Understanding Homeostasis through Feedback Loops
Human Biology and Homeostasis
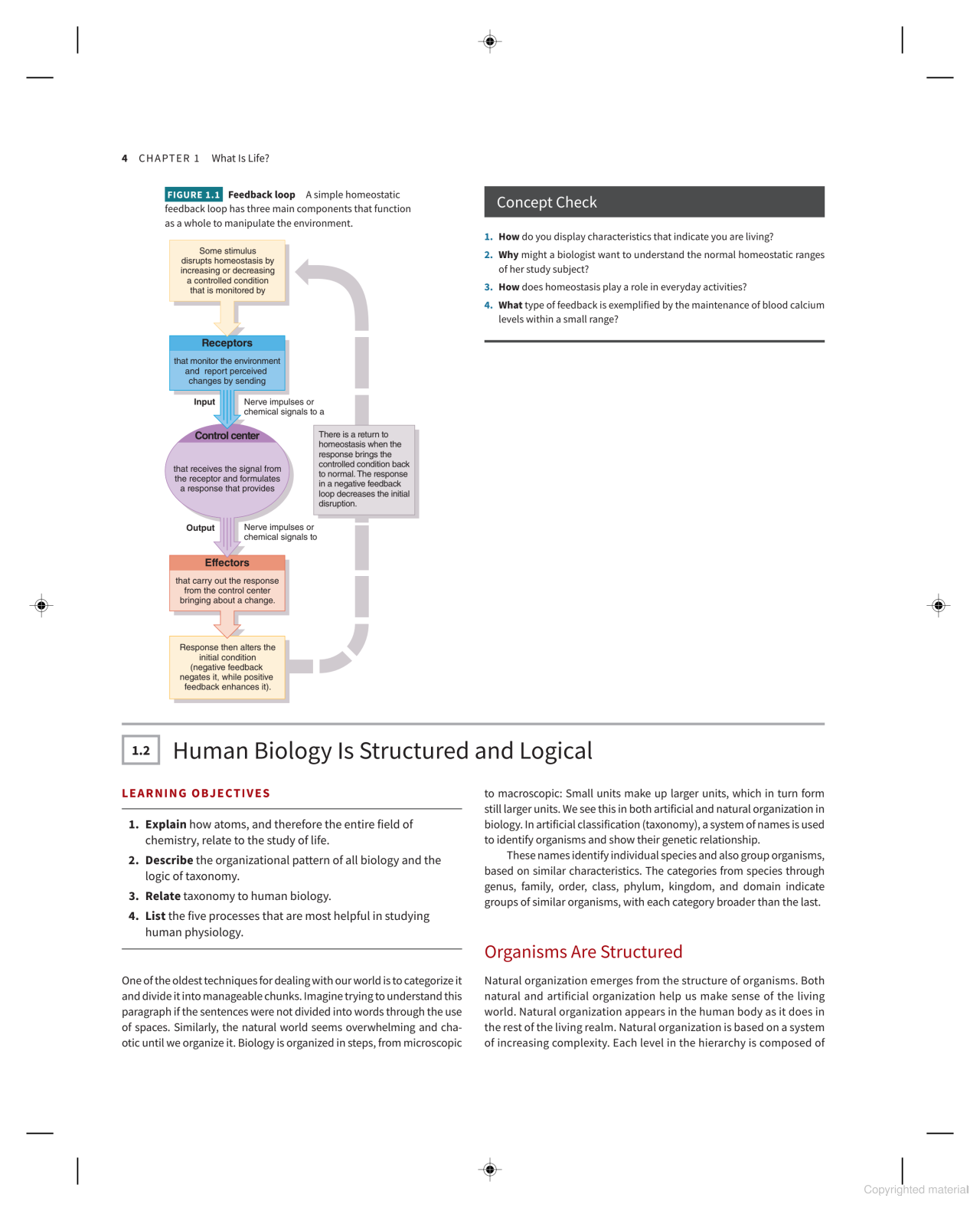
Feedback Loop
-
Definition: A feedback loop is a process that helps maintain homeostasis in an organism by utilizing three main components: receptors, control centers, and effectors.
- Receptors: They monitor environmental changes and relay signals (via nerve impulses or chemical signals) about deviations from a normal state.
- Thought: Understanding how receptors function is crucial for comprehending how organisms maintain balance within their internal environment.
- Control Center: This receives signals from receptors and formulates a response to return to homeostasis.
- Additional Info: The control center acts like a decision-maker, determining the necessary action to counteract the stimulus.
- Effectors: These carry out the response directed by the control center to bring about a change.
- Example: Muscles may contract or glands may secrete hormones in response to signals received from the control center to correct a deviation.
- Receptors: They monitor environmental changes and relay signals (via nerve impulses or chemical signals) about deviations from a normal state.
-
Types of Feedback:
- Negative Feedback: Works to reverse changes and restore balance (e.g., lowering high blood sugar).
- Positive Feedback: Enhances a change or output (e.g., the process of childbirth where contractions increase).
Concept Check Questions
-
Living Characteristics: Organisms display characteristics such as growth, reproduction, response to stimuli, and metabolism that indicate they are alive.
- Thought: Understanding these indicators helps in identifying living organisms in diverse environments.
-
Biologist's Interest in Homeostasis: A biologist might study homeostasis to understand how organisms adapt to their environments and maintain stable conditions necessary for survival.
- Additional Info: This knowledge can inform conservation efforts and medical research.
-
Homeostasis in Everyday Activities: Homeostasis plays a role in maintaining body temperature, pH levels, and fluid balance, which are essential for normal physiological functions.
- Thought: Recognizing homeostasis in daily life can lead to better health practices, such as staying hydrated and regulating sleep.
-
Calcium Levels Maintenance: Feedback mechanisms are important for keeping blood calcium levels within a small, optimal range, which is critical for processes like muscle contraction and blood clotting.
- Additional Info: Hormones such as parathyroid hormone and calcitonin regulate these calcium levels through negative feedback.
Learning Objectives
-
Atoms and Chemistry: Understanding atoms provides a foundation for studying the larger field of chemistry, which is essential in biology.
- Thought: Chemical reactions at the atomic level drive biological processes, highlighting the interdependence of these sciences.
-
Organizational Patterns: Biology is structured hierarchically from cells to organisms, which aids in systematic study and comprehension.
- Additional Info: Recognizing these patterns can deepen our understanding of complex biological systems and their interactions.
-
Taxonomy Relation: Taxonomy organizes living organisms based on shared characteristics, influencing how we classify and study them.
- Thought: Taxonomic classification fosters an understanding of evolutionary relationships among species.
-
Processes in Studying Physiology: Key processes in physiology include circulation, respiration, digestion, and homeostasis which inform our understanding of bodily functions.
- Additional Info: Mastery of these processes is essential for fields such as medicine and biology.
Reference: