Understanding the Product Life Cycle and Development Stages
What is Product Life Cycle?
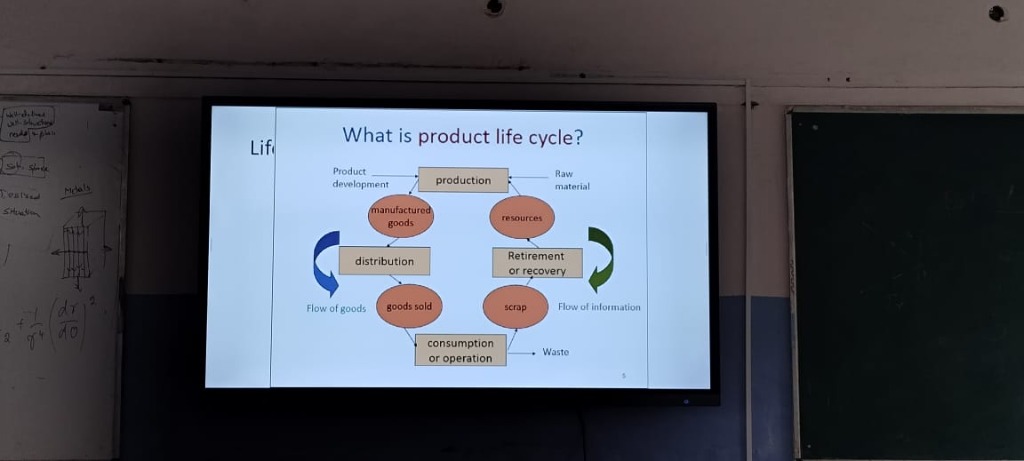
The image presents a diagram outlining the concept of the product life cycle, which includes various stages that a product goes through from inception to retirement. Here are the key notes extracted from the image along with additional thoughts and ideas for clarity.
Key Stages of Product Life Cycle
-
Product Development
- This is the initial phase where ideas are generated, and the product concept is developed. It involves market research and feasibility studies.
- Thoughts: Companies often invest significant resources in this stage to ensure that the product meets market needs and customer expectations.
-
Production
- This stage involves the actual manufacturing of the product. Resources such as raw materials and skilled labor are utilized.
- Additional Info: Efficient production processes can help reduce costs and improve product quality.
-
Distribution
- Once produced, the goods need to be distributed to various stakeholders. This may include wholesalers, retailers, and direct customers.
- Thoughts: Effective distribution strategies are crucial for ensuring that products reach the target market in a timely manner.
-
Goods Sold
- This component represents the sales aspect of the product life cycle where the product is marketed and sold to consumers.
- Additional Info: Marketing strategies play a significant role here, influencing consumer perception and demand.
-
Consumption or Operation
- After purchase, consumers use the product, which engages them in its value proposition.
- Thoughts: User experience during this phase can greatly influence repeat purchases and brand loyalty.
-
Retirement or Recovery
- This phase marks the end of the product's lifecycle, where it may either be scrapped or recovered for parts and materials.
- Additional Info: Sustainable practices are gaining traction, allowing companies to recover valuable resources from retired products.
Flow of Goods and Information
- The diagram emphasizes the flow of goods throughout the lifecycle and suggests that there is also a flow of information that supports decision-making at each stage.
- Thoughts: Managing this flow effectively can lead to improved efficiency and responsiveness to market trends.
Waste Management
- The final stage discusses waste generation and management associated with scrapping products.
- Additional Info: Companies are increasingly focusing on minimizing waste through recycling and efficient disposal methods as part of their corporate social responsibility efforts.
This comprehensive understanding of the product life cycle is essential for businesses looking to optimize their product management processes and improve overall efficiency.
Extended readings:
Product Design and Development
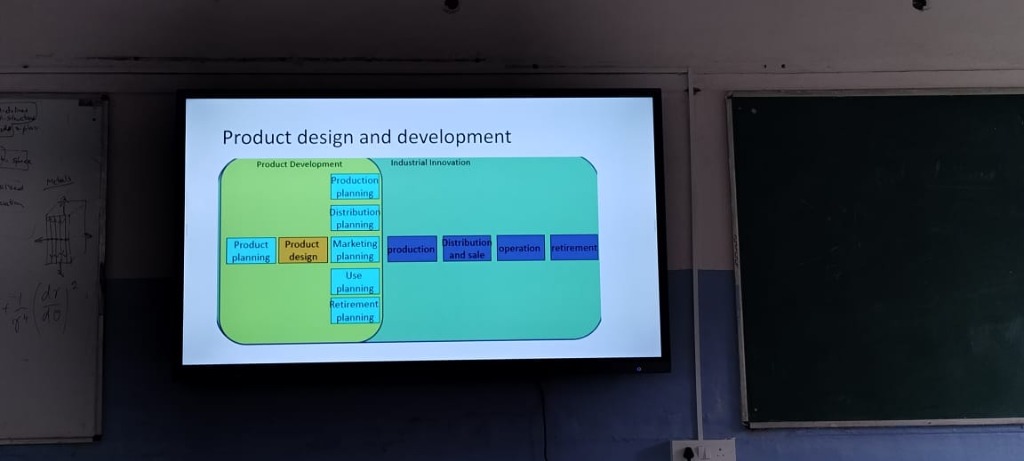
Key Concepts
-
Product Development
- This involves multiple stages to bring a product from conception to market. It requires thorough planning and integration of various functions such as production and marketing.
- Product development is crucial for companies to innovate and stay competitive in the market.
-
Industrial Innovation
- Represents the transition of new ideas into usable products or improvements in existing products.
- Emphasizes the importance of adapting to market needs and technology changes to meet customer expectations efficiently.
Elements of Product Development
| Category | Planning Activities |
|---|---|
| Product Planning | Determining product specifications and requirements. It ensures that the product meets market demands. |
| Production Planning | Organizing resources and processes for efficient manufacturing. Proper production planning saves time and costs. |
| Distribution Planning | Establishing channels for delivering the product to the customer. This can include logistics and supplier management. |
| Marketing Planning | Strategies to promote the product and reach potential customers. Effective marketing is key to product visibility and sales success. |
| Use Planning | Understanding how the customer will use the product to improve design and functionality. |
| Retirement Planning | Planning for the phasing out of a product, including managing inventory and reallocation of resources. This helps organizations manage product lifecycle effectively. |
Additional Thoughts
- The integration of product design with planning activities enhances teamwork and can lead to innovative solutions that meet both user needs and business objectives.
- Continuous feedback at each stage of development is essential to refine the product and address any potential issues.
- Companies should regularly review and adapt their product development strategies in response to technological advances and changing consumer preferences.
Extended readings:
Total Materials Cycle
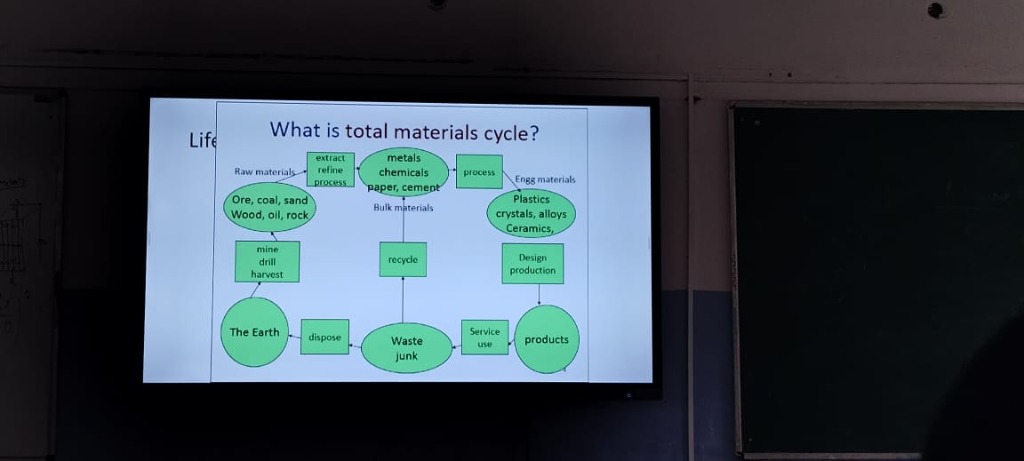
Overview
The total materials cycle refers to the process of extracting, processing, using, and disposing of raw materials. It outlines the journey of materials from sourcing to end-of-life management, highlighting the need for sustainability in resource use.
Key Components
-
Raw Materials
- Sources: Ore, coal, sand, wood, oil, rock
- Thoughts: The extraction of these materials can have significant environmental impacts. Sustainable sourcing practices are essential to minimize damage.
-
Extraction and Refinement
- Processes: Extract, refine
- Considerations: The processes involved in extraction can vary based on the material; for instance, drilling for oil differs from harvesting timber. Innovations in extraction technology can lead to less environmental disruption.
-
Bulk Materials
- Categories: Metals, chemicals, paper, cement
- Ideas: Understanding the different types of bulk materials allows for a better grasp of their end applications and the importance of recycling these materials to reduce waste.
-
Engineering Materials
- Types: Plastics, crystals, alloys, ceramics
- Insights: Engineering materials are crucial for manufacturing various products. Emphasizing biodegradable or recyclable materials can enhance sustainability.
-
Design and Production
- Process: Design production
- Reflection: The design phase is critical as it determines the product's lifecycle. Eco-design approaches consider the materials used and potential for recycling or repurposing.
-
End-of-Life Management
- Components: Recycle, waste, junk
- Thoughts: Effective waste management strategies, such as recycling and reusing materials, are vital for closing the loop in the materials cycle. Communities can benefit from better waste segregation practices.
-
Final Products
- Outcome: Products
- Conclusion: The end goal of the total materials cycle is responsible production and consumption that prioritizes sustainability, reducing dependency on virgin resources while fostering a circular economy.
Extended readings: