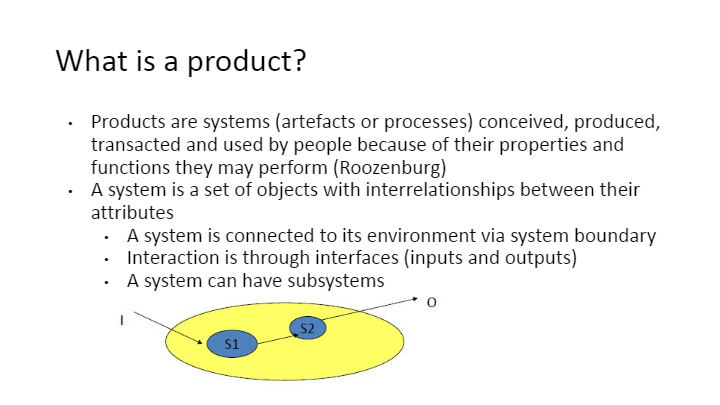
- A system is a set of objects with interrelationships and attributes.
- System Boundary: It defines the limits of a system and differentiates it from the environment.
- Insight: Understanding system boundaries is essential in identifying what interactions and influences affect it, which is crucial for troubleshooting and optimization.
- Additional Info: System boundaries help in determining scope and focus during problem-solving and system management.
-
Interactions and Interfaces
- Systems interact with their environments through interfaces, which include inputs and outputs.
- Insight: Interfaces are critical in ensuring that systems function correctly within their intended environments. Properly designed interfaces facilitate seamless integration and communication.
- Additional Info: Inputs and outputs often define the performance metrics and operational expectations for systems.
-
Subsystems
- A system can contain subsystems, each with specific roles and functions contributing to the overall system.
- Insight: Recognizing and managing subsystems allows for modularity and scalability in system design, making it easier to upgrade or modify specific parts without overhauling the entire system.
- Additional Info: In software engineering, subsystems allow for division into manageable units, often referred to as modular design.
Visualization
- Diagram Explanation
- The provided diagram likely illustrates how systems (S1, S2) and their boundaries (l, o) interact and are organized within a larger system.
- Insight: Diagrams are powerful tools for visualizing complex structures and relationships within systems, aiding in comprehension and communication.
- Additional Info: Use of visual aids like diagrams can enhance learning and retention of complex information in fields like engineering and project management.
Extended readings:
Role Playing in Design Thinking
Role Play: A Technique for Empathy
- Definition: Role play helps individuals empathize with a subject by stepping into their shoes and experiencing their feelings and perspectives.
- Empathy: Emotional identification, feeling like the subject.
- Sympathy: Cerebral identification, feeling for the subject.
- Apathy: No identification, not feeling for the object.
Applications of Role Play
- Products: Gain insights by imagining oneself as a product. For example, if you are a pen, consider how you might feel.
- People: Understand stakeholders by adopting their viewpoints. For example, consider being a user of a pen and how it influences your daily life.
Steps for Effective Role Play
- Situating the Subject in Context:
- Include factors like name, age, education, family, and past experiences to build a comprehensive profile.
- Describing Daily Life and Activities:
- Examine what typically happens, focusing on daily routines and actions.
- Narrating Aspirations and Achievements:
- Explore what the subject desires to accomplish and the motivations behind these goals.
- Identifying Pain Points and Failures:
- Analyze what the subject could not achieve and understand the reasons for these challenges.
- Imagining Personal Experience:
- Feel as though this life is one's own to gain deeper emotional insights.
Practical Implementation
- Upcoming slides in the presentation will feature examples of role play exercises by students from CPDM, IISc, showcasing both individual and product-focused role plays highlighting empathy.
Insight
Role playing is a powerful tool in design thinking, enabling deeper understanding and better user-centered design by fostering empathy and insight into users' lives and experiences.
Extended readings: